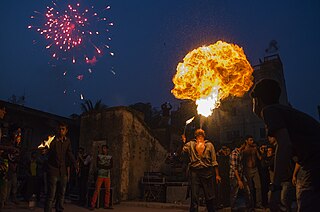Dhaka, formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. It is the ninth-largest and seventh-most densely populated city in the world. Dhaka is a megacity, and has a population of 10.2 million residents as of 2024, and a population of over 23.9 million residents in Dhaka Metropolitan Area. It is widely considered to be the most densely populated built-up urban area in the world. Dhaka is the most important cultural, economic, and scientific hub of Eastern South Asia, as well as a major Muslim-majority city. Dhaka ranks third in South Asia and 39th in the world in terms of GDP. Lying on the Ganges Delta, it is bounded by the Buriganga, Turag, Dhaleshwari and Shitalakshya rivers. Dhaka is also the largest Bengali-speaking city in the world.

Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, popularly known by the honorific prefix Bangabandhu, was a Bangladeshi politician, revolutionary, statesman, activist and diarist. As a politician, Mujib had held continuous positions either as Bangladesh's president or as its prime minister from April 1971 until his assassination in August 1975. Mujib successfully led the Bangladeshi independence movement and restored Bengali sovereignty after over two centuries following the Battle of Plassey in 1757, for which he is honoured as the "Father of the Nation" in Bangladesh who declared independence. In the 2004 BBC opinion poll, Mujib was voted as the Greatest Bengali of all time.

Sylhet is a metropolitan city located in the northeastern region of Bangladesh. It is the administrative center of Sylhet Division and is situated on the banks of the Surma River. Sylhet is the fifth-largest city in Bangladesh, with a population of around 700,000 people.

Zainul Abedin, also known as Shilpacharya was a Bangladeshi painter. He became well known in 1944 through his series of paintings depicting some of the great famines in Bengal during its British colonial period. After the Partition of Indian subcontinent he moved to East Pakistan. In 1948, he helped to establish the Institute of Arts and Crafts at the University of Dhaka. The Indian Express has described him as a legendary Bangladeshi painter and activist. Like many of his contemporaries, his paintings on the Bengal famine of 1943 are viewed as his most characteristic works. His homeland honored him with the title "Shilpacharya" "Great teacher of the arts" for his artistic and visionary attributes. He was the pioneer of the modern art movement that took place in Bangladesh and was rightly considered by Syed Manzoorul Islam as the founding father of Bangladeshi modern arts, soon after Bangladesh earned the status of an independent republic.
Miss Bangladesh is a national beauty pageant in Bangladesh that annually selectes representatives to compete in Miss World (1994-2001), one of the Big Four international beauty pageants.

Suhrawardy Udyan is a national memorial and public space located in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Originally known as Ramna Race Course, it holds significant historical importance due to its association with key events in the country's history.

Shahbagh is a major neighbourhood and a police precinct or thana in Dhaka, the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. It is also a major public transport hub. It is a junction between two contrasting sections of the city—Old Dhaka and New Dhaka—which lie, respectively, to its south and north. Developed in the 17th century during Mughal rule in Bengal, when Old Dhaka was the provincial capital and a centre of the flourishing muslin industry, it came to neglect and decay in early 19th century. In the mid-19th century, the Shahbagh area was developed as New Dhaka became a provincial centre of the British Raj, ending a century of decline brought on by the passing of Mughal rule.

Gulshan is a thana situated in Dhaka, Bangladesh. It is an affluent residential and business neighbourhood and is now home to a number of the city's restaurants, five star hotels, shopping centers, schools, banks, offices and members' clubs; it also hosts the majority of embassies and high commissions in Bangladesh. Many Bangladeshi and international companies have their offices in Gulshan.
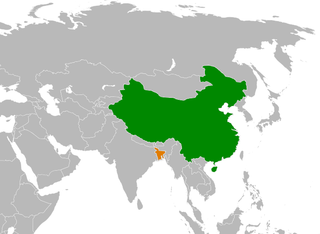
Bangladesh–China relations are the bilateral relations of Bangladesh and China. China has an embassy in Dhaka and Bangladesh has one in Beijing and consulates in Hong Kong and Kunming. Both countries are members of the BCIM Forum. According to Chinese government designations, Bangladesh and China are in a "comprehensive strategic cooperative partnership".

