Related Research Articles

Plastic surgery is a surgical specialty involving the restoration, reconstruction or alteration of the human body. It can be divided into two main categories: reconstructive surgery and cosmetic surgery. Reconstructive surgery includes craniofacial surgery, hand surgery, microsurgery, and the treatment of burns. While reconstructive surgery aims to reconstruct a part of the body or improve its functioning, cosmetic surgery aims to improve the appearance of it. A comprehensive definition of plastic surgery has never been established, because it has no distinct anatomical object and thus overlaps with practically all other surgical specialties. An essential feature of plastic surgery is that it involves the treatment of conditions that require or may require tissue relocation skills.
Facial feminization surgery (FFS) is a set of reconstructive surgical procedures that alter typically male facial features to bring them closer in shape and size to typical female facial features. FFS can include various bony and soft tissue procedures such as brow lift, rhinoplasty, cheek implantation, and lip augmentation.
An osteotomy is a surgical operation whereby a bone is cut to shorten or lengthen it or to change its alignment. It is sometimes performed to correct a hallux valgus, or to straighten a bone that has healed crookedly following a fracture. It is also used to correct a coxa vara, genu valgum, and genu varum. The operation is done under a general anaesthetic.
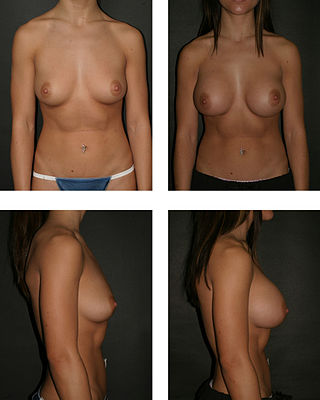
Breast augmentation and augmentation mammoplasty is a cosmetic surgery technique using breast-implants and fat-graft mammoplasty techniques to increase the size, change the shape, and alter the texture of the breasts. Augmentation mammoplasty is applied to correct congenital defects of the breasts and the chest wall. As an elective cosmetic surgery, primary augmentation changes the aesthetics – of size, shape, and texture – of healthy breasts.

A dental implant is a prosthesis that interfaces with the bone of the jaw or skull to support a dental prosthesis such as a crown, bridge, denture, or facial prosthesis or to act as an orthodontic anchor. The basis for modern dental implants is a biological process called osseointegration, in which materials such as titanium or zirconia form an intimate bond to the bone. The implant fixture is first placed so that it is likely to osseointegrate, then a dental prosthetic is added. A variable amount of healing time is required for osseointegration before either the dental prosthetic is attached to the implant or an abutment is placed which will hold a dental prosthetic/crown.
Oral and maxillofacial surgery is a surgical specialty focusing on reconstructive surgery of the face, facial trauma surgery, the oral cavity, head and neck, mouth, and jaws, as well as facial cosmetic surgery/facial plastic surgery including cleft lip and cleft palate surgery.

Orthognathic surgery, also known as corrective jaw surgery or simply jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and lower face related to structure, growth, airway issues including sleep apnea, TMJ disorders, malocclusion problems primarily arising from skeletal disharmonies, and other orthodontic dental bite problems that cannot be treated easily with braces, as well as the broad range of facial imbalances, disharmonies, asymmetries, and malproportions where correction may be considered to improve facial aesthetics and self-esteem.
Lip augmentation is a cosmetic procedure that modifies the shape of the lips using fillers, such as collagen or implants. The procedure may be performed to increase lip size, correct asymmetry, create protrusion, or adjust the ratio of the top and bottom lips. The procedure typically involves surgical injection, though temporary non-surgical alternatives exist.
Gluteoplasty denotes the plastic surgery and the liposuction procedures for the correction of the congenital, traumatic, and acquired defects and deformities of the buttocks and the anatomy of the gluteal region; and for the aesthetic enhancement of the contour of the buttocks.

