
Lesothosaurus is a monospecific genus of ornithischian dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic in what is now South Africa and Lesotho. It was named by paleontologist Peter Galton in 1978, the name meaning "lizard from Lesotho". The genus has only one valid species, Lesothosaurus diagnosticus. Lesothosaurus is one of the most completely-known early ornithischians, based on numerous skull and postcranial fossils from the Upper Elliot Formation. It had a simpler tooth and jaw anatomy than later ornithischians, and may have been omnivorous in some parts of the year.
Steropodon is a genus of prehistoric platypus-like monotreme, or egg-laying mammal. It contains a single species, Steropodon galmani, that lived about 105 to 93.3 million years ago (mya) in the Early to Late Cretaceous period. It is one of the oldest monotremes discovered, and is one of the oldest Australian mammal discoveries.

Hipposideros besaoka is an extinct bat from Madagascar in the genus Hipposideros. It is known from numerous jaws and teeth, which were collected in a cave at Anjohibe in 1996 and described as a new species in 2007. The site where H. besaoka was found is at most 10,000 years old; other parts of the cave have yielded H. commersoni, a living species of Hipposideros from Madagascar, and some material that is distinct from both species. H. besaoka was larger than H. commersoni, making it the largest insectivorous bat of Madagascar, and had broader molars and a more robust lower jaw. As usual in Hipposideros, the second upper premolar is small and displaced from the toothrow, and the second lower premolar is large.
Argentodites is a possible multituberculate mammal from the Cretaceous of Argentina. The single species, Argentodites coloniensis, is known from a single blade-like fourth lower premolar (p4) from the La Colonia Formation, which is mostly or entirely Maastrichtian in age. The p4 is 4.15 mm long and bears eight cusps on its upper margin and long associated ridges on both sides. The enamel consists of prisms that are completely or partly surrounded by a sheath and that are on average 6.57 μm apart. Zofia Kielan-Jaworowska, who described and named the fossil in 2007, regarded it as a multituberculate, perhaps a cimolodontan—and thus, a member of a mostly Laurasian (northern) group and an immigrant to Argentina from North America—on the basis of the shape of the tooth and features of its enamel. In 2009, however, two teams argued that Argentodites may in fact be close to or identical with Ferugliotherium, a member of the small Gondwanan (southern) group Gondwanatheria; although their relationships are disputed, gondwanatheres may themselves be multituberculates.
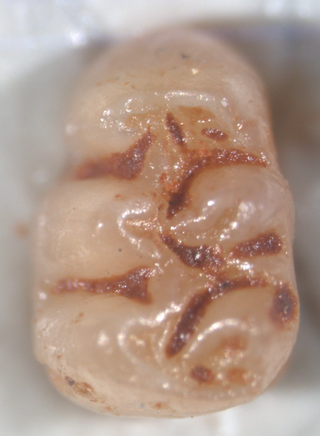
Agathaeromys is an extinct genus of oryzomyine rodents from the Pleistocene of Bonaire, Netherlands Antilles. Two species are known, which differ in size and some details of tooth morphology. The larger A. donovani, the type species, is known from hundreds of teeth that are probably 900,000 to 540,000 years old, found in four localities. A. praeuniversitatis, the smaller species, is known from 35 teeth found in a single fossil site, which is probably 540,000 to 230,000 years old.

Cyclommatus is a genus of the family Lucanidae, also known as the stag beetle. The majority of the species from the genus Cyclommatus are located in Southeast Asia, though some species are found in China and Taiwan as well. The genus Cyclommatus also consists of three subgenera: Cyclommatus, Cyclommatinus and Cyclommatellus. Each subgenera contains 80, 24 and 3 species respectively. In total, the genus Cyclommatus consists of a total of 134 species, though more are still being discovered to this day.

Deinodryinus areolatus is an extinct species of Deinodryinus in the wasp family Dryinidae. The species is solely known from an Eocene fossil found in the Baltic region.
Procaris hawaiana is a species of shrimp in the family Procarididae, from Maui, Hawaii. The species is very similar to Procaris ascensionis from Ascension Island. In P. ascensionis the integument is less firm, the rostrum is shorter, the cervical groove is more distinct, and the third abdominal somite reaches less far posteriorly over the fourth; also the scaphocerite has the final tooth still less distinct than in P. hawaiana, and the last segment of its antennal peduncle is less slender.
Periclimenes pholeter, is a species of shrimp belonging to the family Palaemonidae. The species is closest to Periclimenes indicus, P. obscurus and P. toloensis, resembling these species in the presence of an epigastric tooth on the carapace, the shape of the abdomen, the spinulation of the carapace, and the unarmed fingers of the first chelipeds. P. pholeter most resembles P. indicus by the elongatecarpus and long fingers of the second pereiopods, differing in these features from P. toloensis, which has the fingers slightly less than half as long as the palm. In P. obscurus the fingers are shorter than the palm, but the carpus is about as long as the palm. From P. indicus, this species differs: by the greater size; by the much higher rostrum and the greater number of ventral rostral teeth; by the shorter eye; by the less slender antennular peduncle; by the more deeply cleft upper antennular flagellum; by the more robust scaphocerite; by the fingers of the first pereiopods ; by the more slender pereiopods, especially the fifth, which is much longer than the ischium.

