
Fucus is a genus of brown algae found in the intertidal zones of rocky seashores almost throughout the world.

Ulothrix is a genus of green algae in the family Ulotrichaceae.

Atractophora hypnoides is a rare red alga (Rhodophyta) found in the British Isles, France and some Atlantic Islands and is the only species of the genus found in the British Isles. It is attached to the rock or other algae by a small basal disc and is much branched with downgrowing filaments which enclose the main branch or axis forming a cortex. Short filaments of limited growth radiate in whorls from the axis and frequently convert into hairs. The spreading filaments grow irregularly in a diffuse manner. Microscope examination is required for identification.
Schmitzia hiscockiana is a small, rare, red seaweed or marine alga of the phylum Rhodophyta or red algae. It was discovered and named in 1985.

Colpomenia peregrina, sometimes referred to by its vernacular names oyster thief and bladder weed, is a species of brown seaweed.
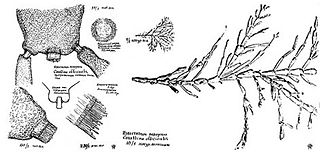
Corallina officinalis is a calcareous red seaweed which grows in the lower and mid-littoral zones on rocky shores.

Polysiphonia is a genus of filamentous red algae with about 19 species on the coasts of the British Isles and about 200 species worldwide, including Crete in Greece, Antarctica and Greenland. Its members are known by a number of common names. It is in the order Ceramiales and family Rhodomelaceae.
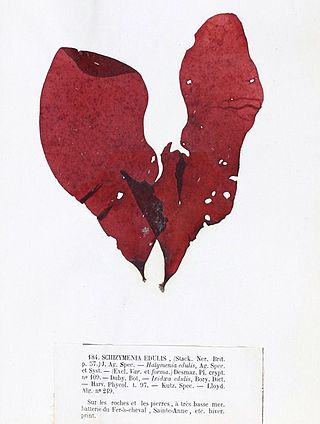
Dilsea carnosa, commonly known as the poor man's weather glass or the sea belt, is a species of red algae in the Dumontiaceae family of the order Gigartinales.

Chaetomorpha aerea is a species of green algae of the family Cladophoraceae.

Chaetomorpha melagonium is a species of green algae of the family Cladophoraceae.
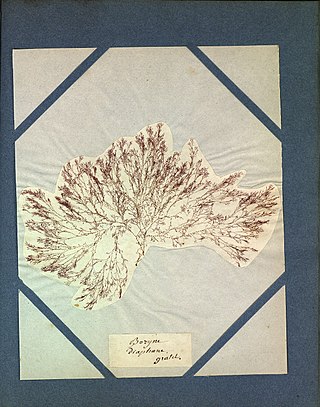
Ceramium diaphanum is a species of marine red algae.

Polysiphonia elongata is a small red marine algae in the Rhodophyta.
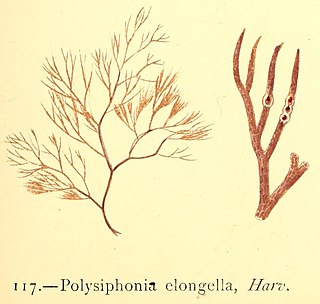
Polysiphonia elongella Harvey in W.J. Hooker is a branched species of marine red algae in the genus in the Polysiphonia in the Rhodophyta.
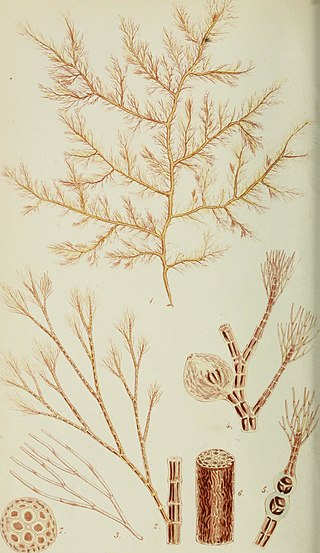
Polysiphonia fibrillosa (Dillwyn) Sprengel is a species of marine red alga in the Rhodophyta.

Polysiphonia stricta is a small red marine alga in the Division Rhodophyta.

Ceramium echionotum is a small marine alga in the division Rhodophyta.

Ceramium ciliatum is a small marine red alga in the Division Rhodophyta.
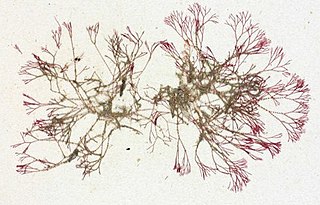
Ceramium cimbricum is a small red alga in the division Rhodophyta.
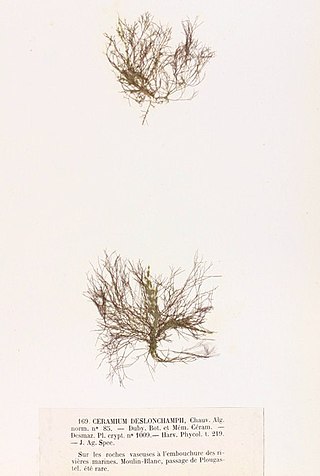
Ceramium deslongchampsii is a small marine red alga in the Division Rhodophyta.

Codium bursa is a green marine algae of medium size.

















