Related Research Articles

The Roman Forum, also known by its Latin name Forum Romanum, is a rectangular forum (plaza) surrounded by the ruins of several important ancient government buildings at the center of the city of Rome. Citizens of the ancient city referred to this space, originally a marketplace, as the Forum Magnum, or simply the Forum.
Gaius Sempronius Gracchus was a reformist Roman politician in the 2nd century BC. He is most famous for his tribunate for the years 123 and 122 BC, in which he proposed a wide set of laws, including laws to establish colonies outside of Italy, engage in further land reform, reform the judicial system, and create a subsidised grain supply for Rome.
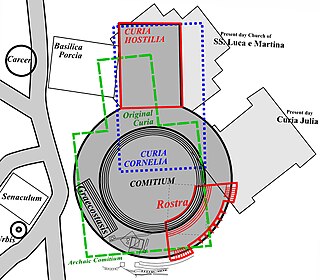
The Curia Hostilia was one of the original senate houses or "curiae" of the Roman Republic. It was believed to have begun as a temple where the warring tribes laid down their arms during the reign of Romulus. During the early monarchy, the temple was used by senators acting as a council to the king. Tullus Hostilius was believed to have replaced the original structure after fire destroyed the converted temple. It may have held historic significance as the location of an Etruscan mundus and altar. The Lapis Niger, a series of large black marble slabs, was placed over the altar where a series of monuments was found opposite the Rostra. This curia was enlarged in 80 BC by Lucius Cornelius Sulla during his renovations of the comitium. That building burned down in 52 BC when the supporters of the murdered Publius Clodius Pulcher used it as a pyre to cremate his body.

Gaius Duilius was a Roman general and statesman. As consul in 260 BC, during the First Punic War, he won Rome's first ever victory at sea by defeating the Carthaginians at the Battle of Mylae. He later served as censor in 258, and was appointed dictator to hold elections in 231, but never held another command.

The rostra was a large platform built in the city of Rome that stood during the republican and imperial periods. Speakers would stand on the rostra and face the north side of the comitium towards the senate house and deliver orations to those assembled in between. It is often referred to as a suggestus or tribunal, the first form of which dates back to the Roman Kingdom, the Vulcanal.

The Mamertine Prison, in antiquity the Tullianum, was a prison (carcer) with a dungeon (oubliette) located in the Comitium in ancient Rome. It is said to have been built in the 7th century BC and was situated on the northeastern slope of the Capitoline Hill, facing the Curia and the imperial fora of Nerva, Vespasian, and Augustus. Located between it and the Tabularium was a flight of stairs leading to the Arx of the Capitoline known as the Gemonian stairs.
Gaius Maenius was a Roman statesman and general who was elected consul in 338 BC and appointed dictator twice, in 320 BC and 314 BC.
The Plutei of Trajan are carved stone balustrades built for the Roman emperor Trajan. They are on display inside the Curia Julia in the Roman Forum today, but are not part of the original structure.

The Comitium was the original open-air public meeting space of Ancient Rome, and had major religious and prophetic significance. The name comes from the Latin word for "assembly". The Comitium location at the northwest corner of the Roman Forum was later lost in the city's growth and development, but was rediscovered and excavated by archaeologists at the turn of the twentieth century. Some of Rome's earliest monuments; including the speaking platform known as the Rostra, the Columna Maenia, the Graecostasis and the Tabula Valeria were part of or associated with the Comitium.

A rostral column is a type of victory column originating in ancient Greece and Rome, where they were erected to commemorate a naval military victory. Its defining characteristic is the integrated prows or rams of ships, representing captured or destroyed enemy ships. The name derives from the Latin rostrum meaning the bow of a naval vessel.

The Curia Julia is the third named curia, or senate house, in the ancient city of Rome. It was built in 44 BC, when Julius Caesar replaced Faustus Cornelius Sulla's reconstructed Curia Cornelia, which itself had replaced the Curia Hostilia. Caesar did so to redesign both spaces within the Comitium and the Roman Forum. The alterations within the Comitium reduced the prominence of the Senate and cleared the original space. The work, however, was interrupted by Caesar's assassination at the Curia of Pompey of the Theatre of Pompey, where the Senate had been meeting temporarily while the work was completed. The project was eventually finished by Caesar's successor, Augustus Caesar, in 29 BC.

The Curia Cornelia was a place where the Roman Senate assembled beginning c. 52 BC. It was the largest of all the Curiae built in Rome. Its construction took over a great deal of the traditional comitium space and brought the senate building into a commanding location within the Roman Forum as a whole. It was the Senate House of the time of Julius Caesar and is significant because its location was moved by him to diminish the Senate's dominance within the City and Republic.
The Graecostasis was a platform in the Comitium near the Roman Forum, located to the west of the Rostra. The name refers to the Greek ambassadors for whom the platform was originally built after the Roman Republic conquered Greece. Placed at the southwest end of the Comitium, the platform was the designated spot for all representatives of foreign nations and dignitaries from the Republic and Empire's domain.

Rostratus (masculine), rostrata (feminine) or rostratum (neuter) is a Latin adjective meaning "beaked, curved, hooked, with a crooked point, or with a curved front".
The lautumiae were tufa quarries that became a topographical marker in ancient Rome. They were located on the northeast slope of the Capitoline Hill, forming one side of the Graecostasis, where foreign embassies gathered prior to appearing before the Roman Senate.

The Curia of Pompey, sometimes referred to as the Curia Pompeia, was one of several named meeting halls from Republican Rome of historic significance. A curia was a designated structure for meetings of the senate. The Curia of Pompey was located at the entrance to the Theater of Pompey. While the main senate house was being moved from the Curia Cornelia to a new Curia Julia, the senate would meet in this smaller building, which is best known as the place that members of the Roman Senate murdered Gaius Julius Caesar.
The gens Maenia, occasionally written Mainia, was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are first mentioned soon after the establishment of the Republic, and occur in history down to the second century BC. Several of them held the position of tribune of the plebs, from which they strenuously advocated on behalf of their order. The most illustrious of the family was Gaius Maenius, consul in 338 BC, and dictator in both 320 and 314. In some manuscripts, the nomen Maenius appears to have been erroneously substituted for Menenius or Manlius; there are also instances of confusion with Manilius, Maelius, and Maevius.

The Five-Columns monument is a dedicatory addition to the Rostra in the Roman Forum dating to the early fourth century CE. This monument was part of the Tetrarchy’s expansion of the Forum and is connected to the tenth anniversary of the Caesares within the four-ruler system. It is also referred to as the Fünfsäulendenkmal as well as the four-column monument, depending on Jupiter’s inclusion.
The Battle of Pedum was fought in 338 BC, near Pedum between the Roman Republic and multiple cities in Latium: Tibur, Praeneste, Antium, Aricia, Lanuvium, and Velitrae. The Roman army was led by the consuls Gaius Maenius and Lucius Furius Camillus. The battle resulted in a Roman victory.
References
- ↑ Briscoe, John (February 25, 2008). A commentary on Livy, books 38-40. Oxford University Press, USA. pp. 366. ISBN 978-0-19-929051-2.
- ↑ L. Richardson, jr (1 October 1992). A New Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome . JHU Press. pp. 94–. ISBN 978-0-8018-4300-6 . Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- ↑ O'Connor, Charles James (September 1909). "The Graecostasis and its vicinity". Bulletin: Philology and Literature Series. 3: 188. Retrieved 2009-08-15.
- ↑ Cyril M. Harris (28 February 2013). Illustrated Dictionary of Historic Architecture. Courier Corporation. pp. 128–. ISBN 978-0-486-13211-2.