
Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, or Tarquin the Elder, was the legendary fifth king of Rome and first of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned for thirty-eight years. Tarquinius expanded Roman power through military conquest and grand architectural constructions. His wife was the prophetess Tanaquil.

Lucius Tarquinius Superbus was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic. He is commonly known as Tarquin the Proud, from his cognomen Superbus.
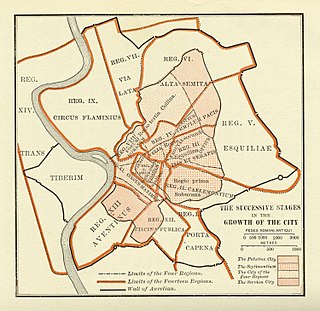
The Roman Kingdom was the earliest period of Roman history when the city and its territory were ruled by kings. According to oral accounts, the Roman Kingdom began with the city's founding c. 753 BC, with settlements around the Palatine Hill along the river Tiber in central Italy, and ended with the overthrow of the kings and the establishment of the Republic c. 509 BC.

The Circus Maximus is an ancient Roman chariot-racing stadium and mass entertainment venue in Rome, Italy. In the valley between the Aventine and Palatine hills, it was the first and largest stadium in ancient Rome and its later Empire. It measured 621 m (2,037 ft) in length and 118 m (387 ft) in width and could accommodate over 150,000 spectators. In its fully developed form, it became the model for circuses throughout the Roman Empire. The site is now a public park.

Publius Horatius Cocles was an officer in the army of the early Roman Republic who famously defended the Pons Sublicius from the invading army of Etruscan King Lars Porsena of Clusium in the late 6th century BC, during the war between Rome and Clusium. By defending the narrow end of the bridge, he and his companions were able to hold off the attacking army long enough to allow other Romans to destroy the bridge behind him, blocking the Etruscans' advance and saving the city.

In Roman mythology, Vertumnus is the god of seasons, change and plant growth, as well as gardens and fruit trees. He could change his form at will; using this power, according to Ovid's Metamorphoses (xiv), he tricked Pomona into talking to him by disguising himself as an old woman and gaining entry to her orchard, then using a narrative warning of the dangers of rejecting a suitor to seduce her. The tale of Vertumnus and Pomona has been called "the first exclusively Latin tale."

Summanus was the god of nocturnal thunder in ancient Roman religion, as counterposed to Jupiter, the god of diurnal (daylight) thunder. His precise nature was unclear even to Ovid.
In Etruscan mythology, Voltumna or Veltha was the chthonic deity, who became the supreme god of the Etruscan pantheon, the deus Etruriae princeps, according to Varro. Voltumna's cult was centered in Volsini, a city of the Etruscan civilization of central Italy. Voltumna is shown with contrasting characteristics, such as a maleficent monster, a chthonic vegetation god of uncertain sex, or a mighty war god.
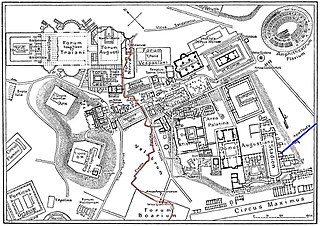
The Cloaca Maxima was one of the world's earliest sewage systems. Its name derives from Cloacina, a Roman goddess. Built during either the Roman Kingdom or early Roman Republic, it was constructed in Ancient Rome in order to drain local marshes and remove waste from the city. It carried effluent to the River Tiber, which ran beside the city. The sewer started at the Forum Augustum and ended at the Ponte Rotto and Ponte Palatino. It began as an open air canal, but it developed into a much larger sewer over the course of time. Agrippa renovated and reconstructed much of the sewer. This would not be the only development in the sewers. By the first century CE all eleven Roman aqueducts were connected to the sewer. After the Roman Empire fell the sewer still was used. By the 1800s it became a tourist attraction. Some parts of the sewer are still used today. Whilst still being used it was highly valued as a sacred symbol of Roman culture, and Roman engineering.
Titus Larcius was a Roman general and statesman during the early Republic, who served twice as consul and became the first Roman dictator.

The Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus, also known as the Temple of Jupiter Capitolinus was the most important temple in Ancient Rome, located on the Capitoline Hill. It was surrounded by the Area Capitolina, a precinct where numerous shrines, altars, statues and victory trophies were displayed.
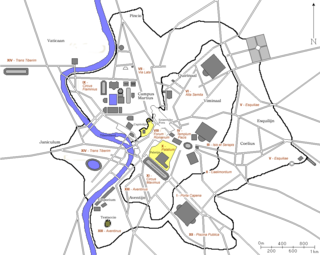
In 7 BC, Augustus divided the city of Rome into 14 administrative regions. These replaced the four regiones—or "quarters"—traditionally attributed to Servius Tullius, sixth king of Rome. They were further divided into official neighborhoods.

Vulcan is the god of fire including the fire of volcanoes, deserts, metalworking and the forge in ancient Roman religion and myth. He is often depicted with a blacksmith's hammer. The Vulcanalia was the annual festival held August 23 in his honor. His Greek counterpart is Hephaestus, the god of fire and smithery. In Etruscan religion, he is identified with Sethlans.
The Roman–Etruscan Wars were a series of wars fought between ancient Rome and the Etruscans. Information about many of the wars is limited, particularly those in the early parts of Rome's history, and in large part is known from ancient texts alone. The conquest of Etruria was completed in 265–264 BC.
Spurius Larcius was one of the leading men of the early Roman Republic, of which he was twice consul. However, his greatest fame was won as one of the defenders of the Sublician bridge against the army of Lars Porsena, the King of Clusium.

Titus Herminius, surnamed Aquilinus, was one of the heroes of the Roman Republic. He participated in two of the most famous conflicts that attended the birth of the Republic, and was elected consul in 506 BC. However, his greatest fame was won as one of the defenders of the Sublician bridge against the army of Lars Porsena, the King of Clusium.

In ancient Rome, the pompa circensis was the procession that preceded the official games (ludi) held in the circus as part of religious festivals and other occasions.

The Regio XI Circus Maximus is the eleventh regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio XI took its name from the Circus Maximus, located in the valley between the Palatine and the Aventine hills.