Cheek augmentation is a cosmetic surgical procedure that is intended to emphasize the cheeks on a person's face. To augment the cheeks, a plastic surgeon may place a solid implant over the cheekbone. Injections with the patients' own fat or a soft tissue filler, like Restylane, are also popular. Rarely, various cuts to the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) may be performed. Cheek augmentation is commonly combined with other procedures, such as a face lift or chin augmentation.
Jaw reduction or mandible angle reduction is a type of surgery to narrow the lower one-third of the face—particularly the contribution from the mandible and its muscular attachments. There are several techniques for treatment—including surgical and non-surgical methods. A square lower jaw can be considered a masculine trait, especially in Asian countries. As a result, whereas square lower jaws are often considered a positive trait in men, a wide mandible can be perceived as discordant or masculine on women, or sometimes in certain men, particularly when there is asymmetry.
Guided bone regeneration (GBR) and guided tissue regeneration (GTR) are dental surgical procedures that use barrier membranes to direct the growth of new bone and gingival tissue at sites with insufficient volumes or dimensions of bone or gingiva for proper function, esthetics or prosthetic restoration. Guided bone regeneration typically refers to ridge augmentation or bone regenerative procedures; guided tissue regeneration typically refers to regeneration of periodontal attachment.
Bone segment navigation is a surgical method used to find the anatomical position of displaced bone fragments in fractures, or to position surgically created fragments in craniofacial surgery. Such fragments are later fixed in position by osteosynthesis. It has been developed for use in craniofacial and oral and maxillofacial surgery.
Zygoma reduction, also known as cheekbone reduction surgery, is a surgery used to reduce the facial width by excising part of the zygomatic bone and arch. Wide cheekbones are a characteristic facial trait of Asians, whose skull shapes tend to be more brachycephalic in comparison with Caucasian counterparts, whose skull shapes tend to be more dolichocephalic .This surgery is popular among Asians due to their inherent wide cheekbones. Due to the advanced surgical skills of Korean surgeons who perform facial contouring surgeries, the number of Asian people undergoing this surgery is increasing.
Facial implants are used to enhance certain features of the face. The surgery may be elective, or needed as the result of prior surgery on the face. Each involves placing synthetic materials deep under the subcutaneous tissue and onto the underlying bone. A maxillofacial or plastic surgeon uses them to aesthetically improve facial contours, proportion and correct imbalances caused by injury or hereditary traits. However, in cases that require orthognathic osteotomies, those should be done before any implants are considered.

A lip lift is a plastic surgery procedure that modifies the cosmetic appearance of the lips by reshaping them to increase the prominence of the vermilion border; and to enhance the facial area above the lips into a more aesthetically pleasing shape. In corrective praxis, a lip lift procedure is distinguished from lip enhancement, the augmentation of the lips, which can be effected with a non-surgical procedure.
Non-surgical rhinoplasty is a medical aesthetic procedure in which injectable fillers, most commonly hyaluronic acid ones like Restylane and Juvederm or calcium hydroxyapatite (Radiesse), are used to alter and shape a person's nose without a surgery. The procedure fills in depressed areas on the nose, lifting the angle of the tip or smoothing the appearance of bumps on the bridge. Non surgical rhinoplasty is an augmentation procedure, so it cannot reduce the size of someone's nose. The cosmetic procedure carries the risk of causing serious skin damage or distant complications like blindness. If the filler product is injected into an artery, filler can travel in the arteries and blocks smaller size arteries like ophthalmic artery and cause blindness. If blood vessels of the skin is blocked, skin necrosis can develop. Hyaluronic acid based fillers can be reversed even if injected into a blood vessel with an enzyme called hyaluronidase, which can be also injected like fillers.
Facial masculinization surgery (FMS) is a set of plastic surgery procedures that can transform the patient's face to exhibit typical masculine morphology. Cisgender men may elect to undergo these procedures, and in the context of transgender people, FMS is a type of facial gender confirmation surgery (FGCS), which also includes facial feminization surgery (FFS) for transgender women.
Alloplasty is a surgical procedure performed to substitute and repair defects within the body with the use of synthetic material. It can also be performed in order to bridge wounds. The process of undergoing alloplasty involves the construction of an alloplastic graft through the use of computed tomography (CT), rapid prototyping and "the use of computer-assisted virtual model surgery." Each alloplastic graft is individually constructed and customised according to the patient's defect to address their personal health issue. Alloplasty can be applied in the form of reconstructive surgery. An example where alloplasty is applied in reconstructive surgery is in aiding cranial defects. The insertion and fixation of alloplastic implants can also be applied in cosmetic enhancement and augmentation. Since the inception of alloplasty, it has been proposed that it could be a viable alternative to other forms of transplants. The biocompatibility and customisation of alloplastic implants and grafts provides a method that may be suitable for both minor and major medical cases that may have more limitations in surgical approach. Although there has been evidence that alloplasty is a viable method for repairing and substituting defects, there are disadvantages including suitability of patient bone quality and quantity for long term implant stability, possibility of rejection of the alloplastic implant, injuring surrounding nerves, cost of procedure and long recovery times. Complications can also occur from inadequate engineering of alloplastic implants and grafts, and poor implant fixation to bone. These include infection, inflammatory reactions, the fracture of alloplastic implants and prostheses, loosening of implants or reduced or complete loss of osseointegration.

