
Shaggy parasol is the common name for three closely related species of mushroom, Chlorophyllum rhacodes, C. olivieri and C. brunneum, found in North America, Europe and Southern Africa.

Didiereaceae is a family of flowering plants found in continental Africa and Madagascar. It contains 20 species classified in three subfamilies and six genera. Species of the family are succulent plants, growing in sub-arid to arid habitats. Several are known as ornamental plants in specialist succulent collections. The subfamily Didiereoideae is endemic to the southwest of Madagascar, where the species are characteristic elements of the spiny thickets.

Abies procera, the noble fir, also called red fir and Christmas tree, is a western North American fir, native to the Cascade Range and Coast Range mountains of extreme northwest California and western Oregon and Washington in the United States. It is a high-altitude tree, typically occurring at 300–1,500 m (980–4,920 ft) altitude, only rarely reaching the tree line.

Calotropis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1810. It is native to southern Asia and North Africa.
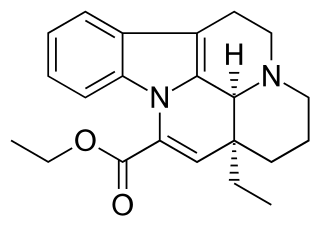
Vinpocetine is a synthetic derivative of the vinca alkaloid vincamine. Vincamine is extracted from either the seeds of Voacanga africana or the leaves of Vinca minor.

Macrolepiota procera, the parasol mushroom, is a basidiomycete fungus with a large, prominent fruiting body resembling a parasol. It is a fairly common species on well-drained soils. It is found solitary or in groups and fairy rings in pastures and occasionally in woodland. Globally, it is widespread in temperate regions.

Juniperus procera is a coniferous tree native to mountainous areas in Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. It is a characteristic tree of the Afromontane flora.

Nobel Biocare is a company that manufactures dental implants and CAD/CAM-based individualized prosthetics and is headquartered in Kloten, Switzerland near the Zürich Airport. Nobel Biocare in its current form was founded in 2002. It originates in a partnership formed in 1978 between Swedish medical researcher Professor Per-Ingvar Brånemark and Bofors, a Swedish company, to industrialize Brånemark's discovery of osseointegration.

The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Atinia Variegata', the Variegated-leaved common English Elm, formerly known as U. procera 'Argenteo-Variegata' and described by Weston (1770) as U. campestris argenteo-variegata, is believed to have originated in England in the seventeenth century and to have been cultivated since the eighteenth. The Oxford botanist Robert Plot mentioned in a 1677 Flora a variegated elm in Dorset, where English Elm is the common field elm. Elwes and Henry (1913) had no doubt that the cultivar was of English origin, "as it agrees with the English Elm in all its essential characters". At the Dominion Arboretum, Ottawa, the tree was listed as U. procera 'Marginata', as the variegation is sometimes most obvious on leaf-margins.

The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Purpurea', the purple-leaved elm, was listed and described as Ulmus Stricta Purpurea, the 'Upright Purpled-leaved Elm', by John Frederick Wood, F.H.S., in The Midland Florist and Suburban Horticulturist (1851), as Ulmus purpureaHort. by Wesmael (1863), and as Ulmus campestris var. purpurea, syn. Ulmus purpureaHort. by Petzold and Kirchner in Arboretum Muscaviense (1864). Koch's description followed (1872), the various descriptions appearing to tally. Henry (1913) noted that the Ulmus campestris var. purpureaPetz. & Kirchn. grown at Kew as U. montana var. purpurea was "probably of hybrid origin", Ulmus montana being used at the time both for wych elm cultivars and for some of the U. × hollandica group. His description of Kew's U. montana var. purpurea matches that of the commonly-planted 'Purpurea' of the 20th century. His discussion of it (1913) under U. campestris, however, his name for English Elm, may be the reason why 'Purpurea' is sometimes erroneously called U. procera 'Purpurea' (as in USA and Sweden.
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Globosa' was first described in the Späth nursery catalogue of 1892–93. Considered "probably Ulmus carpinifolia " by Green
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Aspera' was listed without description by Loddiges,, in his catalogue of 1823. Considered only "possibly procera" by Green.
The elm cultivar Ulmus 'Myrtifolia', the Myrtle-leaved Elm, first appeared in nursery and horticultural lists from the 1830s, as Ulmus myrtifolia and Ulmus campestris myrtifolia, the name Ulmus myrtifoliaVolxem being used at Kew Gardens from 1880. Lawson's nursery of Edinburgh appears to have been the earliest to list the tree. 'Myrtifolia' was listed by Nicholson in Kew Hand-List Trees & Shrubs (1896), but without description. It was later listed as a cultivar and described by Rehder in 1939 and by Krüssmann in 1962.
The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Rugosa' was distributed by the Späth nursery, Berlin, in the 1890s and early 1900s as U. campestris rugosaKirchner. Kirchner's tree, like Späth's a level-branched suberose field elm, was received from Belgium in 1864 as Ulmus rugosa pendula. Kirchner stressed that it was different from Loudon's Ulmus montana var. rugosa, being "more likely to belong to U. campestris or its subspecies, the Cork-elm".

The cloaked pug is a moth of the family Geometridae. The species was first described by Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1781 and it can be found in Europe and to the east in Siberia.

Spondiadoideae is a plant subfamily in the cashew and sumac family Anacardiaceae.

Cyrtocarpa is a genus of trees in the subfamily Spondiadoideae of the cashew and sumac family Anacardiaceae. Their habitat is dry forests to open arid areas. They grow naturally in Mexico and northern South America.

Ammophila procera, the common thread-waisted wasp, is a species of thread-waisted wasp in the family Sphecidae. It is a common species, found in southern Canada, the United States, and Mexico, and south to Central America.

Ophiopsiella is an extinct genus of prehistoric ray-finned fish closely related to the bowfin.

Cyrtocarpa edulis, the rock currant, rock redcurrant, or Bieberstein's rock currant is a species of Cyrtocarpa found in Mexico.















