
Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar was a Castilian knight and ruler in medieval Spain. Fighting both with Christian and Muslim armies during his lifetime, he earned the Arabic honorific as-Sayyid, which would evolve into El Çid, and the Spanish honorific El Campeador. He was born in Vivar, a village near the city of Burgos.
A cantar de gesta is the Spanish equivalent of the Old French medieval chanson de geste or "songs of heroic deeds".

El Cantar de mio Cid, or El Poema de mio Cid, also known in English as The Poem of the Cid, is the oldest preserved Castilian epic poem. Based on a true story, it tells of the deeds of the Castilian hero and knight in medieval Spain Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar—known as El Cid—and takes place during the eleventh century, an era of conflicts in the Iberian Peninsula between the Kingdom of Castile and various Taifa principalities of Al-Andalus. It is considered a national epic of Spain.

Tizona is the name of one of the swords carried by Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar, El Cid, according to the Cantar de Mio Cid. The name of the second sword of El Cid is Colada.
Diego is a Spanish masculine given name. The Portuguese equivalent is Diogo. The etymology of Diego is disputed, with two major origin hypotheses: Tiago and Didacus.
Ramiro Sánchez of Monzón (1070–1129/1130) was a noble kinsman of the kings of Navarre. In 1104 he was tenente of Urroz, of Monzón between 1104 and 1116, probably of Tudela in 1117 and from 1122 to 1129 in Erro.

The Mocedades de Rodrigo is an anonymous Castilian cantar de gesta, composed around 1360, that relates the origins and exploits of the youth of the legendary hero El Cid.
Old Spanish, also known as Old Castilian or Medieval Spanish, refers to the varieties of Ibero-Romance spoken predominantly in Castile and environs during the Middle Ages. The earliest, longest, and most famous literary composition in Old Spanish is the Cantar de mio Cid.

Doña Jimena Díaz, also spelled Ximena, reigned as Princess of Valencia from 1099 to 1102. She was the wife and successor of El Cid, whom she married between July 1074 and 12 May 1076. The Principality of Valencia was an independent state founded by Jimena's husband.

Urraca of Zamora was a Leonese infanta, one of the five children of Ferdinand I the Great, who received the city of Zamora as her inheritance and exercised palatine authority in it. Her story was romanticized in the cantar de gesta called the Cantar de Mio Cid, and Robert Southey's Chronicle of the Cid. Urraca's mother was Sancha of León.

The Carmen Campi Doctoris is an anonymous medieval Latin epic poem, consisting of 32 accentual-syllabic Sapphic stanzas, for a total of 128 lines, with one line from an unfinished thirty-third. It is the earliest poem about the Spanish folk hero El Cid Campeador, and was found in the monastery of Santa Maria de Ripoll in the 17th century, after which it was transferred to the Bibliothèque nationale de France where it currently resides as manuscript lat. 5132.

The Battle of Bairén was fought between the forces of Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar, also known as "El Cid", in coalition with Peter I of Aragon, against the forces of the Almoravid dynasty, under the command of Muhammad ibn Tasufin. The battle was part of the long Reconquista of Spain, and resulted in a victory for the forces of the Kingdom of Aragon and the Principality of Valencia.
Diego Fernández, also known as Diego Fernández de Oviedo, was a member of one of the most noble lineages of the Kingdom of León as the son of Fernando Flaínez and Elvira Peláez, daughter of count Pelayo Rodríguez. He was the second cousin of King Ferdinand I since both shared the same great-grandfather, Count Fernando Bermúdez de Cea. Distinguished with the title of Count at an early age, Diego was the father of Jimena Díaz, wife of Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar El Cid.
Fernando Flaínez was a powerful magnate from the Kingdom of León, a member of the aristocratic lineage of the Flaínez. His parents were Flaín Muñoz and his wife Justa Fernández, daughter of count Fernando Bermúdez de Cea. He was the paternal grandfather of Jimena Díaz, wife of Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar El Cid, and the direct ancestor of the important medieval noble lineage of the Osorios. He married Elvira Peláez, daughter of Pelayo Rodríguez and Gotina Fernández de Cea, with whom he had at least seven children: Flaín, Oveco, Justa, Pedro, Pelayo, Muño and Diego. He was the tenente of Aguilar and documented with the title of count as of 1028. Jointly with his son, Flaín Fernández, he governed the city of León until 1038 when the kingdom was already under the control of King Sancho III of Pamplona.
María Rodríguez (1080–1105) was countess consort of Barcelona.

The castle of Alcocer was a fortified Muslim village located in the archaeological site of La Mora Encantada in the Aragonese municipality of Ateca, Zaragoza, Spain.

The Way of El Cid is a cultural and tourist route that crosses Spain from the northwest to the southeast, from Castilla to the Mediterranean coast. It follows the history and the legend of Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar, El Cid Campeador, a medieval knight of the 11th century and one of Spain’s greatest characters. El Cid is not only a literary character, also a historical figure.
Cristina Rodríguez was a daughter of Rodrigo Díaz also known as El Cid and Jimena Díaz.
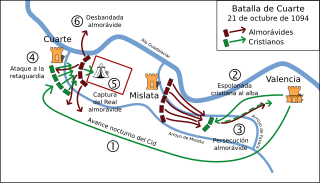
The Battle of Cuarte or Battle of Quart de Poblet was a military encounter that took place on 21 October 1094 between the forces of El Cid and the Almoravid Empire near the towns of Mislata and Quart de Poblet, located a few kilometres from Valencia.












