
Mato Grosso is one of the states of Brazil, the third largest by area, located in the Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP.

Cuiabá is the capital city of the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso. It is located near the geographical centre of South America. Also, it forms the metropolitan area of Mato Grosso, along with the neighbouring town of Várzea Grande. The city's name is an indigenous Bororo word meaning 'arrow-fishing', The city was founded in 1719, during the gold rush, and it has been the state capital since 1818. The city is a trading centre for an extensive cattle-raising and agricultural area. The capital is among the fastest-growing cities in Brazil, followed by the growth of agribusiness in Mato Grosso, despite the recession that is affecting Brazilian industries. Cuiabá was one of the host cities for the 2014 FIFA World Cup.

The Chapada dos Guimarães National Park is a national park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. It is a region of rugged terrain with dramatic cliffs and waterfalls, and contains the geographical centre of the continent.
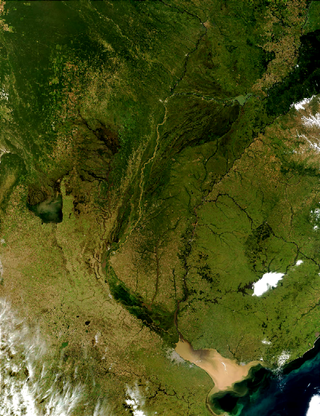
The Río de la Plata basin, more often called the River Plate basin in scholarly writings, sometimes called the Platine basin or Platine region, is the 3,170,000-square-kilometre (1,220,000 sq mi) hydrographical area in South America that drains to the Río de la Plata. It includes areas of southeastern Bolivia, southern and central Brazil, the entire country of Paraguay, most of Uruguay, and northern Argentina. Making up about one fourth of the continent's surface, it is the second largest drainage basin in South America and one of the largest in the world.

The Pantanal Matogrossense National Park is a national park in the state of Mato Grosso at the border to Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil.
The Alegre River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil. It is a tributary of the Caçanje River, which in turn is a tributary of the Cuiabá River.
The Caçanje River, also called the Cassange River, is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil. It is a tributary of the Cuiabá River.

The São Lourenço River is a tributary of the Paraguay River within the Pantanal, an alluvial plain that spans portions of Brazil, Bolivia and Paraguay. The São Lourenço river basin lies in the Mato Grosso state of Brazil.
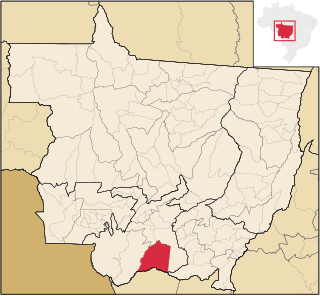
Barão de Melgaço is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil.

Poconé is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil. The Bento Gomes River passes within a few kilometers of the village.
Águas do Cuiabá Ecological Station, formerly the Águas do Cuiabá State Park, is an ecological station in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil, a fully protected conservation unit in the cerrado biome. There was controversy about the acquisition of land to expand the unit's area when it was made an ecological station.
The Rio da Casca Ecological Station is an ecological station in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. It protects a partly deforested area of savanna.

The Águas Quentes State Park is a state park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil

The Massairo Okamura State Park is a state park in the city of Cuiabá, capital of Mato Grosso, Brazil. It preserves an area of typical cerrado forest in a densely urbanised area.

The Encontro das Águas State Park is a state park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. It covers an area of the pantanal rich in watercourses.

The Piquirí River is a river of Mato Grosso state in western Brazil. It is a tributary of the São Lourenço River.
The Serra de Santa Bárbara State Park is a state park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. It preserves a unique environment where the Amazon rainforest, pantanal and cerrado meet, and holds many endemic or endangered species.
The Guirá State Park is a State park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil.
The Nascentes do Rio Taquari State Park is a state park in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. It protects the headwaters of the Taquari River in an area in the transition between the cerrado and pantanal biomes.
















