
A gametophyte is one of the two alternating multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the sexual phase in the life cycle of plants and algae. It develops sex organs that produce gametes, haploid sex cells that participate in fertilization to form a diploid zygote which has a double set of chromosomes. Cell division of the zygote results in a new diploid multicellular organism, the second stage in the life cycle known as the sporophyte. The sporophyte can produce haploid spores by meiosis that on germination produce a new generation of gametophytes.

A sporophyte is the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or alga which produces asexual spores. This stage alternates with a multicellular haploid gametophyte phase.
Plant reproduction is the production of new offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from either parent. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, resulting in clonal plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant and each other, unless mutations occur.

The Caytoniales are an extinct order of seed plants known from fossils collected throughout the Mesozoic Era, around 252 to 66 million years ago. They are regarded as seed ferns because they are seed-bearing plants with fern-like leaves. Although at one time considered angiosperms because of their berry-like cupules, that hypothesis was later disproven. Nevertheless, some authorities consider them likely ancestors or close relatives of angiosperms. The origin of angiosperms remains unclear, and they cannot be linked with any known seed plants groups with certainty.

Sagenopteris is a genus of extinct seed ferns from the Triassic to late Early Cretaceous.
Caytonanthus is an extinct genus of seed ferns.

A seed plant or spermatophyte, also known as a phanerogam or a phaenogam, is any plant that produces seeds. It is a category of embryophyte that includes most of the familiar land plants, including the flowering plants and the gymnosperms, but not ferns, mosses, or algae.

Dicroidium is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed plants. It is the archetypal genus of the corystosperms, an extinct group of seed plants, often called "seed ferns", assigned to the order Corystospermales or Umkomasiales. Species of Dicroidium were widely distributed and dominant over Gondwana during the Triassic. Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar, the Indian subcontinent and Antarctica.

Lepidopteris is a form genus for leaves of Peltaspermaceae, an extinct family of seed plants, which lived from around 260 to 190 million years ago, from the Late Permian to Early Jurassic. Fossils of the genus have been found across both hemispheres. Nine species are currently recognized.Lepidopteris was a common and widespread seed fern, which survived the Permian-Triassic extinction event but was largely wiped out by the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. Lepidopteris callipteroides is especially common between the first two episodes of the Permian-Triassic extinction event, and L. ottonis forms a comparable acme zone immediately before the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. Lepidopteris would persist into the Early Jurassic in Patagonia, represented by the species Lepidopteris scassoi.

The Peltaspermales are an extinct order of seed plants, often considered "seed ferns". They span from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Jurassic or the Jurassic-Cretaceous Boundary. It includes at least one valid family, Peltaspermaceae, which spans from the Permian to Early Jurassic, which is typified by a group of plants with Lepidopteris leaves, Antevsia pollen-organs, and Peltaspermum ovulate organs, though the family now also includes other genera like Peltaspermopsis, Meyenopteris and Scytophyllum. Along with these, two informal groups of uncertain taxonomic affinities exist, each centered around a specific genus ; Supaia and Comia, known from the Early Permian of the Northern Hemisphere, especially of North America. Both the "Comioids" and the "Supaioids" are associated with the peltaspermacean ovulate organ Autunia. The Late Triassic-Middle Jurassic genus Pachydermophyllum may also have affinities to the peltasperms.

Umkomasia is a genus of seed bearing organs produced by corystosperm seed ferns, first based on fossils collected by Hamshaw Thomas from the Burnera Waterfall locality near the Umkomaas River of South Africa. He recognized on the basis of cuticular similarities that the same plant produced pollen organs Pteruchus and the leaves Dicroidium. Various other corystosperm seed bearing organs from the Jurassic and Cretaceous have been assigned to this genus, but recently have been given distinct genera, with Umkomasia being restricted to the Triassic.

Umkomasia macleanii is an ovulate structure of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta and the nominate genus of Family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa.

Pteruchus africanus is a pollen organ of a seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta). It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa.

Pteruchus is a form genus for pollen organs of the seed fern (Pteridospermatophyta family Umkomasiaceae. It was first described by Hamshaw Thomas from the Umkomaas locality of South Africa. It is associated with the seed bearing organs Umkomasia and Dicroidium leaves.
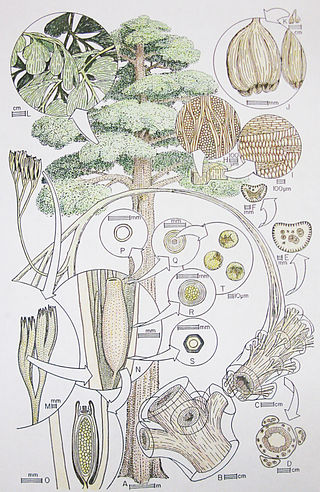
Moresnetiaceae is a natural family of seed ferns in the Division Pteridospermatophyta that appears in the North American and European Devonian to Carboniferous coal measures.

Caytonia nathorstii is an extinct species of seed ferns.

Sagenopteris phillipsii are leaves of extinct species of seed ferns.

Dictyopteridiaceae are an extinct family of glossopterid plants known from the Permian period. It generally refers to reproductive organs, which are associated with Glossopteris leaves.

Stamnostoma is an extinct genus of seed ferns based on cupules with seeds. These are among the earliest known seed plants and of earliest Carboniferous (Tournaisian) age.

Dictyopteridium is an extinct genus of plants belonging to Glossopteridaceae, but the name is used only for compression fossils of elongate multiovulate reproductive structures adnate to Glossopteris leaves. Permineralized remains identical to Dictyopteridium have been referred to the organ genus Homevaleia














