
Vernonia is a genus of about 350 species of forbs and shrubs in the family Asteraceae. Some species are known as ironweed. Some species are edible and of economic value. They are known for having intense purple flowers. There have been numerous distinct subgenera and subsections named in this genus, and some botanists have divided the genus into several distinct genera. For instance, the Flora of North America recognizes only about twenty species in Vernoniasensu stricto, seventeen of which are in North America north of Mexico, with the others being found in South America.
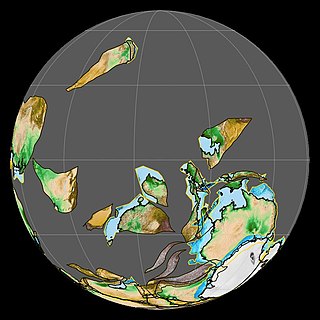
The Tournaisian is in the ICS geologic timescale the lowest stage or oldest age of the Mississippian, the oldest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Tournaisian age lasted from 358.9 Ma to 346.7 Ma. It is preceded by the Famennian and is followed by the Viséan. In global stratigraphy, the Tournaisian contains two substages: the Hastarian and Ivorian. These two substages were originally designated as European regional stages.

Anderson's four-eyed opossum is an opossum species from South America. It is found in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Venezuela. Its dorsal fur is dark, with a black stripe, about 3–4 cm wide, going vertically down the midline of its back. Its dorsal fur is short, about 10 mm long. Its ventral fur is dark gray, but still distinctly lighter than the sides and dorsum. Its tail is furred for the first (approximately) 18% of its length, going from the base to the tip. Its species name "andersoni" was chosen to honor American scientific collector Malcolm Playfair Anderson.

The Indian flapshell turtle is a freshwater species of turtle found in South Asia. The "flap-shelled" name stems from the presence of femoral flaps located on the plastron. These flaps of skin cover the limbs when they retract into the shell. It is unclear what protection the flaps offer against predators. Indian flapshell turtles are widespread and common in the South Asian provinces. It is morphologically an evolutionary link between the softshell and hardshell aquatic turtles. Exploitation for profit and habitat change are threats to their survival.

Anderson's salamander is a neotenic salamander from Zacapu Lagoon in the Mexican state of Michoacán.

Corymbophanes is a genus of armored catfish native to South America where they are only known from Guyana. Corymbophanes was originally placed in its own tribe Corymbophanini, but the first comprehensive molecular phylogenetic analysis of the subfamily Hypostominae found Corymbophanes to be nested within the tribe Ancistrini.
The Japanese red-backed vole, Wakayama red-backed vole, or Anderson's red-backed vole is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found only on the island of Honshu in Japan. It was first described by the British zoologist Oldfield Thomas in 1905. Thomas named it in honor of scientific collector Malcolm Playfair Anderson. The International Union for Conservation of Nature lists it as "least concern".

Raorchestes andersoni is a species of frog in the family Rhacophoridae. It is found in northeast India, northern Myanmar, and Tibet and Yunnan, China. The common names Anderson's bubble-nest frog, Anderson's bush frog and tuberculed small treefrog have been coined for it.

The heavy-browed mouse opossum, or Anderson's mouse opossum, is a species of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It is endemic to a restricted range in southern Peru. This opossum inhabits forests; it is nocturnal and probably arboreal.

The Anderson's shrew mole is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is endemic to China. Its species name "andersoni" was chosen to honor American scientific collector Malcolm Playfair Anderson.

Epinephelus andersoni, the catface grouper, brown-spotted grouper, catface rockcod or brown spotted rockcod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in the southwestern Indian Ocean where it is associated with reefs.

Prophysaon, common name taildropper slugs, is a genus of air-breathing land slugs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Ariolimacidae.

Dermacentor andersoni, commonly known as the Rocky Mountain wood tick, is a hard tick, or member of the Ixodidae family, with three life stages including larvae, nymph, and finally adult, or, more entomologically, imago. This tick is generally located in the northwest United States and southwest Canada along the Rocky Mountains. This tick is generally a vector for Colorado tick fever, but can also be a vector for Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia. During the larval and nymphal stages, the tick does not feed on humans, but during the adult stage, it will. Prevention of infections associated with these ticks is based on control of exposure to the vector, including wearing proper clothing when in woods/wet areas, and checking oneself thoroughly after returning home. Adult female ticks can feed for 5 to 15 days, thus removing a tick if present is very important. Follow general tick removal tips.
Cerradomys scotti, also known as Lindbergh's oryzomys, is a rodent species from South America in the genus Cerradomys. It is terrestrial and is found in the cerrado (savanna) ecozone of south central Brazil, Bolivia and Paraguay. The species is common and appears to tolerate a degree of agricultural habitat modification.
Patrognathus is an extinct genus of conodonts.
Amynothrips is a genus of thrips in the family Phlaeothripidae.
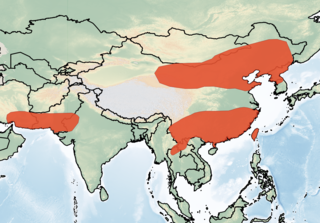
The Oriental serotine is a species of bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is widespread and found throughout Asia.
Yaluwak is a genus of armored catfish native to South America where they are only known from Guyana, containing only a single species Yaluwak primus. It was first described in a 2020 study and placed within the tribe Ancistrini.
Corymbophanes ameliae is a species of armored catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America where it is known only from the Kuribrong River in Guyana.
Corymbophanes kaiei is a species of catfish in the family Loricariidae. It is native to South America, where it occurs in the Potaro River basin in the Essequibo River drainage. It is usually found in fast-moving, sunlit riffles among cobble and submerged logs. The species reaches 6.6 centimetres (2.6 in) SL.













