
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 150 species of unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.

Dictyosphaeriaceae is a family of green algae. As of February 2022, AlgaeBase places two genera in the family:
The Palmellaceae are a family of green algae, specifically of the Chlamydomonadales. Members of this group are typically found in atmophytic or terrestrial habitats, or as phycobionts associated with lichens; a few are found in fresh water.
Characiochloris is a genus of green algae in the family Characiochloridaceae. Characiochloris is epiphytic on freshwater algae, or found in soil.

Characium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is very commonly found in freshwater habitats, where it is attached to phytoplankton or zooplankton.

Chlamydocapsa is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae.
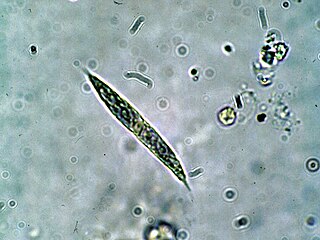
Quadrigula is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is commonly found in freshwater habitats as phytoplankton.

Schroederia is a genus of green algae in the family Schroederiaceae. Schroederiaceae is a monotypic taxon; Schroederia is its only genus.

Stephanosphaera is a genus of green algae in the family Haematococcaceae, containing the single species Stephanosphaera pluvialis. It forms colonies of flagellated cells. Although it was once placed in the family Volvocaceae, it is not closely related to them; its sister is the unicellular genus Balticola. The name comes from the Greek roots stephanos, meaning "crown", and sphaira, meaning "ball".
Tetracystis is a genus of green algae, in the family Chlorococcaceae. It is a terrestrial genus typically found in soils.

Characiaceae is a family of green algae in the order Sphaeropleales. It contains epiphytic or planktonic algae that are unicellular or colonial. The cells are heteropolar, with basal and apical ends having different shapes. The daughter cells are often retained in the cell wall of the old mother cell, whose cell wall becomes gelatinized.
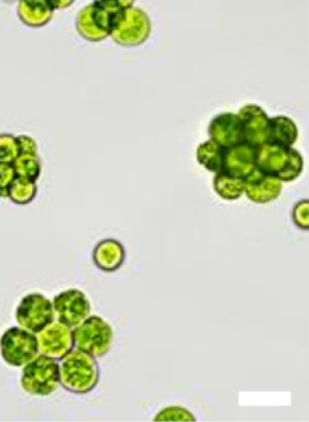
Deasonia is a genus of green algae, in the family Actinochloridaceae. It is found in soils.
Characiellopsis is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. Two species are known: Characiellopsis anophelesii and Characiellopsis skujae.
Deuterocharacium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is found in freshwater habitats, attached to algae or detritus. It is rare and has only been recorded from Europe.

Chlorotetraedron is a genus of green algae, in the family Neochloridaceae. The name may also be written as Chlorotetraëdon. It is found as freshwater plankton or in soil.
Characium marinum is a species of green algae (Chlorophyta).
Chlorolobion, sometimes spelled Chlorolobium, is a genus of algae belonging to the family Selenastraceae. The species of this genus are found in freshwater habitats in Europe and America.

Chlorosarcinaceae is a family of chlorophyte green algae, in the order Chlamydomonadales. Members of this genus are found in soils.










