
An acetylcholine receptor is an integral membrane protein that responds to the binding of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter.
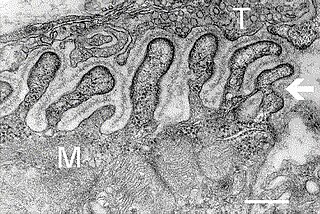
A neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.

Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways. In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system.
Achlys, in the Hesiodic Shield of Heracles, is one of the figures depicted on Heracles' shield, perhaps representing the personification of sorrow. In Homer, achlys is the mist which fogs or blinds mortal eyes. Her Roman counterpart Caligo was said to have been the mother of Chaos. In Nonnus's Dionysiaca, she seems to be a witch.
Lithophiles are micro-organisms that can live within the pore interstices of sedimentary and even fractured igneous rocks to depths of several kilometers.

The Advanced Combat Helmet (ACH) is the United States Army's current combat helmet, used since the early 2000s. It was developed by the United States Army Soldier Systems Center, the U.S. Army Special Operations Command, and the U.S. Army Research Laboratory to be the next generation of protective combat helmets for use by the American ground forces. The ACH is derived from the Modular Integrated Communications Helmet. The ACH is currently in the process of being phased out and replaced by the Enhanced Combat Helmet (ECH), an improvement upon the ACH derived from its design; however, both the ACH and the newer ECH are being replaced by the Integrated Head Protection System.

The analysis of competing hypotheses (ACH) is a methodology for evaluating multiple competing hypotheses for observed data. It was developed by Richards (Dick) J. Heuer, Jr., a 45-year veteran of the Central Intelligence Agency, in the 1970s for use by the Agency. ACH is used by analysts in various fields who make judgments that entail a high risk of error in reasoning. ACH aims to help an analyst overcome, or at least minimize, some of the cognitive limitations that make prescient intelligence analysis so difficult to achieve.

ACH Volley is a Slovenian men's volleyball club based in Ljubljana that competes in the Slovenian League. They play their home matches at Tivoli Hall. The club was founded in 1970 and was based in Bled until 2011, when the team relocated to Ljubljana.

Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters:

Collema coccophorum is a cyanolichen also known as soil pulp lichen or jelly lichen. It can be found in many areas of the world, including North America, Eastern Europe and Norway, Australia, and South America. It has also been recorded in Antarctica.

Collema is a genus of lichens in the family Collemataceae. The photobiont is the cyanobacterium genus Nostoc.

The Collemataceae are a lichenized family of fungi in the order Peltigerales. The family contains ten genera and about 325 species. The family has a widespread distribution.

Ach wie flüchtig, ach wie nichtig, BWV 26, is a church cantata by Johann Sebastian Bach. He composed the chorale cantata in Leipzig for the 24th Sunday after Trinity and first performed it on 19 November 1724.

Asplenium flaccidum is a species of fern in the family Aspleniaceae. The plant common name is drooping spleenwort or weeping spleenwort, and the species name flaccidum derives from the Latin root meaning drooping. An example occurrence of A. flaccidum is within a Nothofagus-Podocarp forest at Hamilton Ecological District on New Zealand's North Island in association with other fern species understory plants, crown fern, Blechnum discolor being an example.

"Ach wie flüchtig, ach wie nichtig" is a German Lutheran hymn with lyrics by Michael Franck, who published it with his own melody and a four-part setting in 1652. Johann Crüger's reworked version of the hymn tune was published in 1661. Several Baroque composers used the hymn, including Johann Sebastian Bach, who wrote a chorale cantata. It is part of the current Protestant hymnal Evangelisches Gesangbuch, and has also been used by 20th-century composers such as Ernst Pepping and Mauricio Kagel.
An automated clearing house (ACH) is a computer-based electronic network for processing transactions, usually domestic low value payments, between participating financial institutions. It may support both credit transfers and direct debits. The ACH system is designed to process batches of payments containing numerous transactions, and it charges fees low enough to encourage its use for low value payments.













