Lake Titicaca is a large freshwater lake in the Andes mountains on the border of Bolivia and Peru. It is often called the highest navigable lake in the world. Titicaca is the second largest lake in South America, both in terms of the volume of water and surface area. It has a surface elevation of 3,812 m (12,507 ft).

The Aymara or Aimara, people are an indigenous people in the Andes and Altiplano regions of South America. Approximately 2.3 million Aymara live in northwest Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Peru. The ancestors of the Aymara lived in the region for many centuries before becoming a subject people of the Inca Empire in the late 15th or early 16th century, and later of the Spanish in the 16th century. With the Spanish American wars of independence (1810–1825), the Aymaras became subjects of the new nations of Bolivia and Peru. After the War of the Pacific (1879–1883), Chile annexed territory with the Aymara population.

Pachacuti Inca Yupanqui, also called Pachacútec, was the ninth Sapa Inca of the Chiefdom of Cusco, which he transformed into the Inca Empire. Most archaeologists now believe that the famous Inca site of Machu Picchu was built as an estate for Pachacuti.

Juliaca is the capital of San Román Province in the Puno Region of southeastern Peru. It is the region's largest city with a population of 276,110 inhabitants (2017). On the Altiplano, Juliaca is 3,825 metres (12,549 ft) above sea level, is located on the Collao Plateau and is northwest of Lake Titicaca (45 km). It is the largest trade center in the Puno region.

Puno is a city in southeastern Peru, located on the shore of Lake Titicaca. It is the capital city of the Puno Region and the Puno Province with a population of approximately 140,839. The city was established in 1668 by viceroy Pedro Antonio Fernández de Castro as capital of the province of Paucarcolla with the name San Juan Bautista de Puno. The name was later changed to San Carlos de Puno, in honor of king Charles II of Spain. Puno has several churches dating back from the colonial period; they were built to service the Spanish population and evangelize the Quechua people.

Moquegua is a department and region in southern Peru that extends from the coast to the highlands. Its capital is the city of Moquegua, which is among the main Peruvian cities for its high rates of GDP and national education.

Puno is a department and region in southeastern Peru. It is the fifth largest department in Peru, after Cuzco, Madre de Dios, Ucayali, and Loreto. It is bordered by Bolivia on the east, the departments of Madre de Dios on the north, Cusco and Arequipa on the west, Moquegua on the southwest, and Tacna on the south. Its capital is the city of Puno, which is located on Lake Titicaca in the geographical region known as the Altiplano or high sierra.

The Altiplano, Collao or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north–south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile.

The Chachapoyas, also called the "Warriors of the Clouds", was a culture of the Andes living in the cloud forests of the southern part of the Department of Amazonas of present-day Peru. The Inca Empire conquered their civilization shortly before the Spanish conquest in the 16th century. At the time of the arrival of the conquistadors, the Chachapoyas were one of the many nations ruled by the Incas, although their incorporation had been difficult due to their constant resistance to Inca troops.

Topa Inca Yupanqui or Túpac Inca Yupanqui, also Topa Inga Yupangui, erroneously translated as "noble Inca accountant" was the tenth Sapa Inca (1471–93) of the Inca Empire, fifth of the Hanan dynasty. His father was Pachacuti, and his son was Huayna Capac. Topa Inca belonged to the Qhapaq Panaca. His quya was his older sister, Mama Ocllo.

The Uru or Uros are an indigenous people of Bolivia and Peru. They live on a still-growing group of about 120 self-fashioned floating islands in Lake Titicaca near Puno. They form three main groups: the Uru-Chipaya, Uru-Murato, and Uru-Iruito. The Uru-Iruito still inhabit the Bolivian side of Lake Titicaca and the Desaguadero River.

Sillustani is a pre-Inca cemetery on the shores of Lake Umayo near Puno in Peru. The tombs, which are built above ground in tower-like structures called chullpas, are the vestiges of the Qulla people, most likely a Puquina-speaking people, conquered by the Inca Empire in the 15th century.

