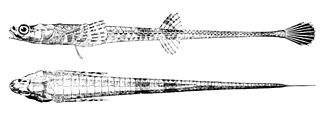
Agonidae is a family of small, bottom-dwelling, cold-water marine fish. Common names for members of this family include poachers, Irish lords, sea ravens, alligatorfishes, starsnouts, hooknoses, and rockheads. They are notable for having elongated bodies covered by scales modified into bony plates, and for using their large pectoral fins to move in short bursts. The family includes about 59 species in some 25 genera, some of which are quite widespread.

Sebastinae is a subfamily of marine fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae in the order Scorpaeniformes. Their common names include rockfishes, rock perches, ocean perches, sea perches, thornyheads, scorpionfishes, sea ruffes and rockcods. Despite the latter name, they are not closely related to the cods in the genus Gadus, nor the rock cod, Lotella rhacina.

The Congridae are the family of conger and garden eels. Congers are valuable and often large food fishes, while garden eels live in colonies, all protruding from the sea floor after the manner of plants in a garden. The family includes over 220 species in 32 genera.

Grunters or tigerperches are ray-finned fishes in the family Terapontidae. This family is part of the superfamily Percoidea of the order Perciformes.

The sea chubs, also known as rudderfish and pilot fish and in Hawaiian as enenue or nenue, are a family, Kyphosidae, of fishes in the order Perciformes native to the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans usually close to shore in marine waters.

Stichaeidae, the pricklebacks or shannies, are a family of marine ray-finned fishes in the suborder Zoarcoidei of the order Scorpaeniformes. Most species are found in the North Pacific Ocean with a few in the North Atlantic Ocean.

Little velvetfishes or simply velvetfishes are a family, the Aploactinidae, of marine ray-finned fishes classified within the order Scorpaeniformes. They are small fish that have skin with a velvet texture. They live on the sea bottom close to the shore, at depths of up to 100 metres (330 ft). They are found in the Indo-Pacific region.
Gnathophis is a genus of marine congrid eels.

The Platycephalidae are a family of marine ray-finned fish, most commonly referred to as flatheads. They are relatives of the lionfish, and belong to the order Perciformes.
Bathycongrus is a genus of eels in the family Congridae.

Bathymyrinae is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Congridae, which includes the conger and garden eels. The eels of this subfamily are most diverse in the Indo-Pacific region but are also found in both the Eastern and Western Atlantic Oceans.

Myrophinae, the worm eels, is a subfamily of ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Ophichthidae, which also includes the snake eels in the subfamily Ophichthinae.

Congroidei is a suborder of ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Anguilliformes, the eels. These eels are mostly marine, although a few species of snake eel will enter freshwater, and they are found in tropical and tempareate waters throughout the world.

Kyphosus is a genus of sea chubs native to the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans.

The Girardini is a tribe of killifishes from the "livebearer" family Poeciliidae, consisting of three genera and 10 species. The tribe was originally delineated by Carl Leavitt Hubbs in 1924.

Sebastini is a tribe of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae of the family Scorpaenidae in the order Scorpaeniformes.

Scorpaeninae is a subfamily of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae in the order Scorpaeniformes, it includes the scorpionfishes, the lionfishes and turkeyfishes. They bear venomous spines in the anal, dorsal and pelvic fins which can cause severe pain in envenomated humans. The subfamily is distributed in the tropical and temperate seas around the world.
Xiphisterinae is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes, classified within the family Stichaeidae, the pricklebacks or shannies. These fishes are found in the North Pacific Ocean.

Brachyopsinae is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Agonidae, part of the sculpin superfamily Cottoidea. These fishes are found in the North Pacific Ocean.

Dorosomatidae is a family of clupeiform fishes. It is now recognized by FishBase as a family in its own right; it had been considered to be a subfamily of Clupeidae. It contains 31 extant genera.

















