| Celtis hypoleuca | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Cannabaceae |
| Genus: | Celtis |
| Species: | C. hypoleuca |
| Binomial name | |
| Celtis hypoleuca | |
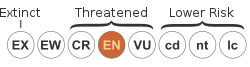
Celtis hypoleuca is a species of plant in the family Cannabaceae. It is endemic to New Caledonia.