Old Dhaka is a term used to refer to the historic old city of Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh. It was founded in 1608 as Jahangirabad or Jahangirnagar, the capital of Mughal Province of Bengal and named after the Mughal emperor Jahangir. It is located on the banks of the Buriganga River. It was one of the largest and most prosperous cities of the Indian subcontinent and the center of the worldwide muslin trade. The then Nawab of Bengal Murshid Quli Khan shifted the capital from Dhaka to Murshidabad in the early-18th century. With the rise of Calcutta during the British rule, Dhaka began to decline and came to be known as the "City of Magnificent Ruins". The British however began to develop the modern city from the mid-19th century.
Friendship is a needs-driven non-governmental organisation that works in the Char islands and riverbanks of northern Bangladesh, the coastal belt in the south, and as of 2017, the Rohingya refugee camps in Ukhia, Cox's Bazar in the southeast. Established by Runa Khan in 2002, Friendship works to empower people through a sustainable, integrated development approach.
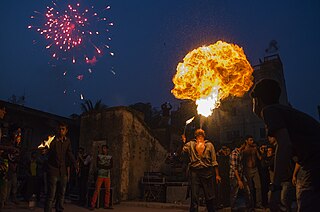
Shakrain Festival is an annual Bengali celebration in Dhaka, Bangladesh, observed with the flying of kites. The celebration is uniquely celebrated by the Bengali Muslim Dhakaiya community based on Old Dhaka. It occurs at the end of Poush, the ninth month of the Bengali calendar. The festival coincides with the holiday of Poush Sankranti This day is known as Poush Sankranti.

Hashem Khan is a Bangladeshi painter. His paintings mostly focus rural life of Bangladesh. He has important contribution to enrich Bangladeshi art and culture. Hashem Khan participated in Bangladesh liberation war and his many artworks on the war. He is the Chairman of Bangladesh National Museum.
The 32nd National Film Awards, presented by Ministry of Information, Bangladesh to felicitate the best of Bangladeshi Cinema released in the year 2007. Bangladesh National Film Awards is a film award ceremony in Bangladesh established in 1975 by Government of Bangladesh. Every year, a national panel appointed by the government selects the winning entry, and the award ceremony is held in Dhaka. 2007 was the 32nd installment of Bangladesh National Film Award. Chief Adviser Dr. Fakhruddin Ahmed presented the awards at the Bangladesh-China Friendship Conference Centre on October 23, 2008.

Bengali Beauty is a Bangladeshi period romantic comedy-drama film written and directed by Rahsaan Noor. It stars Noor as a brash radio deejay and Mumtaheena Toya as a demure medical student, who fall in love in Dhaka during a politically turbulent 1975. Sarah Alam and Ashfique Rizwan make their feature film debuts in supporting roles.
Sexuality in Bangladesh is primarily influenced by religion and culture. The culture in Bangladesh is predominantly conservative and patriarchal. Several topics, including sex education, romantic relationship, and sexual behavior are considered taboo. Over the years, the perception towards a very few taboos have changed, such as sex education is now somewhat taught in high schools though in a conservative way.
The COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh was a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus was confirmed to have spread to Bangladesh in March 2020. The first three known cases were reported on 8 March 2020 by the country's epidemiology institute, IEDCR. Since then, the pandemic has spread day by day over the whole nation and the number of affected people has been increasing. Bangladesh is the second most affected country in South Asia, after India.

Bangladesh began the administration of COVID-19 vaccines on 27 January 2021 while mass vaccination started on 7 February 2021.