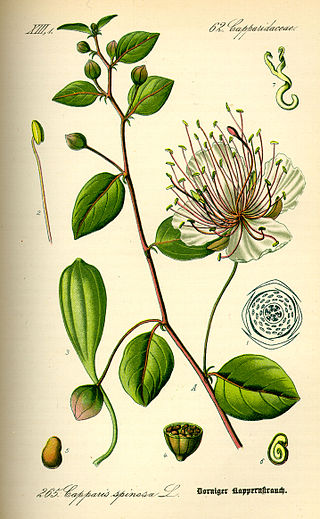
Capparis spinosa, the caper bush, also called Flinders rose, is a perennial plant that bears rounded, fleshy leaves and large white to pinkish-white flowers.

Eremophila is a genus of more than 260 species of plants in the figwort family, Scrophulariaceae all of which are endemic to mainland Australia.. Eremophilas are widespread in the arid areas of Australia, especially Western Australia and range in size from low-growing shrubs to small trees. The petals are joined, at least at their bases, into a tube with the upper petals different in size and shape from the lower ones. Some species have common names including emu bush, poverty bush or fuchsia bush, reflecting the belief that emus eat the fruit, their arid environment or a superficial resemblance to the flowers of plants in the genus Fuchsia.

Acacia ligulata is a species of Acacia, a dense shrub widespread in all states of mainland Australia. It is not considered rare or endangered. Its common names include sandhill wattle, umbrella bush, marpoo, dune wattle, small coobah, wirra, and watarrka.

Pakistan's native flora reflects its varied climatic zones, which range from arid and semi-arid to temperate and tropical.

Chenopodium curvispicatum is a species of plant in the family Amaranthaceae, endemic to Australia.

Lasiopetalum behrii, commonly known as the pink velvet bush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae and is endemic to southern continental Australia. It is an erect shrub with lance-shaped, narrowly oblong to narrowly elliptic leaves and groups of white to pink and reddish-brown flowers.

The Yathong Nature Reserve is a protected nature reserve that is also a nationally and internationally recognized biosphere situated in the central-western region of New South Wales, in eastern Australia. The 107,240-hectare (265,000-acre) reserve was listed by UNESCO in 1977 as a Biosphere Reserve under the Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB). The reserve is significant for its biodiversity in both native plant and animal species. Cultural heritage and historical grazing activities add to the significance of this site as a conservation area.

Dodonaea microzyga, commonly known as brilliant hopbush, is a dioecious spreading shrub in the family Sapindaceae. It grows between 0.3 and 1.5 metres tall.

Eremophila gilesii, commonly known Charleville turkey bush, green turkey bush, desert fuchsia and Giles emu bush is a flowering plant in the figwort family, Scrophulariaceae and is endemic to Australia. It is usually a low, spreading shrub with pinkish-lilac to purple flowers and is widespread in the Northern Territory and all mainland states except Victoria. It is considered a difficult agricultural weed in some parts of Queensland but is often used as a bush medicine by Aboriginal people.

Lechenaultia divaricata, commonly known as tangled leschenaultia, wirenetting bush or wirebush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Goodeniaceae and is endemic to arid and semi-arid areas of central Australia.

Dodonaea procumbens, commonly known as trailing hop bush or creeping hop-bush, is a species of shrub in the genus Dodonaea found in eastern Australia. It occurs in many places in Australia such as South Australia, New South Wales and Victoria. Although the information on the abundance of this species is limited, it is estimated that about 5,000 plants occur in about 55 wild populations. The species is currently facing many threats such as the expansion of road facilities, the development of residential and agricultural areas, increased grazing regimes, weed invasions, and regimes changing of fire. As a result, it is listed as vulnerable and threatened. Therefore, it is necessary to provide protective solutions for the long-term development and survival of this species.

Micromyrtus flaviflora is a species of flowering plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to inland areas of Australia. It is an erect shrub with overlapping, keeled, oblong leaves, and yellow flowers arranged singly in leaf axils, but often appearing clustered.

Acacia carneorum, also referred to as purple-wood wattle, needle wattle, dead finish or by its former scientific name, Acacia carnei, is a plant species in the genus Acacia.

Boronia adamsiana, commonly known as Barbalin boronia, is a plant in the citrus family, Rutaceae and is endemic to a small area in the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, hairy shrub with trifoliate leaves and pink or white, four-petalled flowers.

Asterolasia phebalioides, commonly known as downy starbush, is a species of shrub in the family Rutaceae and is endemic to south-eastern continental Australia. It has densely crowded heart-shaped to wedge-shaped leaves densely covered with star-shaped hairs, and single yellow flowers borne on the ends of branchlets with star-shaped hairs on the back of the petals.

Sarcozona praecox, commonly known as sarcozona, is species of flowering plant in the family Aizoaceae and is endemic to Australia. It is a small erect to low-lying, succulent shrub with leaves that are triangular in cross-section and arranged in opposite pairs, and daisy-like flowers with twenty to eighty pink, petal-like staminodes and 20 to 150 stamens.

Thryptomene parviflora is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae and is endemic to Queensland. It is a slender, erect shrub with decussate, linear to egg-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base, and flowers with five petals and five stamens arranged singly in leaf axils.

Senna notabilis, commonly known as cockroach bush, is a species of flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae, and is endemic to northern Australia. It is an erect, softly-hairy, annual or perennial shrub with pinnate leaves with six to twelve pairs of lance-shaped leaflets, and yellow flowers arranged in groups of twenty to thirty, with seven fertile stamens in each flower.

Capparis loranthifolia, also known as the narrowleaf bumble or narrow-leaved bumble tree, is a shrub or small tree in the caper family. It is endemic to the arid and semi-arid interior of northern and eastern Australia from Western Australia to New South Wales.

Senna pleurocarpa, commonly known as fire bush or chocolate bush, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to Australia. It is a spreading shrub with pinnate leaves with five to seven pairs of broadly elliptic to egg-shaped leaflets, and groups of five to twelve yellow flowers arranged in dense groups of twenty to sixty on the ends of branches and in upper leaf axils.




