Mandibular setback surgery is a surgical procedure performed along the occlusal plane to prevent bite opening on the anterior or posterior teeth and retract the lower jaw for both functional and aesthetic effects in patients with mandibular prognathism. It is an orthodontic surgery that is a form of reconstructive plastic surgery. There are three main types of procedures for mandibular setback surgery: Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy (BSSO), Intraoral Vertical Ramus Osteotomy (IVRO) and Extraoral Ramus Osteotomy (EVRO), depending on the magnitude of mandibular setback for each patient. Postoperative care aims to minimise postoperative complications, complications includes bite changes, relapse and nerve injury.
References
- ↑ "Preparing for Your Chin Reduction Surgery". Solomon Facial Plastic. 2020-02-21. Retrieved 2021-12-14.
- ↑ Aufricht, G: combined plastic surgery of the nose and chin; resume of twenty seven years' experiences. Am J Surg 1958 Feb;95(2): 231-6
- ↑ "Benefits Of Chin Implants Toronto | Dr. Solomon". Solomon Facial Plastic. 2016-10-03. Retrieved 2021-10-22.
- ↑ Lee, Tae Sung; Kim, Hye Young; Kim, Takho; Lee, Ji Hyuck; Park, Sanghoon (October 2014). "Importance of the Chin in Achieving a Feminine Lower Face". The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery. 25 (6): 2180–3. doi:10.1097/scs.0000000000001096. ISSN 1049-2275. PMID 25329849. S2CID 27463104.
- 1 2 Lee, Tae Sung; Kim, Hye Young; Kim, Tak Ho; Lee, Ji Hyuck; Park, Sanghoon (March 2014). "Contouring of the Lower Face by a Novel Method of Narrowing and Lengthening Genioplasty". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 133 (3): 274e–282e. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000438054.21634.4a. ISSN 0032-1052. PMID 24572871. S2CID 2679583.
- 1 2 Lee, Tae Sung (December 2015). "Standardization of surgical techniques used in facial bone contouring". Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery. 68 (12): 1694–1700. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2015.08.010. ISSN 1748-6815. PMID 26346781.
- ↑ Park, Sanghoon (2017-06-14), "The Osseous Genioplasty", Facial Bone Contouring Surgery, Springer Singapore, pp. 63–77, doi:10.1007/978-981-10-2726-0_8, ISBN 9789811027253
- ↑ Lim, Jongwoo (2017-06-14), "Essential Surgical Anatomy for Facial Bone Contouring Surgery", Facial Bone Contouring Surgery, Springer Singapore, pp. 7–13, doi:10.1007/978-981-10-2726-0_2, ISBN 9789811027253
- ↑ Lee, Tae Sung (2017-06-14), "Surgical Approaches for Facial Bone Surgery", Facial Bone Contouring Surgery, Springer Singapore, pp. 15–22, doi:10.1007/978-981-10-2726-0_3, ISBN 9789811027253
- ↑ Costantino PD. FriedmanCD: Soft-tissue augmentation and replacement in the head and neck. General considerations, Ontolaryngol Clin North Am 1994 Feb;27(1): 1-12
- ↑ White JB, Dufresne CR. Management and avoidance of complications in chin augmentation. Aesthet Surg J. 2011 Aug 1;31(6):634-42.
- ↑ Gore Medical Products Maas CS, Merwin GE, Wilson J, et al.: Comparison of biomaterials for facial augmentation. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1990 May; 116(5): 551-6.
- ↑ Guyuron B, Raszewski RL: A critical comparison of osteoplasic and alloplastic augmentation genioplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg 1990 Summer, 14(3): 199-206