Related Research Articles

Since independence, with Jaja Wachuku as the first Minister for Foreign Affairs and Commonwealth Relations, later called External Affairs, Nigerian foreign policy has been characterised by a focus on Africa as a regional power and by attachment to several fundamental principles: African unity and independence; capability to exercise hegemonic influence in the region: peaceful settlement of disputes; non-alignment and non-intentional interference in the internal affairs of other nations; and regional economic cooperation and development. In carrying out these principles, Nigeria participates in the African Union, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), the Non-Aligned Movement, the Commonwealth of Nations, and the United Nations.
Xenophobia is the fear or hatred of that which is perceived to be foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an ingroup and an outgroup and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a desire to eliminate their presence, and fear of losing national, ethnic or racial identity.

Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, formerly Rhodesia, is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa, Botswana, Zambia and Mozambique. The capital and largest city is Harare. The second largest city is Bulawayo. A country of roughly 14 million people, Zimbabwe has 16 official languages, with English, Shona, and Ndebele the most common.

The economy of Zimbabwe is mainly made of tertiary industry which makes up to 60% of the total GDP as of 2017. Zimbabwe has the second biggest informal economy as a share of its economy which has a score of 60.6%. Agriculture and mining largely contribute to exports. The economy of Zimbabwe grew at average of 12% from 2009 to 2013 making it one of the fastest growing economies in the world recovering from negative growth from 1998 to 2008 before it slowed to 0.7% growth in 2016.

The foreign relations of Zimbabwe emphasize a close relationship with the People's Republic of China and South Africa, nations with close economic ties to Zimbabwe.

Harare is the capital and most populous city of Zimbabwe. The city proper has an area of 960.6 km2 (371 mi2) and an estimated population of 1,606,000 in 2009, with 2,800,000 in its metropolitan area in 2006. Situated in north-eastern Zimbabwe in the country's Mashonaland region, Harare is a metropolitan province, which also incorporates the municipalities of Chitungwiza and Epworth. The city sits on a plateau at an elevation of 1,483 metres above sea level and its climate falls into the subtropical highland category.
The economy of Africa consists of the trade, industry, agriculture, and human resources of the continent. As of 2019, approximately 1.3 billion people were living in 54 countries in Africa. Africa is a resource-rich continent. Recent growth has been due to growth in sales in commodities, services, and manufacturing. West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa and Southern Africa in particular, are expected to reach a combined GDP of $29 trillion by 2050.
BRIC is a grouping acronym referring to the countries of Brazil, Russia, India and China, deemed to be developing countries at a similar stage of newly advanced economic development, on their way to becoming developed countries. It is typically rendered as "the BRICs" or "the BRIC countries" or "the BRIC economies" or alternatively as the "Big Four". A related acronym, BRICS, adds South Africa.
The Tanzania People’s Defence Force (TPDF) is the armed forces of Tanzania. They were set up in September 1964, following a mutiny by the former colonial military force: the Tanganyika Rifles. From its inception, it was ingrained in the troops of the new TPDF that they were a people’s force under civilian control. Unlike some of its neighbors, Tanzania has never suffered a coup d'état or civil war.

China and Zimbabwe have had a close, but chequered, relationship since the latter's independence.
Prior to 1994, immigrants from elsewhere faced discrimination and even violence in South Africa. After majority rule in 1994, contrary to expectations, the incidence of xenophobia increased. Between 2000 and March 2008, at least 67 people died in what were identified as xenophobic attacks. In May 2008, a series of attacks left 62 people dead; although 21 of those killed were South African citizens. The attacks were motivated by xenophobia. In 2015, another nationwide spike in xenophobic attacks against immigrants in general prompted a number of foreign governments to begin repatriating their citizens. A Pew Research poll conducted in 2018 showed that 62% of South Africans viewed immigrants as a burden on society by taking jobs and social benefits and that 61% of South Africans thought that immigrants were more responsible for crime than other groups. Between 2010 and 2017 the immigrant community in South Africa increased from 2 million people to 4 million people. The proportion of South Africa's total population that is foreign born increased from 2.8% in 2005 to 7% in 2019, according to the United Nations International Organization for Migration, in spite of widespread xenophobia in the country. This made South Africa the largest recipient of immigrants on the African continent in 2019.
There is a significant population of Zimbabweans in South Africa, making up South Africa's largest group of foreign migrants. Estimates of their numbers range from one to five million.

