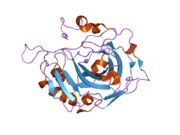
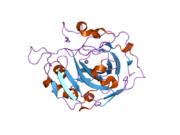
Utrophin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UTRN gene.
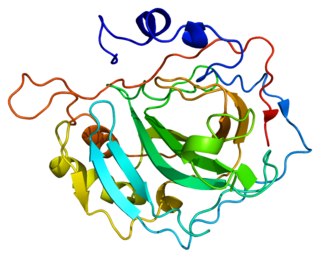
Carbonic anhydrase II, is one of sixteen forms of human α carbonic anhydrases. Carbonic anhydrase catalyzes reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. Defects in this enzyme are associated with osteopetrosis and renal tubular acidosis. Renal carbonic anhydrase allows the reabsorption of bicarbonate ions in the proximal tubule. Loss of carbonic anhydrase activity in bones impairs the ability of osteoclasts to promote bone resorption, leading to osteopetrosis.

Four and a half LIM domains protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FHL1 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA1 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA4 gene.

Troponin I, fast skeletal muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNNI2 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 12 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA12 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA6 gene. It is also called 'gustin' because of its presence in saliva, and lower-than-normal levels of salivary zinc in individuals with hypogeusia.

Carbonic anhydrase-related protein 10 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA10 gene.
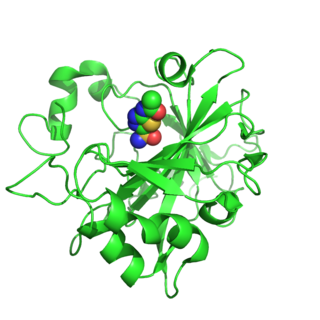
Carbonic anhydrase 14 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA14 gene.

Hemoglobin subunit theta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HBQ1 gene.

Troponin C, skeletal muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNNC2 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 5B, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA5B gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 7 (CA7) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA7 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase-related protein 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CA11 gene.

Ryanodine receptor 3 is one of a class of ryanodine receptors and a protein that in humans is encoded by the RYR3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is both a calcium channel and a receptor for the plant alkaloid ryanodine. RYR3 and RYR1 control the resting calcium ion concentration in skeletal muscle.

Myosin light chain kinase 2 also known as MYLK2 is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the MYLK2 gene.

Myosin-4 also known as myosin, heavy chain 4 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the MYH4 gene.

RTL1 is a retrotransposon derived protein coding gene. It is also known as PEG11 and is a paternally expressed imprinted gene, part of genomic imprinting. RTL1 plays an important role in the maintenance of fetal capillaries and is expressed in high quantities during late stage of fetal development. The expression of this gene is important for the development of the placenta, the fetus-maternal interface. Because the placenta is the first organ to form during the development of an embryo, problems in its establishment and biological role lead to complications during gestation. This organ maintains the fetus throughout the pregnancy and is therefore sensitive to disruptions. Studies in mice suggest that disruption of the RTL1 concentration, whether increasing or decreasing the amount of this protein coding gene, can lead to serious errors in the conservation of placental fetal capillaries. RTL1 knockout mice have shown obstruction in fetal development along with late fetal/neonatal death. Studies from sheep homologs suggest that high expression levels of RTL1 can lead to skeletal muscle hypertrophy This is due to over-expression patterns in the paternal allele specific gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 5A, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CA5A gene.