
Albert Camus was an Algerian-French philosopher, author, dramatist, journalist, and political activist. He was the recipient of the 1957 Nobel Prize in Literature at the age of 44, the second-youngest recipient in history. His works include The Stranger, The Plague, The Myth of Sisyphus, The Fall, and The Rebel.

The Cyperaceae are a family of graminoid (grass-like), monocotyledonous flowering plants known as sedges. The family is large, with some 5,500 known species described in about 90 genera, the largest being the "true sedges" genus Carex with over 2,000 species.

Lithocarpus is a genus in the beech family, Fagaceae. Trees in this genus are commonly known as the stone oaks and differ from Quercus primarily because they produce insect-pollinated flowers on erect spikes and the female flowers have short styles with punctate stigmas. At current, around 340 species have been described, mostly restricted to Southeast Asia. Fossils show that Lithocarpus formerly had a wider distribution, being found in North America and Europe during the Eocene to Miocene epochs. The species extend from the foothills of the Hengduan Mountains, where they form dominant stands of trees, through Indochina and the Malayan Archipelago, crossing Wallace's Line and reaching Papua. In general, these trees are most dominant in the uplands and have many ecological similarities to the Dipterocarpaceae, the dominant lowland tree group. These trees are intolerant of seasonal droughts, not being found on the Lesser Sunda Islands, despite their ability to cross numerous water barriers to reach Papua.

Carex is a vast genus of nearly 2,000 species of grass-like plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the family Cyperaceae are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called true sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as caricology.

Cephalanthera, abbreviated Ceph in horticultural trade, is a genus of mostly terrestrial orchids. Members of this genus have rhizomes rather than tubers. About 15 species are currently recognized, most of them native to Europe and Asia. The only species found in the wild in North America is Cephalanthera austiniae, the phantom orchid or snow orchid. Ecologically, this species is partially myco-heterotrophic. Some of the Eurasian species hybridise.

Tso Moriri or Lake Moriri or "Mountain Lake", is a lake in the Changthang Plateau of Ladakh in India. The lake and surrounding area are protected as the Tso Moriri Wetland Conservation Reserve.

Ophrys sphegodes, commonly known as the early spider-orchid, is a species of sexually-deceptive orchid native to Europe and the Middle East. It is a very varied species with many subspecies recognised.

The Circumboreal Region in phytogeography is a floristic region within the Holarctic Kingdom in Eurasia and North America, as delineated by such geobotanists as Josias Braun-Blanquet and Armen Takhtajan.

Carex pauciflora, the few-flowered sedge, is a perennial species of sedge in the family Cyperaceae native to bogs and fens in cool temperate, subarctic, and mountainous regions of the Northern Hemisphere. The specific epithet pauciflora refers to the Latin term for 'few flowered'.

Carex scoparia is a species of sedge known by the common names broom sedge and pointed broom sedge. It should not be confused with the unrelated grass species known as "broom sedge," Andropogon virginicus.

Hesperilla munionga, the alpine sedge-skipper, is a butterfly of the family Hesperiidae. It is found in the Australian Capital Territory, New South Wales, Tasmania and Victoria.

Carex hirta, the hairy sedge or hammer sedge, is a species of sedge native across Europe. It has characteristic hairy leaves and inflorescences, and is the type species of the genus Carex.

Carex subg. Carex is a subgenus of the sedge genus Carex. It is the largest of the four traditionally recognised subgenera, containing around 1400 of the 2000 species in the genus. Its members are characterised by the presence of one or more exclusively male (staminate) terminal spikes, quite dissimilar in appearance from the lateral female (pistillate) spikes below. In most species, the female flowers have three stigmas, but a few species, including Carex nigra, have female flowers with only two stigmas.
Edmond Gustave Camus was a French pharmacist and botanist known for his work with orchids.

Carex pulicaris, the flea sedge, is a species of sedge in the genus Carex native to Europe.

Carex remota, the remote sedge, is a species in the genus Carex, native to Europe, the Atlas Mountains in Africa, and western Asia. It is a riparian forest specialist. It is known as one of the most frequently hybridizing species of Carex, forming hybrids with C. appropinquata, C. arenaria, C. brizoides, C. canescens, C. divulsa, C. echinata, C. elongata, C. leporina, C. otrubae, C. paniculata, and C. spicata.
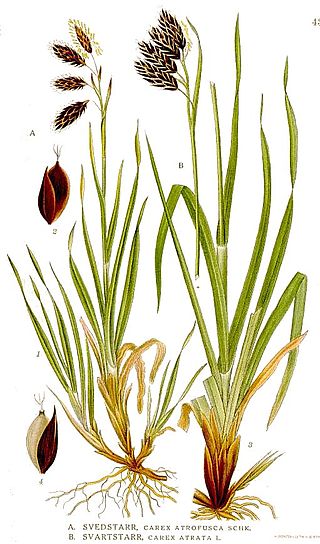
Carex atrata, called black alpine sedge, is a widespread species of flowering plant in the genus Carex, native to Greenland, Iceland, and most of Europe, plus scattered locations across temperate Asia, including Anatolia, Siberia and the Himalaya, as far as Taiwan and Japan. Its chromosome number is 2n=52, with some variants reported, e.g. n2=54 for Greenland material.
Carex adrienii, known in China as guang dong tai cao, is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native from southern China in the north to Vietnam in the south.
Carex manginii is a tussock-forming species of perennial sedge in the family Cyperaceae. It is native to parts of Manchuria.















