Related Research Articles

Bluetongue disease is a noncontagious, insect-borne, viral disease of ruminants, mainly sheep and less frequently cattle, yaks, goats, buffalo, deer, dromedaries, and antelope. It is caused by Bluetongue virus (BTV). The virus is transmitted by the midges Culicoides imicola, Culicoides variipennis, and other culicoids.
The highland midge is a species of small flying insect, found across the Palearctic in upland and lowland areas. In the north west of Scotland and northern Wales the highland midge is usually very prevalent from late spring to late summer. Female highland midges are well known for gathering in clouds and biting humans, though the majority of the blood they obtain comes from cattle, sheep and deer. The bite of Culicoides is felt as a sharp prick. It is often followed by irritating lumps that may disappear in a few hours or last for days, depending on the individual.

Sandfly is a colloquial name for any species or genus of flying, biting, blood-sucking dipteran (fly) encountered in sandy areas. In the United States, sandfly may refer to certain horse flies that are also known as "greenheads", or to members of the family Ceratopogonidae. Outside the United States, sandfly may refer to members of the subfamily Phlebotominae within the Psychodidae. Biting midges (Ceratopogonidae) are sometimes called sandflies or no-see-ums. New Zealand sandflies are in the genus Austrosimulium, a type of black fly.

Culicoides imicola is a species of Ceratopogonidae that transmits the bluetongue virus (BTV) and the African horse sickness virus. This particular species has been recorded in Africa, Asia and Europe. African midges feed on animal blood, including horse, cattle, and sheep. Unlike other species within the Culicoides genus, this species prefers drier habitats for egg laying but retains a preference for moist soil to support larvae growth. Other suspected BTV vectors are Culicoides (Culicoides) pulicaris and species in the Culicoides (Avaritia) obsoletus complex.

Oropouche fever is a tropical viral infection transmitted by biting midges and mosquitoes from the blood of sloths to humans. This disease is named after the region where it was first discovered and isolated at the Trinidad Regional Virus Laboratory in 1955 by the Oropouche River in Trinidad and Tobago. Oropouche fever is caused by a specific arbovirus, the Oropouche virus (OROV), of the Bunyaviridae family.

Ceratopogonidae is a family of flies commonly known as no-see-ums, or biting midges, generally 1–3 mm in length. The family includes more than 5,000 species, distributed worldwide, apart from the Antarctic and the Arctic.
Oropouche orthobunyavirus (OROV) is one of the most common orthobunyaviruses. When OROV infects humans, it causes a rapid fever illness called Oropouche fever. OROV was originally reported in Trinidad and Tobago in 1955 from the blood sample of a fever patient and from a pool of Coquillettidia venezuelensis mosquitoes. In 1960, OROV was isolated from a sloth and a pool of Ochlerotatus serratus mosquitoes in Brazil. The virus is considered a public health threat in tropical and subtropical areas of Central and South America, with over half million infected people as of 2005. OROV is considered to be an arbovirus due to the method of transmission by the mosquitoes Aedes serratus and Culex quinquefasciatus among sloths, marsupials, primates, and birds.
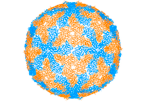
Orbivirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae and subfamily Sedoreovirinae. Unlike other reoviruses, orbiviruses are arboviruses. They can infect and replicate within a wide range of arthropod and vertebrate hosts. Orbiviruses are named after their characteristic doughnut-shaped capsomers.
African horse sickness (AHS) is a highly infectious and deadly disease caused by African horse sickness virus. It commonly affects horses, mules, and donkeys. It is caused by a virus of the genus Orbivirus belonging to the family Reoviridae. This disease can be caused by any of the nine serotypes of this virus. AHS is not directly contagious, but is known to be spread by insect vectors.

