
The Chlorophyceae are one of the classes of green algae, distinguished mainly on the basis of ultrastructural morphology. They are usually green due to the dominance of pigments chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. The chloroplast may be discoid, plate-like, reticulate, cup-shaped, spiral- or ribbon-shaped in different species. Most of the members have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids located in the chloroplast. Pyrenoids contain protein besides starch. Some green algae may store food in the form of oil droplets. They usually have a cell wall made up of an inner layer of cellulose and outer layer of pectose.

Chlamydomonadales, also known as Volvocales, are an order of flagellated or pseudociliated green algae, specifically of the Chlorophyceae. Chlamydomonadales can form planar or spherical colonies. These vary from Gonium up to Volvox. Each cell has two flagella, and is similar in appearance to Chlamydomonas, with the flagella throughout the colony moving in coordination.

The glaucophytes, also known as glaucocystophytes or glaucocystids, are a small group of unicellular algae found in freshwater and moist terrestrial environments, less common today than they were during the Proterozoic. The stated number of species in the group varies from about 14 to 26. Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and the green algae plus land plants, they form the Archaeplastida.

Dictyosphaeriaceae is a family of green algae. As of February 2022, AlgaeBase places two genera in the family:
The Characiosiphonaceae are a family of algae in the order Chlamydomonadales. Two genera are included in this family, Characiosiphon and Lobocharacium, each containing a single species. The genus Characiochloris may eventually be placed in this family pending future revisions, as it is phylogenetically closely related to the twose genera.

Chlorococcaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlamydomonadales. They are mostly soil-dwelling algae. Many members of this group produce lipids and secondary carotenoids.
The Palmellaceae are a family of green algae, specifically of the Chlamydomonadales. Members of this group are typically found in atmophytic or terrestrial habitats, or as phycobionts associated with lichens; a few are found in fresh water.
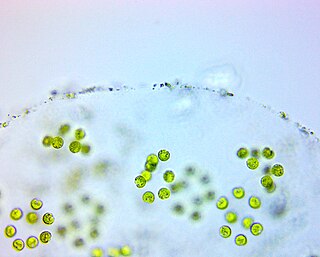
The Tetrasporaceae are a family of green algae, specifically of the Chlamydomonadales. They are found in freshwater habitats.

Ankistrodesmus is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae. It is one of the most common types of phytoplankton in freshwater habitats around the world.
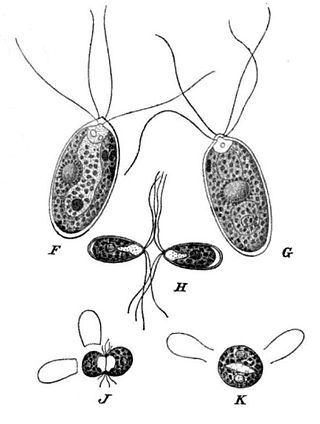
Carteria is a genus of green algae in the family Chlamydomonadaceae. Carteria are similar in morphology to the common genus Chlamydomonas and differ by having four, rather than two, flagella at the vegetative stage.

Characium is a genus of green algae in the family Characiaceae. It is very commonly found in freshwater habitats, where it is attached to phytoplankton or zooplankton.
Chlorococcum is a genus of green algae, in the family Chlorococcaceae. The alga may be useful in the flocculation of lipids from wastewater. It can be found in fresh water, but is more commonly found in soil or subaerial habitats.

Chlorosarcina is a genus of green algae, specifically of the Chlamydomonadales.

Golenkinia is a genus of green algae first described in 1894 by Robert Chodat. The genus is named for the Russian phycologist Mikhail Iljitsch Golenkin. Golenkinia species live in fresh water and are found around the world.

Neochloris is a genus of green algae in the family Neochloridaceae. It is found in freshwater aquatic and terrestrial soil habitats.

Paulschulzia is a genus of green algae, specifically of the family Tetrasporaceae.

Tetraspora is a genus of green algae in the family Tetrasporaceae of the order Chlamydomonadales, division Chlorophyta. Species of Tetraspora are unicellular green algae that exist in arrangements of four and consist of cells being packaged together in a gelatinous envelope that creates macroscopic colonies. These are primarily freshwater organisms, although there have been few cases where they have been found inhabiting marine environments and even contaminated water bodies. Tetraspora species can be found all around the globe, except in Antarctica. Despite the ubiquitous presence, the greatest growth of the genera's species is seen in the polar climatic zones.
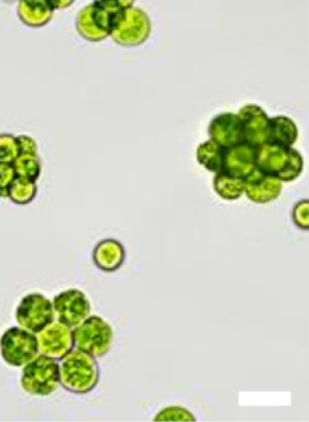
Actinochloridaceae is a family of green algae, in the order Chlamydomonadales.
Follicularia is a genus of green algae, in the family Schizochlamydaceae. It is found in terrestrial habitats, mainly soil.
Protosiphonaceae is a family of chlorophyte green algae, in the order Chlamydomonadales.















