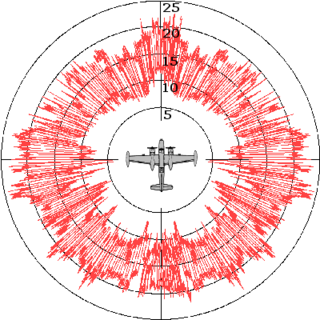
Radar cross-section (RCS), denoted σ, also called radar signature, is a measure of how detectable an object is by radar. A larger RCS indicates that an object is more easily detected.

A metamaterial is any material engineered to have a property that is rarely observed in naturally occurring materials. They are made from assemblies of multiple elements fashioned from composite materials such as metals and plastics. These materials are usually arranged in repeating patterns, at scales that are smaller than the wavelengths of the phenomena they influence. Metamaterials derive their properties not from the properties of the base materials, but from their newly designed structures. Their precise shape, geometry, size, orientation and arrangement gives them their smart properties capable of manipulating electromagnetic waves: by blocking, absorbing, enhancing, or bending waves, to achieve benefits that go beyond what is possible with conventional materials.

Finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) or Yee's method is a numerical analysis technique used for modeling computational electrodynamics. Since it is a time-domain method, FDTD solutions can cover a wide frequency range with a single simulation run, and treat nonlinear material properties in a natural way.

Computational electromagnetics (CEM), computational electrodynamics or electromagnetic modeling is the process of modeling the interaction of electromagnetic fields with physical objects and the environment using computers.
Characteristic modes (CM) form a set of functions which, under specific boundary conditions, diagonalizes operator relating field and induced sources. Under certain conditions, the set of the CM is unique and complete (at least theoretically) and thereby capable of describing the behavior of a studied object in full.
Dr. Raymond J. Luebbers was Professor of Electrical Engineering at The Pennsylvania State University and Ohio University, a Research Scientist at the Lockheed Martin Research Laboratory in Palo Alto, CA and founder of Remcom, Inc.
Richard W. Ziolkowski is an American electrical engineer and academician, who was the president of the IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society (2005), and a former vice president of this same society (2004). In 2006, he became an OSA Fellow. He is also an IEEE Fellow. He was born on November 22, 1952, in Warsaw, New York.
A reconfigurable antenna is an antenna capable of modifying its frequency and radiation properties dynamically, in a controlled and reversible manner. In order to provide a dynamic response, reconfigurable antennas integrate an inner mechanism that enable the intentional redistribution of the RF currents over the antenna surface and produce reversible modifications of its properties. Reconfigurable antennas differ from smart antennas because the reconfiguration mechanism lies inside the antenna, rather than in an external beamforming network. The reconfiguration capability of reconfigurable antennas is used to maximize the antenna performance in a changing scenario or to satisfy changing operating requirements.

An electromagnetic metasurface refers to a kind of artificial sheet material with sub-wavelength thickness. Metasurfaces can be either structured or unstructured with subwavelength-scaled patterns in the horizontal dimensions.

Weng Cho Chew is a Malaysian-American electrical engineer and applied physicist known for contributions to wave physics, especially computational electromagnetics. He is a Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Purdue University.
Kane Shee-Gong Yee is a Chinese-American electrical engineer and mathematician. He is best known for introducing the finite-difference time-domain method (FDTD) in 1966.
Roger Fuller Harrington is an American electrical engineer and professor emeritus at Syracuse University. He is best known for his contributions to computational electromagnetics with his development of method of moments (MoM). Harrington's 1968 book, Field Computation by Moment Methods, is regarded as a pivotal textbook on the subject.
Yuen Tze Lo was a Chinese American electrical engineer and academician. He was a professor emeritus at the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. He is best known for his contributions to the theory and design of antennas. He is the editor of the textbook series, Antenna Handbook.
David Michael Pozar is an American electrical engineer, educator and professor emeritus at the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at University of Massachusetts Amherst. His research interests concentrate mainly on antenna theory and design. Pozar is also the author of the textbook, Microwave Engineering.
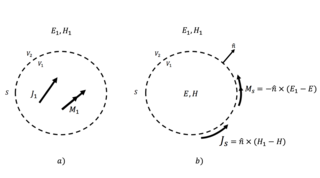
In electromagnetism, surface equivalence principle or surface equivalence theorem relates an arbitrary current distribution within an imaginary closed surface with an equivalent source on the surface. It is also known as field equivalence principle, Huygens' equivalence principle or simply as the equivalence principle. Being a more rigorous reformulation of the Huygens–Fresnel principle, it is often used to simplify the analysis of radiating structures such as antennas.
Tapan Kumar Sarkar was an Indian-American electrical engineer and Professor Emeritus at the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at Syracuse University. He was best known for his contributions to computational electromagnetics and antenna theory.

Douglas Henry Werner is an American scientist and engineer. He holds the John L. and Genevieve H. McCain Chair Professorship in the Penn State Department of Electrical Engineering and is the director of the Penn State University Computational Electromagnetics and Antennas Research Laboratory. Werner holds 20 patents and has over 1090 publications. He is the author/co-author of 8 books. According to Google Scholar, his h-index is 77 with more than 25,600 citations. He is internationally recognized for his expertise in electromagnetics, antenna design, optical metamaterials and metamaterial-enabled devices as well as for the development/application of inverse-design techniques.

The method of moments (MoM), also known as the moment method and method of weighted residuals, is a numerical method in computational electromagnetics. It is used in computer programs that simulate the interaction of electromagnetic fields such as radio waves with matter, for example antenna simulation programs like NEC that calculate the radiation pattern of an antenna. Generally being a frequency-domain method, it involves the projection of an integral equation into a system of linear equations by the application of appropriate boundary conditions. This is done by using discrete meshes as in finite difference and finite element methods, often for the surface. The solutions are represented with the linear combination of pre-defined basis functions; generally, the coefficients of these basis functions are the sought unknowns. Green's functions and Galerkin method play a central role in the method of moments.
Georges Armand Deschamps was a French American engineer and Professor Emeritus at the Department of Electrical Engineering at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He is best known for his contributions to electromagnetic theory, microwave engineering and antenna theory. He is also regarded as an early pioneer of microstrip and patch antennas, which he proposed in 1953.
Arthur Aaron Oliner was an American physicist and electrical engineer, who was professor emeritus at department of electrical and computer engineering at New York University-Polytechnic. Best known for his contributions to engineering electromagnetics and antenna theory, he is regarded as a pioneer of leaky wave theory and leaky wave antennas.