The Incas were most notable for establishing the Inca Empire which was centered in modern-day South America in Peru and Chile. It was about 4,000 kilometres (2,500 mi) from the northern to southern tip. The Inca Empire lasted from 1438 to 1533. It was the largest Empire in America throughout the Pre-Columbian era. The Inca state was known as the Kingdom of Cuzco before 1438. Over the course of the Inca Empire, the Inca used conquest and peaceful assimilation to incorporate the territory of modern-day Peru, followed by a large portion of western South America, into their empire, centered on the Andean mountain range. However, shortly after the Inca Civil War, the last Sapa Inca (emperor) of the Inca Empire was captured and killed on the orders of the conquistador Francisco Pizarro, marking the beginning of Spanish rule. The remnants of the empire retreated to the remote jungles of Vilcabamba and established the small Neo-Inca State, which was conquered by the Spanish in 1572.

Inti is the ancient Inca sun god. He is revered as the national patron of the Inca state. Although most consider Inti the sun god, he is more appropriately viewed as a cluster of solar aspects, since the Inca divided his identity according to the stages of the sun. Worshiped as a patron deity of the Inca Empire, Pachacuti is often linked to the origin and expansion of the Inca Sun Cult. The most common belief was that Inti was born of Viracocha, who had many titles, chief among them being the God of Creation.

The Kingdom of Cusco, also called the Cusco confederation, was a small kingdom based in the Andean city of Cusco that began as a small city-state founded by the Incas around the start of 13th century. In time, through warfare or peaceful assimilation, it began to grow into the Inca Empire (1438–1533).

The Lupaca, Lupaka, or Lupaqa people were one of the divisions of the ancestral Aymaras. The Lupaca lived for many centuries near Lake Titicaca in Peru and their lands possibly extended into Bolivia. The Lupacas and other Aymara peoples formed powerful kingdoms after the collapse of the Tiwanaku Empire in the 11th century. In the mid 15th century they were conquered by the Inca Empire and in the 1530s came under the control of the Spanish Empire.

The Qulla are an Indigenous people of western Bolivia, northern Chile, and the western portions of Jujuy and Salta provinces in Argentina. The 2004 Complementary Indigenous Survey reported 53,019 Qulla households living in Argentina. They moved freely between the borders of Argentina and Bolivia. While mostly living in arid highlands, their easternmost lands are part of the yungas, a altitude forests at the edge of the Amazon rainforest.

Pre-Columbian Bolivia covers the historical period between 10,000 BCE, when the Upper Andes region was first populated and 1532, when Spanish conquistadors invaded Inca empire. The Andes region of Pre-Columbian South America was dominated by the Tiwanaku civilization until about 1200, when the regional kingdoms of the Aymara emerged as the most powerful of the ethnic groups living in the densely populated region surrounding Lake Titicaca. Power struggles continued until 1450, when the Incas incorporated upper Bolivia into their growing empire. Based in present-day Peru, the Incas instituted agricultural and mining practices that rivaled those put in place many years later by European conquerors. They also established a strong military force, and centralized political power. Despite their best efforts however, the Incas never completely controlled the nomadic tribes of the Bolivian lowlands, nor did they fully assimilate the Aymara kingdoms into their society. These internal divisions doomed the Inca Empire when European conquerors arrived.
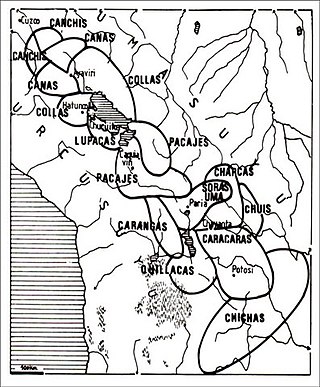
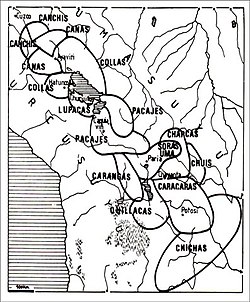
The Aymara kingdoms, Aymara lordships or lake kingdoms were a group of native polities that flourished towards the Late Intermediate Period, after the fall of the Tiwanaku Empire, whose societies were geographically located in the Qullaw. They were developed between 1150 and 1477, before the kingdoms disappeared due to the military conquest of the Inca Empire. But the current Aymara population is estimated at two million located in the countries of Bolivia, Peru, Chile and Argentina. They used the Aymara and Puquina languages.

The Colla-Inca War was a military conflict fought between the Inca Empire and the Colla Kingdom between 1445 and 1450. It is one of the first wars of conquest led by Pachacuti.