Related Research Articles

Sarcophagidae are a family of flies commonly known as flesh flies. They differ from most flies in that they are ovoviviparous, opportunistically depositing hatched or hatching maggots instead of eggs on carrion, dung, decaying material, or open wounds of mammals, hence their common name. Some flesh fly larvae are internal parasites of other insects such as Orthoptera, and some, in particular the Miltogramminae, are kleptoparasites of solitary Hymenoptera. The adults mostly feed on fluids from animal bodies, nectar, sweet foods, fluids from animal waste and other organic substances. Juveniles need protein to develop and may be laid on carrion, dung or sweet plant foods.

Heteractis magnifica, also known by the common names magnificent sea anemone or Ritteri anemone, is a species of sea anemone belonging to the Stichodactylidae family native to the Indo-Pacific area.

The Thiotrichales are an order of Pseudomonadota, including Thiomargarita magnifica, the largest known bacterium.

Abies magnifica, the red fir or silvertip fir, is a western North American fir, native to the mountains of southwest Oregon and California in the United States. It is a high-elevation tree, typically occurring at 1,400–2,700 metres (4,600–8,900 ft) elevation, though only rarely reaching tree line. The name red fir derives from the bark color of old trees.
Kentiopsis magnifica is a species of flowering plant in the family Arecaceae. It is found only in New Caledonia.
Altrivalvina is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae. Its only species, Altrivalvina magnifica, was described from Yunnan, China. Both the genus and species were described by Wehrli in 1939.

MSC Magnifica is a Musica-class cruise ship operated by MSC Cruises. Constructed by STX Europe in Saint-Nazaire, the ship was launched in January 2009, completed in January 2010, and entered service in March 2010.

Haworthia magnifica is a species of the genus Haworthia belonging to the family Asphodelaceae.

Haworthia mirabilis is a species of the genus Haworthia belonging to the family Asphodelaceae.
Autochloris magnifica is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Rothschild in 1931. It is found in Bolivia and Peru.
Chrysochlorosia callistia is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by George Hampson in 1900. It is found in Bolivia.
Chrysochlorosia superba is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It is found in Colombia.

Amblyprora magnifica is a moth of the family Erebidae described by William Schaus and W. G. Clements in 1893. This species is found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sierra Leone and South Africa.
Limnaecia magnifica is a moth in the family Cosmopterigidae. It is found in Pakistan.
Metaprotus magnifica is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Edward Meyrick in 1887. It is found in Australia, where it has been recorded from New South Wales.
Gonojana magnifica is a moth in the family Eupterotidae. It was described by Rothschild in 1917. It is found in Nigeria.
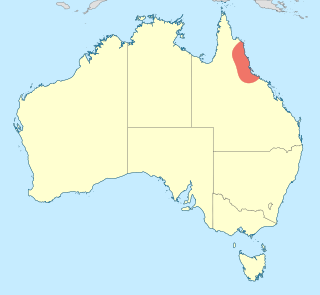
Archaeophya magnifica is a species of dragonfly in the family Gomphomacromiidae, known as the magnificent urfly. It is a large, metallic-black dragonfly with yellow markings and clear wings. It is endemic to north-east Queensland, Australia. where it inhabits rainforest streams.
Donacia magnifica is a species of aquatic leaf beetle in the family Chrysomelidae. It is found in North America.

Sabinaria magnifica is a species of palm tree and the only member of the genus Sabinaria. Native to the Darién Gap on the border between Colombia and Panama, it grows from 1 to 6 metres tall with large, deeply-divided leaf blades. It has been described as "striking", "spectacular" and "beautiful" by taxonomists.

Gudeoconcha is a genus of glass snails that is endemic to Australia’s Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea. The single species is G. sophiae(Reeve, 1854). It has four subspecies, only two of which are extant:
References
- ↑ Beccaloni, G.; Scoble, M.; Kitching, I.; Simonsen, T.; Robinson, G.; Pitkin, B.; Hine, A.; Lyal, C., eds. (2003). "Chrysochlorosia magnifica". The Global Lepidoptera Names Index . Natural History Museum . Retrieved April 30, 2018.