Related Research Articles

This is a demography of the population of Ecuador including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia.
A macron is a diacritical mark: it is a straight bar ¯ placed above a letter, usually a vowel. Its name derives from Ancient Greek μακρόν (makrón) "long", since it was originally used to mark long or heavy syllables in Greco-Roman metrics. It now more often marks a long vowel. In the International Phonetic Alphabet, the macron is used to indicate a mid-tone; the sign for a long vowel is instead a modified triangular colon ⟨ː⟩.

Quechua, usually called Runasimi in Quechuan languages, is an indigenous language family spoken by the Quechua peoples, primarily living in the Peruvian Andes. Derived from a common ancestral language, it is the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with an estimated 8–10 million speakers as of 2004. Approximately 25% of Peruvians speak a Quechuan language. It is perhaps most widely known for being the main language family of the Inca Empire. The Spanish encouraged its use until the Peruvian struggle for independence of the 1780s. As a result, Quechua variants are still widely spoken today, being the co-official language of many regions and the second most spoken language family in Peru.

Thai, or Central Thai, is a Tai language of the Kra–Dai language family spoken by the Central Thai people and a vast majority of Thai Chinese. It is the sole official language of Thailand.

Imbabura is a province located in the Andes of northern Ecuador. The capital is Ibarra. The people of the province speak Spanish, and a large portion of the population also speaks the Imbaburan Kichwa variety of the Quechua language.

The Marshallese language, also known as Ebon, is a Micronesian language spoken in the Marshall Islands. Spoken by the ethnic Marshallese people, the language is spoken by nearly the country's entire population of 59,000, making it the principal language of the country. There are also roughly 27,000 Marshallese citizens residing in the United States, nearly all of whom speak Marshallese, as well as in other countries including Nauru.

Barbacoan is a language family spoken in Colombia and Ecuador.
Chachi may refer to:

Sunuwar, Sunuwar, or Kõinch, is a Kiranti language spoken in Nepal and India by the Sunuwar people. It was first comprehensively attested by the Himalayan Languages Project. It is also known as Kõits Lo, Kiranti-Kõits, Mukhiya.
The Sikkimese language, also called Sikkimese, Bhutia, or Drenjongké, Dranjoke, Denjongka, Denzongpeke and Denzongke, belongs to the Tibeto-Burman languages. It is spoken by the Bhutia in Sikkim, India and in parts of Province No. 1, Nepal. The Sikkimese people refer to their own language as Drendzongké and their homeland as Drendzong. Up until 1975 Sikkimese did not have a written language. After gaining Indian Statehood the language was introduced as a school subject in Sikkim and the written language was developed.
Western Yugur also known as Neo-Uygur is the Turkic language spoken by the Yugur people. It is contrasted with Eastern Yugur, a Mongolic language spoken within the same community. Traditionally, both languages are indicated by the term "Yellow Uygur", from the endonym of the Yugur.
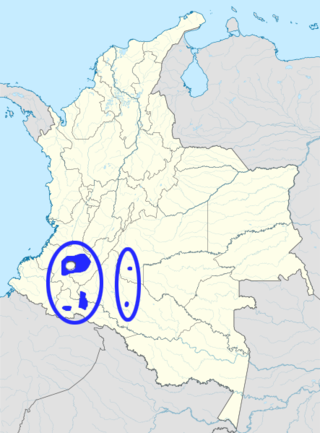
Páez is a language of Colombia, spoken by the Páez people. Crevels (2011) estimates 60,000 speakers out of an ethnic population of 140,000.

Kichwa is a Quechuan language that includes all Quechua varieties of Ecuador and Colombia (Inga), as well as extensions into Peru. It has an estimated half million speakers.

Khamti language is a Southwestern Tai language spoken in Myanmar and India by the Khamti people.
The Chakma Script, also called Ajhā pāṭh, Ojhapath, Ojhopath, Aaojhapath, is an abugida used for the Chakma language, and recently for the Pali language.
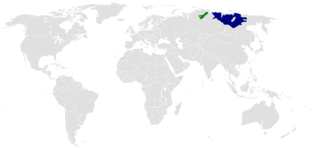
Yakut, also known as Yakutian, Sakha, Saqa or Saxa, is a Turkic language spoken by around 450,000 native speakers, primarily the ethnic Yakuts and one of the official languages of Sakha (Yakutia), a federal republic in the Russian Federation.
Tungag, or Lavongai, is an Austronesian language of New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea, localized New Hanover, the native name of which is Lavongai.
Chachi people are an ethnic group who live in the rainforest area of northwestern Esmeraldas on the northern coast of Ecuador. They live by the Cayapas River in the Centro El Encanto, a section of the Cotacachi Cayapas Ecological Reserve, as do Afro Ecuadorian people; the two groups have co-existed in the forest for about 400 years. There were approximately 5,000 Chachi in 2003.

The Karay-a language is an Austronesian regional language in the Philippines spoken by the Karay-a people, mainly in Antique, Iloilo, Guimaras, and other provinces on the island of Panay, as well as portions of the Soccsksargen region in Mindanao and Palawan.
References
- 1 2 Cha'palaa at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Floyd, Simeon (9 June 2015). "Other-initiated repair in Cha'palaa" (PDF). DeGruyter. Open Linguistics.
- ↑ Floyd, Simeon (2014). "Four Types of Reduplication in the Cha'palaa Language of Ecuador" (PDF). Voort-Goodwin.