Brownimecia is an extinct genus of ants, the only genus in the tribe Brownimeciini and subfamily Brownimeciinae of the Formicidae. Fossils of the single identified species, Brownimecia clavata, are known from the Middle Cretaceous of North America. The genus is one of several ants described from Middle Cretaceous ambers of New Jersey. Brownimecia was initially placed in the subfamily Ponerinae, until it was transferred to its own subfamily in 2003; it can be distinguished from other ants due to its unusual sickle-like mandibles and other morphological features that makes this ant unique among the Formicidae. The ant is also small, measuring 3.43 millimetres (0.135 in), and a stinger is present in almost all of the specimens collected. The morphology of the mandibles suggest a high level of feeding specialization.

Zigrasimecia is an extinct genus of ants which existed in the Cretaceous period approximately 98 million years ago. The first specimens were collected from Burmese amber in Kachin State, 100 kilometres (62 mi) west of Myitkyina town in Myanmar. In 2013, palaeoentomologists Phillip Barden and David Grimaldi published a paper describing and naming Zigrasimecia tonsora. They described a dealate female with unusual features, notably the highly specialized mandibles. Other features include large ocelli, short scapes, 12 antennomeres, small eyes, and a clypeal margin that has a row of peg-like denticles. The genus Zigrasimecia was originally incertae sedis within Formicidae until a second species, Zigrasimecia ferox, was described in 2014, leading to its placement in the subfamily Sphecomyrminae. Later, it was considered to belong to the distinct subfamily Zigrasimeciinae.

Haidomyrmex is an extinct genus of ants in the formicid subfamily Haidomyrmecinae, and is one of nine genera placed in the subfamily Haidomyrmecinae. The genus contains three described species Haidomyrmex cerberus, Haidomyrmex scimitarus, and Haidomyrmex zigrasi. All three are known from single Late Cretaceous fossils which have been found in Asia. H. cerberus is the type species and Haidomyrmex the type genus for the subfamily Haidomyrmecinae.

Anochetus dubius is an extinct species of ant in the subfamily Ponerinae known from two possibly Miocene fossils found on Hispaniola. A. dubius is one of eight species in the ant genus Anochetus to have been described from fossils found in Dominican amber and is one of a number of Anochetus species found in the Greater Antillies.
Alpheus tricolor is a crustacean belonging to the family of snapping shrimp. It was first isolated in Indonesia and Sri Lanka. It counts with a setose carapace, an acute rostrum, shallow adrostral furrows and a basicerite with a strong ventrolateral tooth. The lamella of its scaphocerite is not reduced, with an anterior margin that is concave. Its third maxilliped counts with an epipodial plate bearing thick setae, while its first chelipeds are found with their merus bearing a strong disto-mesial tooth; its third pereiopod has an armed ischium, with a simple and conical dactylus. Its telson is broad, distally tapering, with 2 pairs of dorsal spines. The species is named after its characteristic colour pattern, including white, red and orange.

Pseudectatomma is an extinct genus of ants in the formicid subfamily Ectatomminae described by from fossils found in Europe. The genus contains two species dating from the Eocene, Pseudectatomma eocenica and Pseudectatomma striatula.

Protopone is an extinct genus of ants in the formicid subfamily Ponerinae described from fossils found in Europe and Asia. There are seven described species placed into the genus, Protopone? dubia, Protopone germanica, Protopone magna, Protopone oculata, Protopone primigena, Protopone sepulta, and Protopone vetula. Protopone is one several Lutetian Ponerinae genera.

Cyrtopone is an extinct genus of ants in the formicid subfamily Ponerinae described from fossils found in Europe. There are four described species placed into the genus, Cyrtopone curiosa, Cyrtopone elongata, Cyrtopone microcephala, and Cyrtopone striata. Cyrtopone is one several Lutetian Ponerinae genera.

Gerontoformica is an extinct genus of stem-group ants. The genus contains thirteen described species known from Late Cretaceous fossils found in Asia and Europe. The species were described between 2004 and 2016, with a number of the species formerly being placed into the junior synonym genus Sphecomyrmodes.

Monquirasaurus is an extinct genus of giant short-necked pliosaurs who lived during the Early Cretaceous (Aptian) in what is now Colombia. One species is known, M. boyacensis, described in 2021 from an almost complete fossil skeleton, discovered in 1977 in the town of Villa de Leyva, located in Boyacá. Published descriptions of the holotype specimen estimate that it should reach a total size approaching 8 m (26 ft) in length, making Monquirasaurus a large representative of the pliosaurids.
Eurycephalosuchus is an extinct genus of orientalosuchine alligatoroid from the Late Cretaceous Jiangxi Province of China. Known from a well preserved skull and mandible alongside various postcranial remains, Eurycephalosuchus possessed a short and broad skull with a very short skulltable. Eurycephalosuchus lived with at least one other crocodilian, an indetermined member of the clade Brevirostres. The genus is monotypic, containing only the species Eurycephalosuchus gannanensis.