Also known as Queensland Itch, Seasonal Recurrent Dermatitis (SSRD) , Summer Itch or more technically, Culicoides Hypersensitivity.
Epizootic hemorrhagic disease (EHD) is a hemorrhagic disease of white-tailed deer caused by an infection of a virus from the genus Orbivirus subsequently called Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus (EHDV). It is an infectious, and sometimes fatal, virus that is characterized by extensive hemorrhages, and is found throughout the United States. Large-scale outbreaks in wild ruminants affect livestock and the production industry. EHD has been found in some domestic ruminants and many species of deer including white-tailed deer, mule deer, and pronghorn antelope. Seropositive black-tailed deer, fallow deer, red deer, wapiti, and roe deer have also been found, which essentially means that they were exposed to the disease at some time in the past, but may not be involved in transmission. Outbreaks of EHD have been reported in cattle, although it is rare for them to develop disease or die. Sheep may develop clinical signs; however, this is also rare. EHD is often called bluetongue, but this is incorrect. Bluetongue virus is closely related to EHDV, and has similar clinical signs, but it is a different disease. Bluetongue is a serious disease in cattle, as well as other ruminants, and can have a significant effect on international trade. Testing at animal health laboratories is necessary to distinguish between the viruses that cause bluetongue and EHD.

Orthobunyavirus is a genus of the Peribunyaviridae family in the order Bunyavirales. There are currently ~170 viruses recognised in this genus. These have been assembled into 97 species and 20 serogroups.

Culicoides is a genus of biting midges in the family Ceratopogonidae. There are over 1000 species in the genus, which is divided into many subgenera. Several species are known to be vectors of various diseases and parasites which can affect animals. Like Leptoconops, the genus has a long fossil record, with earliest known fossils being from Burmese amber, around 99 million years old.

Akabane orthobunyavirus is an insect-transmitted virus that causes congenital abnormalities of the central nervous systems in ruminants. The virus is found in Australia, where it is most commonly spread by biting midges of the Culicoides species.

Culicoides obsoletus the name of a species of midges in the subgenus Avaritia. According to a molecular phylogeny, Avaritia is monophyletic, and Culicoides obsoletus, Culicoides scoticus and Culicoides chiopterus should be part of the Obsoletus complex whereas Culicoides dewulfi should be excluded from it.
Dr. Simon Carpenter, Head of the Entomology and Modelling Group in the Vector-borne Diseases Programme at the UK Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council Institute for Animal Health’s Pirbright Laboratory in Woking, Surrey, is an entomologist who was awarded the first Rooker Prize in 2009 in recognition of his research on biting midges that transmit bluetongue virus (BTV), the causative agent of bluetongue disease, an important orbivirus disease of ruminants.
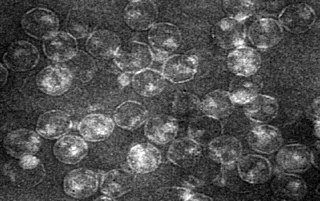
Equine encephalosis virus (EEV) is a species of virus the Orbivirus genus, and a member of the Reoviridae family, related to African horse sickness virus (AHSV) and Bluetongue virus (BTV).

Tibrovirus is a poorly characterized genus of viruses in the family Rhabdoviridae, order Mononegavirales. As of 2019, there are 8 members of the tibrovirus genus. Tibroviruses have been isolated from biting midges, cattle, and humans. None of the tibroviruses, except for Bas-Congo virus, have been associated with any diseases.
Culicoides kalix is a species of midges found in Scandinavia. It can be differentiated from its cogenerated by wing and maxillary palp characteristics.
Culicoides crepuscularis is a species of biting midge in the family Ceratopogonidae.
References
- ↑ "Culicoides paraensis (Goeldi, 1905)". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- ↑ David R. Mercer & Maikol J. Castillo-Pizango (July 2005). "Changes in relative species compositions of biting midges (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) and an outbreak of Oropouche virus in Iquitos, Peru". Journal of Medical Entomology . 42 (4): 554–558. doi: 10.1603/0022-2585(2005)042[0554:CIRSCO]2.0.CO;2 . PMID 16119543.
| | This article related to members of the fly superfamily Chironomoidea is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |