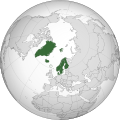
Scandinavia is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. Scandinavia most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. In English usage, it can sometimes also refer more narrowly to the Scandinavian Peninsula, or more broadly to all of the Nordic countries, also including Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands.

The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology.
The extreme points of Norway include the coordinates that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location in Norway; and the highest and the lowest altitudes in the country. The northernmost point is Rossøya on Svalbard, the southernmost is Pysen in Mandal, the easternmost is Kræmerpynten on Svalbard, and the westernmost is Hoybergodden on Jan Mayen. The highest peak is Galdhøpiggen, standing at 2,469 m (8,100 ft) above mean sea level, while the lowest elevation is sea level at the coast.

The Norwegian Polar Institute is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica.

The Nordic Passport Union allows citizens of the Nordic countries – Iceland, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland – to travel and reside in another Nordic country without any travel documentation or a residence permit. Since 25 March 2001, all five states have also been within the Schengen Area.

UTC+01:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +01:00. In ISO 8601, the associated time would be written as 2019-02-07T23:28:34+01:00. This time is used in:

The Nordic Council Music Prize is awarded annually by NOMUS, the Nordic Music Committee. Every two years it is awarded for a work by a living composer. In the intervening years it is awarded to a performing musician or ensemble.

The following outline provides an overview of, and topical guide to, the Kingdom of Norway.

NATO is an international military alliance that consists of 31 member states from Europe and North America. It was established at the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty on 4 April 1949. Article 5 of the treaty states that if an armed attack occurs against one of the member states, it shall be considered an attack against all members, and other members shall assist the attacked member, with armed forces if necessary. Article 6 of the treaty limits the scope of Article 5 to the islands north of the Tropic of Cancer, the North American and European mainlands, the entirety of Turkey, and French Algeria. As such, an attack on Hawaii, Puerto Rico, French Guiana, Ceuta, or Melilla, among other places, would not trigger an Article 5 response.
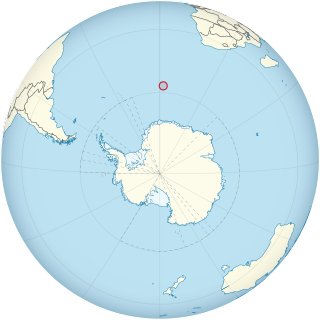
Bouvet Island is an island and dependency of Norway, and declared an uninhabited protected nature reserve. It is a subantarctic volcanic island, situated in the South Atlantic Ocean at the southern end of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, making it the world's most remote island. It is not part of the southern region covered by the Antarctic Treaty System.
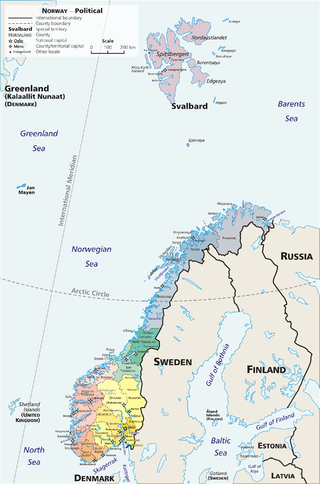
Norway is commonly divided into five major geographical regions. These regions are purely geographical, and have no administrative purpose. However, in 2017 the government decided to abolish the current counties of Norway and to replace them with fewer, larger administrative regions. The first of these new areas came into existence on 1 January 2018, when Nord-Trøndelag and Sør-Trøndelag merged to form Trøndelag.
Norway's elongated shape, its numerous internal geographical barriers, and the often widely dispersed and separated settlements are all factors that have strongly influenced the structure of the country's administrative subdivisions. This structure has varied over time and is subject to continuous review. In 2017 the government decided to abolish some of the counties and to merge them with other counties to form larger ones, reducing the number of counties from 19 to 11, which was implemented on 1 January 2020.


Norway has three dependent territories, all uninhabited and located in the Southern Hemisphere. Bouvet Island (Bouvetøya) is a sub-Antarctic island in the South Atlantic Ocean. Queen Maud Land is a sector of Antarctica which spans between the 20th meridian west and the 45th meridian east. Peter I Island is a volcanic island located 450 kilometres (280 mi) off the coast of Ellsworth Land of continental Antarctica. Svalbard is not formally considered to be a dependency. While the Svalbard Treaty regulates some aspects of that Arctic territory, one article acknowledges that these islands are part of Norway. Similarly, Jan Mayen is recognized as an integral part of the nation. Both are unincorporated areas.
The European Convention on the International Validity of Criminal Judgments is a 1970 treaty of the Council of Europe whereby the states that agree to the treaty recognise the validity of criminal judgments and sentences handed down in other states that have ratified the treaty. The treaty also allows penal sentences to be served in the country of a person's residence if both the sentencing country and the country of residence are parties to the treaty.
Norway Proper as a geographic term in 20th and 21st century usage generally refers to those parts of the Kingdom of Norway that are located on the Scandinavian Peninsula. Before the 20th century the term was often used in English as synonymous with South Norway, the oldest and most densely populated part of the kingdom that historically formed its core territory, and excluded the more recently colonised and sparsely populated Northern Norway. Norway Proper in this original sense included the regions (stiftamt) of Akershus or Christiania, Christianssand, Bergen and Trondheim.