
Catocala amestris, the three-staff underwing, is a species of Catocalini that occurs in North America. It is considered endangered and is legally protected in the state of Michigan.

Catocala retecta, the yellow-gray underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1872. It can be found in North America from southern Ontario and Quebec south through Maine and New Jersey, south through Tennessee to Georgia and west to Arkansas and Kansas and north to Wisconsin. There is one recognised subspecies, Catocala retecta luctuosa, which is sometimes treated as a valid species with the common name yellow-fringed underwing.

Catocala luciana, the shining underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Herman Strecker in 1874. It is found in western North America, as far east as Minnesota and Illinois and northward into extreme southern Alberta and Saskatchewan. It occurs widely across the Great Plains, south to New Mexico, Arizona and California.

Catocala semirelicta, the semirelict underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1874. It is found in North America from Nevada, Colorado, Utah, California, and Nova Scotia south to Maine, west across Canada to British Columbia, and southward in the mountains.

Catocala agrippina, the Agrippina underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Herman Strecker in 1874. It is found in the United States from southern New Jersey south to Florida, west to Texas and eastern Oklahoma and north to southern Indiana.

Catocala angusi, commonly known as Angus' underwing, is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. It is found from Massachusetts and Connecticut south to Georgia west to Arkansas and Kansas and north to Illinois and Michigan.

Catocala dejecta, the dejected underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found from Massachusetts and Connecticut south through New Jersey to Florida, west to Texas and Oklahoma and north to southern Ontario.

Catocala residua, the residua underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1874. It is found in North America from southern Ontario, Quebec and Maine south to North Carolina and Georgia west to Mississippi and Missouri and north to Iowa, Illinois and Michigan.

Catocala insolabilis, the inconsolable underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found in North America from Ontario through Maine and Connecticut south to Florida, west through Arkansas to Texas and Oklahoma and north to South Dakota.

Catocala obscura, the obscure underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Ferdinand Heinrich Hermann Strecker in 1873. In Canada it is found in southern Quebec and Ontario and in the United States it is found from Massachusetts and Connecticut south to North Carolina, west to Mississippi and north to Iowa, Illinois, Ohio, and Michigan.

Catocala sappho, the Sappho underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Ferdinand Heinrich Hermann Strecker in 1874. It is found from Virginia and Tennessee south to Florida and west to Louisiana, Mississippi, Texas, Missouri and Illinois.
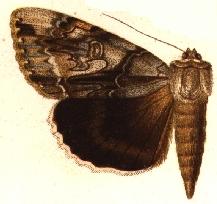
Catocala vidua, the widow underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by James Edward Smith in 1797. It is found in North America from southern Ontario, into Maine, New Hampshire and Connecticut, south at least to Tennessee, Georgia and Alabama, west to Texas and Oklahoma, and north to Wisconsin.

Catocala maestosa, commonly known as the sad underwing, is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. The species was first described by George Duryea Hulst in 1884. It is found in the United States from New York south to Florida and Alabama, west to Texas and eastern Oklahoma and north to Illinois, Indiana and Minnesota.

Catocala palaeogama, the old wife underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Achille Guenée in 1852. It is found in North America from Ontario and Quebec, through Maine, New Jersey, Tennessee, to South Carolina, west to Arkansas and Oklahoma and north through Iowa, Indiana, Illinois and Michigan.

Catocala robinsonii, or Robinson's underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1872. It is found in North America from southern Ontario and New Hampshire south to Florida west to Oklahoma, Missouri and Arkansas and northward to Illinois, Indiana, and Michigan.

Catocala subnata, the youthful underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1864. It is found in North America from Manitoba, Ontario, Quebec, and New Brunswick to Nova Scotia, south through Maine and Connecticut to North Carolina and west to Tennessee, Kentucky, and Texas, then north to Iowa, Wisconsin, and Michigan.

Catocala faustina is a moth of the family Erebidae. It is found from Colorado west to California and north through Washington to British Columbia. It has also been reported in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon and Utah.

Catocala semirelicta hippolyta is a subspecies of moth of the family Erebidae first described by Strecker in 1874. It is found in the US state of California.

Catocala similis, the similar underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by William Henry Edwards in 1864. It is found in North America from Ontario and Quebec south through Maine and Connecticut to Florida, west to Texas and Oklahoma, and north to Minnesota.

Catocala ulalume, the Ulalume underwing, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Herman Strecker in 1878. It is found in the United States from Virginia through Georgia to Florida, west to Texas and Oklahoma and north to Illinois.












