Geography
| Country | Area (km²) | Land area (km²) | Water area (km²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45,227 | 43,214.40 | 2,012.60 | |
| 64,589 | 63,574.96 | 1,014.04 | |
| 65,300 | 64,418.45 | 881.55 |
This article is being considered for deletion in accordance with Wikipedia's deletion policy. Please share your thoughts on the matter at this article's deletion discussion page. |
This article is a comparison of the Baltic states .
| Country | Area (km²) | Land area (km²) | Water area (km²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 45,227 | 43,214.40 | 2,012.60 | |
| 64,589 | 63,574.96 | 1,014.04 | |
| 65,300 | 64,418.45 | 881.55 |
| Country | Political systems | Power source | Power structure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parliamentary system | Constitutional republic | Unitary state | |
| Parliamentary system | Constitutional republic | Unitary state | |
| Semi-presidential system | Constitutional republic | Unitary state |
| Country | Council of Europe | Baltic Assembly | ECHR | European Union | NATO | OECD | United Nations | WTO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 May 1993 | Yes | Yes | 2004 | 29 March 2004 | 9 December 2010 | 17 September 1991 | 13 November 1999 | |
| 10 February 1995 | Yes | Yes | 2004 | 29 March 2004 | 16 June 2016 | 17 September 1991 | 10 February 1999 | |
| 14 May 1993 | Yes | Yes | 2004 | 29 March 2004 | 5 July 2018 [1] | 17 September 1991 | 31 May 2001 |
The three Baltic States are also OSCE participating States www.osce.org. Lithuania was the OSCE Chair in Office in 2011. There were OSCE Missions in Estonia and Latvia between 1993 and 2001.
| Country | GDP total (PPP) | GDP per capita (PPP) | GDP total (nominal) | GDP per capita (nominal) | Gini | HDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $50 billion | $37,605 | $33 billion | $24,802 | 30.6 | 0.882 | |
| $64 billion | $32,986 | $37 billion | $19,105 | 35.6 | 0.866 | |
| $107 billion | $38,751 | $56 billion | $20,355 | 36.9 | 0.869 |
| Country | Population | Density (per km²) | Immigration (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,315,819 | 29.0 | ||
| 1,990,300 | 34.3 | ||
| 2,691,643 | 45.1 |
| Country | Internet TLD | ISO 3166 code | Calling code |
|---|---|---|---|
| .ee | EE | +372 | |
| .lv | LV | +371 | |
| .lt | LT | +370 |

Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the Baltic states; and is bordered by Estonia to the north, Lithuania to the south, Russia to the east, Belarus to the southeast, and shares a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Latvia covers an area of 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq mi), with a population of 1.9 million. The country has a temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Riga. Latvians belong to the ethno-linguistic group of the Balts and speak Latvian, one of the only two surviving Baltic languages. Russians are the most prominent minority in the country, at almost a quarter of the population.
Baltic may refer to:

The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics.
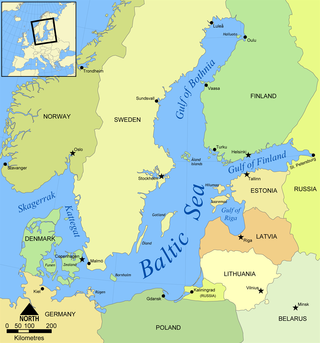
The terms Baltic Sea Region, Baltic Rim countries, and the Baltic Sea countries/states refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. The term "Baltic states" refers specifically to one such grouping.

The three independent Baltic countries – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania – were invaded and occupied in June 1940 by the Soviet Union, under the leadership of Stalin and auspices of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact that had been signed between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union in August 1939, immediately before the outbreak of World War II. The three countries were then annexed into the Soviet Union in August 1940. The United States and most other Western countries never recognised this incorporation, considering it illegal. On 22 June 1941, Nazi Germany attacked the Soviet Union and within weeks occupied the Baltic territories. In July 1941, the Third Reich incorporated the Baltic territory into its Reichskommissariat Ostland. As a result of the Red Army's Baltic Offensive of 1944, the Soviet Union recaptured most of the Baltic states and trapped the remaining German forces in the Courland Pocket until their formal surrender in May 1945.

Baltic Tiger is a term used to refer to any of the three Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania during their periods of economic boom, which started after the year 2000 and continued until 2006–2007. The term is modeled on Four Asian Tigers, Tatra Tiger, and Celtic Tiger, which were used to describe the economic boom periods in East Asia, Slovakia, and Ireland, respectively.
Territorial changes of the Baltic states refers to the redrawing of borders of Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia after 1940. The three republics, formerly autonomous regions within the former Russian Empire and before that of former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and as provinces of the Swedish Empire, gained independence in the aftermath of World War I and the Russian Revolution of 1917. After a two-front independence war fought against both Bolshevist Russian and Baltic German nationalist forces, the countries concluded peace and border treaties with Soviet Russia in 1920. However, with World War II and the occupation and annexation of these republics into the Soviet Union twenty years after their independence, certain territorial changes were made in favour of the Russian SFSR. This has been the source of political tensions after they regained their independence with the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Some of the disputes remain unresolved.

