
Mahogany is a straight-grained, reddish-brown timber of three tropical hardwood species of the genus Swietenia, indigenous to the Americas and part of the pantropical chinaberry family, Meliaceae.

Eucalyptus is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including Corymbia, they are commonly known as eucalypts. Plants in the genus Eucalyptus have bark that is either smooth, fibrous, hard or stringy, leaves with oil glands, and sepals and petals that are fused to form a "cap" or operculum over the stamens. The fruit is a woody capsule commonly referred to as a "gumnut".

The cashew tree is a tropical evergreen tree that produces the cashew seed and the cashew apple pseudofruit. The tree can grow as high as 14 m (46 ft), but the dwarf cultivars, growing up to 6 m (20 ft), prove more profitable, with earlier maturity and greater yields.

A woodland is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood, a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade. Woodlands may support an understory of shrubs and herbaceous plants including grasses. Woodland may form a transition to shrubland under drier conditions or during early stages of primary or secondary succession. Higher-density areas of trees with a largely closed canopy that provides extensive and nearly continuous shade are often referred to as forests.

The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a system of mountains in eastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before experiencing natural erosion. The Appalachian chain is a barrier to east–west travel, as it forms a series of alternating ridgelines and valleys oriented in opposition to most highways and railroads running east–west.

Morus, a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of diverse species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the plant has three main species ostensibly named for the fruit color of the best-known cultivar: white, red, and black mulberry, with numerous cultivars, but more than 200 species are identified in taxonomy. The name “white mulberry” came about because the first specimens named by European taxonomists were a cultivated mutation prized for their white fruit, but wild trees bear black fruit like other mulberries. White mulberry is native to South Asia, but is widely distributed across Europe, Southern Africa, South America, and North America. It is regarded as an invasive species in Brazil and the United States.

A lignotuber is a woody swelling of the root crown possessed by some plants as a protection against destruction of the plant stem, such as by fire. The crown contains buds from which new stems may sprout, as well as stores of starch that can support a period of growth in the absence of photosynthesis. The term "lignotuber" was coined in 1924 by Australian botanist Leslie R. Kerr.

A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of grasses.

Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions.

Celtis is a genus of about 60–70 species of deciduous trees, commonly known as hackberries or nettle trees, widespread in warm temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, in southern Europe, southern and eastern Asia, and southern and central North America, south to central Africa, and northern and central South America. The genus is present in the fossil record at least since the Miocene of Europe, and Paleocene of North America and eastern Asia.

The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions. The tree line is sometimes distinguished from a lower timberline or forest line, which is the line below which trees form a forest with a closed canopy.

Pinus strobus, commonly denominated the eastern white pine, northern white pine, white pine, Weymouth pine (British), and soft pine is a large pine native to eastern North America. It occurs from Newfoundland, Canada west through the Great Lakes region to southeastern Manitoba and Minnesota, United States, and south along the Appalachian Mountains and upper Piedmont to northernmost Georgia and perhaps very rarely in some of the higher elevations in northeastern Alabama. It is considered rare in Indiana.

Temperate rainforests are coniferous or broadleaf forests that occur in the temperate zone and receive heavy rainfall.

Hevea brasiliensis, the Pará rubber tree, sharinga tree, seringueira, or, most commonly, the rubber tree or rubber plant, is a flowering plant belonging to the spurge family Euphorbiaceae. It is the most economically important member of the genus Hevea because the milky latex extracted from the tree is the primary source of natural rubber.

The Sandhills or Carolina Sandhills is a 10-35 mi wide physiographic region within the U.S. Atlantic Coastal Plain province, along the updip (inland) margin of this province in the States of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia. The extent of the Carolina Sandhills is shown clearly in maps of the ecoregions of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia.

Cinnamomum camphora is a species of evergreen tree that is commonly known under the names camphor tree, camphorwood or camphor laurel.
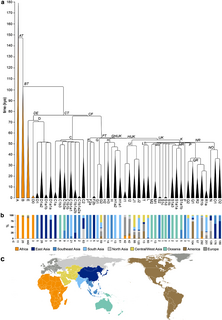
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non-recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome. Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats (STRs) and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs).

The South American coati, also known as the ring-tailed coati, and called quati in Portuguese, is a coati species and a member of the raccoon family (Procyonidae), found in the tropical and subtropical parts of South America. An adult generally weighs from 2–7.2 kg (4.4–15.9 lb) and is 85–113 cm (33–44 in) long, with half of that being its tail. Its colour is highly variable and the rings on the tail may be only somewhat visible, but its most distinguishing characteristic is that it lacks the largely white snout of its northern relative, the white-nosed coati.
Temperate deciduous or temperate broad-leaf forests are a variety of temperate forest 'dominated' by trees that lose their leaves each year. They are found in areas with warm moist summers and cool winters. The six major areas of this forest type occur in the Northern Hemisphere: North America, East Asia, Central and Western Europe, Denmark, southern Sweden and southern Norway. Temperate evergreen forests occur in Australasia, New Zealand and southern South America, however they are not deciduous as their northern-hemisphere equivalents. Examples of typical trees in the Northern Hemisphere's deciduous forests include oak, maple, basswood, beech and elm, while in the Southern Hemisphere, trees of the genus Nothofagus dominate this type of forest. They are also bound to receive heavy rainfall.
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the base of a rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Each node in the tree corresponds to a clade; i.e., clade C may be described as basal within a larger clade D if its root is directly linked to the root of D. The terms deep-branching or early-branching are similar in meaning.


















