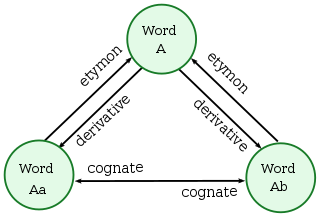
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language.

Etruscan was the language of the Etruscan civilization in the ancient region of Etruria, in Etruria Padana and Etruria Campana in what is now Italy. Etruscan influenced Latin but was eventually completely superseded by it. The Etruscans left around 13,000 inscriptions that have been found so far, only a small minority of which are of significant length; some bilingual inscriptions with texts also in Latin, Greek, or Phoenician; and a few dozen purported loanwords. Attested from 700 BC to AD 50, the relation of Etruscan to other languages has been a source of long-running speculation and study, with it mostly being referred to as one of the Tyrsenian languages, at times as an isolate, and a number of other less well-known hypotheses.

The Italic languages form a branch of the Indo-European language family, whose earliest known members were spoken on the Italian Peninsula in the first millennium BC. The most important of the ancient Italic languages was Latin, the official language of ancient Rome, which conquered the other Italic peoples before the common era. The other Italic languages became extinct in the first centuries AD as their speakers were assimilated into the Roman Empire and shifted to some form of Latin. Between the third and eighth centuries AD, Vulgar Latin diversified into the Romance languages, which are the only Italic languages natively spoken today, while Literary Latin also survived.

The Etruscan civilization was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in ancient Italy, with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania.
The Old Italic scripts are a family of ancient writing systems used in the Italian Peninsula between about 700 and 100 BC, for various languages spoken in that time and place. The most notable member is the Etruscan alphabet, which was the immediate ancestor of the Latin alphabet used by more than 100 languages today, including English. The runic alphabets used in Northern Europe are believed to have been separately derived from one of these alphabets by the 2nd century AD.

Cloacina was a goddess who presided over the Cloaca Maxima, the main interceptor discharge outfall of the system of sewers in Rome.
Lydian is an extinct Indo-European Anatolian language spoken in the region of Lydia, in western Anatolia. The language is attested in graffiti and in coin legends from the late 8th century or the early 7th century to the 3rd century BCE, but well-preserved inscriptions of significant length are so far limited to the 5th century and the 4th century BCE, during the period of Persian domination. Thus, Lydian texts are effectively contemporaneous with those in Lycian.
This is a list of etymological lists.
Etymology is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of a word's semantic meaning across time, including its constituent morphemes and phonemes. It is a subfield of historical linguistics, philology, and semiotics, and draws upon comparative semantics, morphology, pragmatics, and phonetics in order to construct a comprehensive and chronological catalogue of all meanings that a morpheme, phoneme, word, or sign has carried across time.

*Dyḗus, also *Dyḗus ph₂tḗr, is the reconstructed name of the daylight-sky god in Proto-Indo-European mythology. *Dyēus was conceived as a divine personification of the bright sky of the day and the seat of the gods, the *deywṓs. Associated with the vast diurnal sky and with the fertile rains, *Dyēus was often paired with *Dʰéǵʰōm, the Earth Mother, in a relationship of union and contrast.

In modern English, the nouns vates and ovate (, ), are used as technical terms for ancient Celtic bards, prophets and philosophers. The terms correspond to a Proto-Celtic word which can be reconstructed as *wātis. They are sometimes also used as English equivalents to later Celtic terms such as Irish fáith "prophet, seer".

Robert Stephen Paul Beekes was a Dutch linguist who was emeritus professor of Comparative Indo-European Linguistics at Leiden University and an author of many monographs on the Proto-Indo-European language.
Proto-Albanian is the ancestral reconstructed language of Albanian, before the Gheg–Tosk dialectal diversification. Albanoid and other Paleo-Balkan languages had their formative core in the Balkans after the Indo-European migrations in the region. Whether descendants or sister languages of what was called Illyrian by classical sources, Albanian and Messapic, on the basis of shared features and innovations, are grouped together in a common branch in the current phylogenetic classification of the Indo-European language family. The precursor of Albanian can be considered a completely formed independent IE language since at least the first millennium BCE, with the beginning of the early Proto-Albanian phase.
Present-day Irish has numerous loanwords from English. The native term for these is béarlachas, from Béarla, the Irish word for the English language. It is a result of language contact and bilingualism within a society where there is a dominant, superstrate language and a minority substrate language with few or no monolingual speakers and a perceived "lesser" status.
Aulus is a Latin praenomen, or personal name, which was common throughout Roman history from the earliest times to the end of the Western Empire in the fifth century. The feminine form is Aula. An alternative pronunciation leads to the variant spellings Olus or Ollus and Olla. Aulus was widely used by both patrician and plebeian gentes. The name gave rise to the patronymic gens Aulia, and perhaps also to gens Avilia and the cognomen Avitus. The name was usually abbreviated A., but occasionally Av. or Avl.
Spurius is a Latin praenomen, or personal name, which was used primarily during the period of the Roman Republic, and which fell into disuse in imperial times. It was used by both patrician and plebeian families, and gave rise to the patronymic gens Spurilia. The feminine form is Spuria. The name was originally abbreviated S., as it was the most common praenomen beginning with that letter; but, as it grew less common, it was sometimes abbreviated Sp.
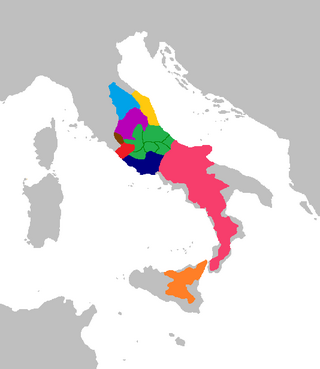
The Proto-Italic language is the ancestor of the Italic languages, most notably Latin and its descendants, the Romance languages. It is not directly attested in writing, but has been reconstructed to some degree through the comparative method. Proto-Italic descended from the earlier Proto-Indo-European language.









