
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east, Belarus to the southeast, and shares a maritime border with Sweden to the west. Latvia covers an area of 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq mi), with a population of 1.9 million. The country has a temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Riga. Latvians belong to the ethnolinguistic group of the Balts and speak Latvian, one of the only two surviving Baltic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family. Russians are the most prominent minority in the country, at almost a quarter of the population.

The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology.

The Baltic states or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term encompassing Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics.
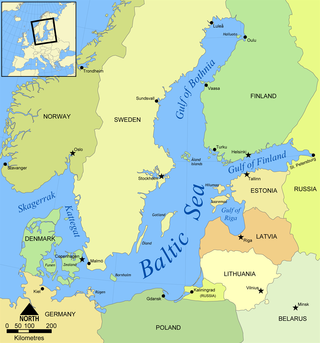
The Baltic Sea Region, alternatively the Baltic Rim countries, and the Baltic Sea countries/states, refers to the general area of surrounding the Baltic Sea, mainly in Northern Europe. Unlike the "Baltic states", the Baltic region includes all countries that border the sea.

European route E 67 is an E-road running from Prague in the Czech Republic to Estonia and by ferry to Finland. It goes via Prague, Wrocław, Warsaw, Kaunas, Panevėžys, Riga, Tallinn, Helsinki.

The Lithuania national football team represents Lithuania in men's international football, and is controlled by the Lithuanian Football Federation, the governing body for football in Lithuania. They played their first match in 1923. In 1940, Lithuania was occupied by the Soviet Union; the country regained its independence in 1990 and played their first match thereafter against Georgia on 27 May of that year.

Lahemaa National Park is a park in northern Estonia, 70 kilometers east from the capital Tallinn. The Gulf of Finland is to the north of the park and the Tallinn-Narva highway (E20) to the south. Its area covers 747 km2. It was the first area to be designated a national park of the former Soviet Union. It is the largest park in Estonia and one of Europe's biggest national parks. Its charter calls for the preservation, research and promotion of North-Estonian landscapes, ecosystems, biodiversity and national heritage.

The Dzūkija National Park is a national park in Dzūkija, Lithuania, located 100 kilometers southwest from the capital, Vilnius, and 100 kilometers south from Kaunas. It was established on April 23, 1991 by the Supreme Court of the Republic of Lithuania. The park was established to protect and manage the territories of the Dainava land. The park mainly consists of marsh areas, lakes, rivers, swamps, inland dunes, and mountain-ridges and is the country's most extensive and protected forest. The national park encompasses 584.53 square kilometers on the banks of the Nemunas River.

Kuršių Nerija National Park is one of the five national parks in Lithuania. It was established in 1991 to protect the unique ecosystems of the Curonian Spit and Curonian Lagoon.

Rāzna National Park is a national park in the Latgale region of Latvia. It was established in 2007 and covers an area of 532 km2 (205 sq mi). The initiative to create the Rāzna National Park out of an already existing nature park came from the Daugavpils University.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Estonia:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Latvia:

Karula National Park is a national park in southern Estonia. It was established in 1979 as a protected area and in 1993 became a national park. It is the smallest national park in Estonia.

Vilsandi National Park is a marine protected area in Saaremaa Parish, Saare County, Estonia. It includes part of the island of Vilsandi, a number of smaller islands, adjacent parts of western Saaremaa including Harilaid peninsula.

Estonia–Lithuania relations refer to the bilateral relations between Estonia and Lithuania. Estonia has an embassy in Vilnius. Lithuania has an embassy in Tallinn. Both countries are situated in the Baltic region and are the full members of NATO and the European Union.

Kikkajärv or Ilgājs as it is known in Latvia, is a lake on the border of Estonia and Latvia. Its area is 20.2 ha. Lake is in the Veclaicene Protected Landscape Area. Nearest settlement to the lake in Latvia is Korneti in Alūksne Municipality.
Latvia is a net energy importer. Primary energy use in Latvia was 49 TWh, or 22 TWh per million persons in 2009. In 2018, electricity consumption per capita was 3731 kWh.

Alatskivi Castle is a neo-Gothic castle in Alatskivi, Estonia. Dating to the 17th century, it is situated in Peipsiääre Parish, Tartu County. It was rebuilt in the late 19th century by Baron Arved von Nolcken, modeled on the royal residence of Balmoral in Scotland. A renovation occurred between 2005 and 2011. Five rooms on the first floor house the Eduard Tubin museum, which documents his accomplishments as a music composer and conductor.

The Residence of the President of Estonia, known officially as the Kadriorg Administrative Building, and since 1992 sometimes colloquially as the "president's palace", is a building located in the Kadriorg Park, Tallinn, capital city of Estonia. The Baroque Revival building serves as the official residence of the president of Estonia.
