Hyperinflation in Zimbabwe was a period of currency instability in Zimbabwe that, using Cagan's definition of hyperinflation, began in February 2007. During the height of inflation from 2008 to 2009, it was difficult to measure Zimbabwe's hyperinflation because the government of Zimbabwe stopped filing official inflation statistics. However, Zimbabwe's peak month of inflation is estimated at 79.6 billion percent month-on-month, 89.7 sextillion percent year-on-year in mid-November 2008.
The media of Zimbabwe has varying amounts of control by successive governments, coming under tight restriction in recent years by the government of Robert Mugabe, particularly during the growing economic and political crisis in the country. The Zimbabwean constitution promotes freedom of the media and expression, however this is hampered by interference and the implementation of strict media laws. In its 2008 report, Reporters Without Borders ranked the Zimbabwean media as 151st out of 173.

The Zimbabwean dollar was the name of 4 official currencies of Zimbabwe from 1980 to 12 April 2009. During this time, it was subject to periods of above-average inflation, followed by a period of hyperinflation.
The Marange diamond fields are an area of widespread small-scale diamond production in Chiadzwa, Mutare District, Zimbabwe. 'Although estimates of the reserves contained in this area vary wildly, some have suggested that it could be home to one of the world's richest diamond deposits'. The hugely prolific fields are regarded by some experts as the world's biggest diamond find in more than a century. Production from Marange is controversial due to ongoing legal wrangles and government crackdowns on illegal miners and allegations of forced labour. In terms of carats produced, the Marange field is the largest diamond producing project in the world, estimated to have produced 16.9 million carats in 2013, or 13% of global rough diamond supply. Marange is estimated to have produced 12.0 million carats in 2012, 8.7 million carats in 2011, and 8.2 million carats in 2010. While some diamond mines produce rough valued at over $1000 per carat, average production at Marange is estimated at under $50 per carat.
There is a small but growing population of Chinese people in Senegal, largely consisting of expatriates from the People's Republic of China who began arriving in the country in the 1980s.

Migration of Chinese people in Ghana dates back to the 1940s. Originally, most came from Hong Kong; migration from mainland China began only in the 1980s. Although an exact number is not clear, one unsubstantiated speculation is that the Chinese living in Ghana might number to be as extremely high as nearly 700,000 people. This would however mean that an impossible 2,4% of the people in Ghana are of Chinese heritage. Furthermore, a careful examination of the cited documents does not yield a validation of the above-estimated number; and in any case, it would in the interest of accuracy be important to critically examine how, and on what basis the estimated numbers were arrived at. If this figure were to be correct, it would mean that there are more Chinese people living in Ghana than anywhere else in Sub-Saharan Africa including South Africa which reportedly has the highest Chinese population on the African Continent. Notably, The China Africa Research Initiative at Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International studies https://www.sais.org cites the total number of Chinese workers in Africa in 2018 as 201,057 as per the National Bureau of Statistics of China which is corroborated by other sources such as The Almanac Of China's Foreign Economic Relations and Trade, and The China Annual Bulletin Of Statistics Of Contracted Projects. This figure indicates a steady decline from the previous years 2015-2017 but however, ostensibly does not account for informal migrants such as traders and shopkeepers.
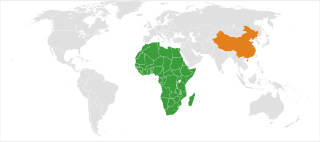
Sino-African relations or Afro-Chinese relations refers to the historical, political, economic, military, social and cultural connections between China and the African continent.
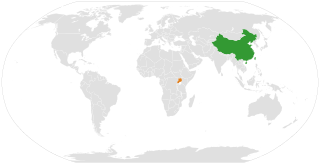
Relations between Uganda and the People's Republic of China were established in 1962. Trade between the two nations totaled over $1 billion in 2017. Additionally, Chinese companies have contributed significantly to the building of infrastructure in Uganda. China also owns about 20% of Uganda's debt, equivalent to about $1.6 billion. The Ugandan ambassador to China is Crispus Kiyonga. The Chinese ambassador to Uganda is Zheng Zhuqiang.
References
- ↑ "10,000 Chinese in Zim". Chronicle. February 24, 2016.
- ↑ "China's Influence in Africa Arouses Some Resistance". New York Times. February 10, 2007.
- 1 2 3 "Africans have mixed perceptions of Chinese migrants, finds study". Radio Australia. August 20, 2012.
- ↑ Chinese Investments in Africa: A Labour Perspective (PDF). 2009. p. 258. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-06-14. Retrieved 2015-06-12.