
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the sixteenth-century Protestant Reformation, a schism in the Western Church. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed, Presbyterian, and Congregational traditions, as well as parts of the Anglican and Baptist traditions.

Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli was a Swiss Christian theologian, musician, and leader of the Reformation in Switzerland. Born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenary system, he attended the University of Vienna and the University of Basel, a scholarly center of Renaissance humanism. He continued his studies while he served as a pastor in Glarus and later in Einsiedeln, where he was influenced by the writings of Erasmus.

John Calvin was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of Christian theology later called Calvinism, including its doctrines of predestination and of God's absolute sovereignty in the salvation of the human soul from death and eternal damnation. Calvinist doctrines were influenced by and elaborated upon the Augustinian and other Christian traditions. Various Congregational, Reformed and Presbyterian churches, which look to Calvin as the chief expositor of their beliefs, have spread throughout the world.

Theodore Beza was a French Calvinist Protestant theologian, reformer and scholar who played an important role in the Protestant Reformation. He was a disciple of John Calvin and lived most of his life in Geneva. Beza succeeded Calvin as the spiritual leader of the Republic of Geneva.

Heinrich Bullinger was a Swiss Reformer and theologian, the successor of Huldrych Zwingli as head of the Church of Zürich and a pastor at the Grossmünster. One of the most important leaders of the Swiss Reformation, Bullinger co-authored the Helvetic Confessions and collaborated with John Calvin to work out a Reformed doctrine of the Lord's Supper.
Crypto-Calvinism is a pejorative term describing a segment of those members of the Lutheran Church in Germany who were accused of secretly subscribing to Calvinist doctrine of the Eucharist in the decades immediately after the death of Martin Luther in 1546. It denotes what was seen as a hidden Calvinist belief, i.e., the doctrines of John Calvin, by members of the Lutheran Church. The term crypto-Calvinist in Lutheranism was preceded by terms Zwinglian and Sacramentarian. Also, Jansenism has been accused of crypto-Calvinism by Roman Catholics.

The real presence of Christ in the Eucharist is the Christian doctrine that Jesus Christ is present in the Eucharist, not merely symbolically or metaphorically, but in a true, real and substantial way.

In Christian theology, the term Body of Christ has two main but separate meanings: it may refer to Jesus Christ's words over the bread at the celebration of the Jewish feast of Passover that "This is my body" in Luke 22:19–20, or it may refer to all individuals who are "in Christ" 1 Corinthians 12:12–14.

The Helvetic Confessions are two documents expressing the common belief of Reformed churches, especially in Switzerland, whose primary author was the Swiss Reformed theologian Heinrich Bullinger. The First Helvetic Confession (1536) contributed to the confessional unity of the Protestant cantons of Switzerland against the Roman Catholic cantons, whereas the Second Helvetic Confession (1566) contributed to the confessional unity of Reformed churches across Europe, particularly due to the patronage it received from Frederick III, Elector Palatine, who had it translated into German.

The reformed confessions of faith are the confessional documents of various Reformed churches. These express the doctrinal views of the churches adopting the confession. Confessions play a crucial part in the theological identity of reformed churches, either as standards to which ministers must subscribe, or more generally as accurate descriptions of their faith. Most confessions date to the 16th and 17th century.

Eucharistic theology is a branch of Christian theology which treats doctrines concerning the Holy Eucharist, also commonly known as the Lord's Supper and Holy Communion.
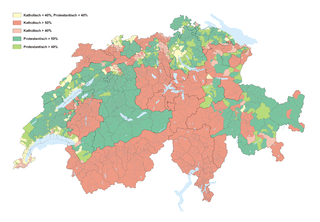
The Reformed branch of Protestantism in Switzerland was started in Zürich by Huldrych Zwingli and spread within a few years to Basel, Bern, St. Gallen,(Joachim Vadian), to cities in southern Germany and via Alsace to France.

Reformed Christianity originated with the Reformation in Switzerland when Huldrych Zwingli began preaching what would become the first form of the Reformed doctrine in Zürich in 1519.

The theology of Ulrich Zwingli was based on an interpretation of the Bible, taking scripture as the inspired word of God and placing its authority higher than what he saw as human sources such as the ecumenical councils and the church fathers. He also recognised the human element within the inspiration, noting the differences in the canonical gospels. Zwinglianism is the Reformed confession based on the Second Helvetic Confession promulgated by Zwingli's successor Heinrich Bullinger in the 1560s.

A sacrament is a Christian rite that is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence, number and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol of the reality of God, as well as a channel for God's grace. Many denominations, including the Roman Catholic, Lutheran, Presbyterian, Anglican, Methodist, and Reformed, hold to the definition of sacrament formulated by Augustine of Hippo: an outward sign of an inward grace, that has been instituted by Jesus Christ. Sacraments signify God's grace in a way that is outwardly observable to the participant.

The theology of John Calvin has been influential in both the development of the system of belief now known as Calvinism and in Protestant thought more generally.
Reformed worship is religious devotion to God as conducted by Reformed or Calvinistic Christians, including Presbyterians. Despite considerable local and national variation, public worship in most Reformed and Presbyterian churches is governed by the Regulative principle of worship.

In Reformed theology, baptism is a sacrament signifying the baptized person's union with Christ, or becoming part of Christ and being treated as if they had done everything Christ had. Sacraments, along with preaching of God's word, are means of grace through which God offers Christ to people. Sacraments are believed to have their effect through the Holy Spirit, but these effects are only believed to accrue to those who have faith in Christ.

Criticism of Protestantism covers critiques and questions raised about Protestantism, the Christian denominations which arose out of the Protestant Reformation. While critics may praise some aspects of Protestantism which are not unique to the various forms of Protestantism, Protestantism is faced with criticism mainly from the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church, although Protestant denominations have also engaged in self-critique and criticized one another. According to both the Catholic Church and Eastern Orthodoxy, many major, foundational Protestant doctrines have been officially declared heretical.

In Reformed theology, the Lord's Supper or Eucharist is a sacrament that spiritually nourishes Christians and strengthens their union with Christ. The outward or physical action of the sacrament is eating bread and drinking wine. Reformed confessions, which are official statements of the beliefs of Reformed churches, teach that Christ's body and blood are really present in the sacrament and that believers receive, in the words of the Belgic Confession, "the proper and natural body and the proper blood of Christ." The primary difference between the Reformed doctrine and that of Catholic and Lutheran Christians is that for the Reformed, this presence is believed to be communicated in a spiritual manner by faith rather than by oral consumption. The Reformed doctrine of real presence is called "pneumatic presence".


