Russians in the Baltic states is a broadly defined subgroup of the Russian diaspora who self-identify as ethnic Russians, or are citizens of Russia, and live in one of the three independent countries – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. As of 2021, there were nearly 900,000 ethnic Russians in the three countries, having declined from ca 1.7 million in 1989, the year of the last census during the 1944–1991 Soviet occupation of the three Baltic countries.

The Baltic Assembly (BA) is a regional organisation that promotes intergovernmental cooperation between Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. It attempts to find a common position in relation to many international issues, including economic, political and cultural issues. The decisions of the assembly are advisory.
Delfi is a news website in Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania providing daily news, ranging from gardening to politics. It ranks as one of the most popular websites among Baltic users.

The three Baltic countries, or the Baltic states – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania – are held to have continued as legal entities under international law while under the Soviet occupation from 1940 to 1991, as well as during the German occupation in 1941–1944/1945. The prevailing opinion accepts the Baltic thesis of illegal occupation and the actions of the USSR are regarded as contrary to international law in general and to the bilateral treaties between the USSR and the three Baltic countries in particular.

Estonia–Lithuania relations refer to the bilateral relations between Estonia and Lithuania. Estonia has an embassy in Vilnius. Lithuania has an embassy in Tallinn. Both countries are situated in the Baltic region and are the full members of NATO and the European Union.

Relevant events began regarding the Baltic states and the Soviet Union when, following Bolshevist Russia's conflict with the Baltic states—Lithuania, Latvia and Estonia—several peace treaties were signed with Russia and its successor, the Soviet Union. In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the Soviet Union and all three Baltic States further signed non-aggression treaties. The Soviet Union also confirmed that it would adhere to the Kellogg–Briand Pact with regard to its neighbors, including Estonia and Latvia, and entered into a convention defining "aggression" that included all three Baltic countries.
The Sovietization of the Baltic states refers to the sovietization of all spheres of life in Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania when they were under control of the Soviet Union. The first period deals with the occupation from June 1940 to July 1941 when the German occupation began. The second period covers 1944 when the Soviet forces pushed the Germans out, until 1991 when independence was declared.

The background of the occupation of the Baltic states covers the period before the first Soviet occupation on 14 June 1940, stretching from independence in 1918 to the Soviet ultimatums in 1939–1940. Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia gained independence in the aftermath of the Russian revolutions of 1917 and the German occupation which in the Baltic countries lasted until the end of World War I in November 1918. All three countries signed non-aggression treaties with the Soviet Union in the 1920s and 1930s. Despite the treaties, in the aftermath of the 1939 German–Soviet pact, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania were occupied, and thereafter forcibly incorporated into the Soviet Union, in 1940.

The three Baltic states – Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania – were re-occupied in 1944–1945 by the Soviet Union (USSR) following the German occupation. The Baltic states regained independence in 1990–1991.

The Soviet occupation of the Baltic states covers the period from the Soviet–Baltic mutual assistance pacts in 1939, to their invasion and annexation in 1940, to the mass deportations of 1941.

The Soviet Union (USSR) occupied most of the territory of the Baltic states in its 1944 Baltic Offensive during World War II. The Red Army regained control over the three Baltic capitals and encircled retreating Wehrmacht and Latvian forces in the Courland Pocket where they held out until the final German surrender at the end of the war.

The Baltic Legations were the missions of the exiled Baltic diplomatic services from 1940 to 1991. After the Soviet occupation of the Baltic states in 1940, the Baltic states instructed their diplomats to maintain their countries' legations in several Western capitals. Members of the Estonian diplomatic service, the Latvian diplomatic service and the Lithuanian diplomatic service continued to be recognised as the diplomatic representatives of the independent pre-World War II states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, whose annexation by the Soviet Union was not recognised by the United States, the United Kingdom, or France. The legations provided consular services to exiled citizens of the Baltic states from 1940 to 1991.

The Baltic states' housing bubble was an economic bubble involving major cities in Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. The three Baltic countries had enjoyed a relatively strong economic growth between 2000 and 2006, and the real estate sectors had performed well since 2000. In fact, in between 2005Q1 and 2007Q1, the official house price index for Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania recorded a sharp jump of 104.6%, 134.3% and 106.7%. By comparison, the official house price index for Euro Area increased by 11.8% for a similar time period.