Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is condemned and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Etymologically, the term capital refers to execution by beheading, but executions are carried out by many methods, including hanging, shooting, lethal injection, stoning, electrocution, and gassing.

Capital punishment, also called the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as a punishment for a crime. It has historically been used in almost every part of the world. Since the mid-19th century many countries have abolished or discontinued the practice. In 2022, the five countries that executed the most people were, in descending order, China, Iran, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and the United States.
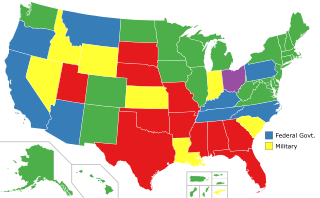
In the United States, capital punishment is a legal penalty in 27 states, throughout the country at the federal level, and in American Samoa. It is also a legal penalty for some military offenses. Capital punishment has been abolished in the other 23 states and in the federal capital, Washington, D.C. It is usually applied for only the most serious crimes, such as aggravated murder. Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, 20 of them have authority to execute death sentences, with the other 7, as well as the federal government and military, subject to moratoriums.

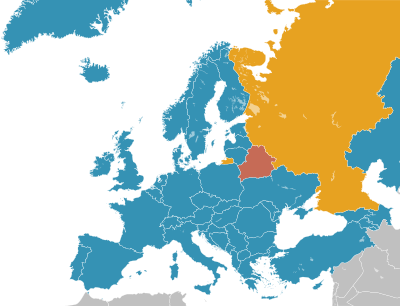
Capital punishment has been completely abolished in all European countries except for Belarus and Russia, the latter of which has a moratorium and has not carried out an execution since September 1996. The complete ban on capital punishment is enshrined in both the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union (EU) and two widely adopted protocols of the European Convention on Human Rights of the Council of Europe, and is thus considered a central value. Of all modern European countries, San Marino, Portugal, and the Netherlands were the first to abolish capital punishment, whereas only Belarus still practises capital punishment in some form or another. In 2012, Latvia became the last EU member state to abolish capital punishment in wartime.
Capital punishment for murder was abolished in Malta in 1971. However, the death penalty continued to be part of the country's military code until it was fully abolished on 21 March 2000. Malta is a signatory of the Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights that commits it to abolition of the death penalty within its borders. Malta has also ratified protocol 13 to the European Convention on Human Rights, that bans the death penalty in all circumstances.
Capital punishment is a long unused form of punishment in Brazil. The last recorded instance of a death penalty convict being executed in the country was in 1876. Although virtually abolished, it is still legal during wartime, according to the Article 5, XLVII, "a", of the Federal Constitution. Brazil is the most populous country in the world that does not retain the death penalty in practice. It is also one of seven countries to have abolished capital punishment for ordinary crimes only.
Capital punishment in Andorra was abolished in 1990, having last been used in 1943.

Capital punishment in Armenia was a method of punishment that was implemented within Armenia's Criminal Code and Constitution until its eventual relinquishment in the 2003 modifications made to the Constitution. Capital punishment's origin in Armenia is unknown, yet it remained present in the Armenia Criminal Code of 1961, which was enforced and applied until 1999. Capital punishment was incorporated into Armenian legislation and effectuated for capital crimes, which were crimes that were classified to be punishable by death, including treason, espionage, first-degree murder, acts of terrorism and grave military crimes.

Capital punishment in Austria was abolished in 1787, although restored in 1795. Unlike other countries with a minimum age of 18, the Habsburg Law enacted in 1919 set the minimum age for execution in Austria at 20.
Capital punishment in Azerbaijan was abolished in 1998. The last execution took place in Azerbaijan in 1993 by method of single shot. Protocol No. 6 to the ECHR came into force in this country on 25 January 2001 and the death penalty was replaced with life imprisonment.

Capital punishment in Belgium was formally abolished on August 1, 1996, for all crimes, in both peacetime and wartime. The last execution for crimes committed in peacetime took place in July 1863, when in Ypres a farmer was executed for murder. The last execution for an ordinary crime took place on 26 March 1918 at Veurne Prison when Emile Ferfaille, a military officer found guilty of killing his pregnant girlfriend, was guillotined. This was the first execution to be carried out since 1863. The guillotine that was used had to be imported from France.

Capital punishment in Croatia existed until 1991 when it was constitutionally abolished. The last execution had taken place there in 1987 when Croatia was still part of Yugoslavia.

Capital punishment in modern Greece was carried out using the guillotine or by firing squad. It was last applied in 1972 during the military junta. The death penalty was abolished in stages between 1975 and 2005.
Capital punishment is no longer applied in San Marino: the last execution was carried out in 1468 or in 1667, by hanging.
Capital punishment in Montenegro was first prescribed by law in 1798. It was abolished on 19 June 2002. The last execution, by shooting, took place on 29 January 1981, and the two last death sentences were pronounced on 11 October 2001. Montenegro is bound by the following international conventions prohibiting capital punishment : Second Optional Protocol to the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, as well as Protocols No. 6 and No. 13 to the European Convention on Human Rights. Article 26 of the Montenegrin Constitution (2007) that outlawed the death penalty states: "In Montenegro, capital punishment punishment is forbidden”.

Capital punishment in Luxembourg was abolished for all crimes in 1979.

Capital punishment in Moldova was abolished in 2005.
Capital punishment in Chile is legally sanctioned, albeit with significant limitations. Since its abolition for civilian offenses in 2001, its application has been restricted to military personnel convicted of war crimes and crimes against humanity committed during wartime. This places Chile among the seven countries globally that have abolished capital punishment solely for ordinary crimes.
Capital punishment in Burkina Faso has been abolished. In late May 2018, the National Assembly of Burkina Faso adopted a new penal code that omitted the death penalty as a sentencing option, thereby abolishing the death penalty for all crimes.
Capital punishment in Gabon was officially abolished for all crimes in 2010. Gabon's last execution took place in 1985. Prior to abolition, Gabon was classified as de facto abolitionist, or "abolitionist in practice," due to the length of time since their last execution.