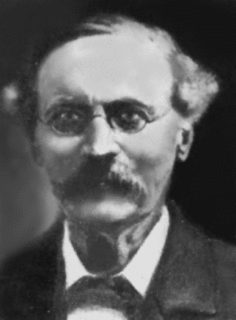Moa were nine species of now-extinct flightless birds endemic to New Zealand. The two largest species, Dinornis robustus and Dinornis novaezelandiae, reached about 3.6 m (12 ft) in height with neck outstretched, and weighed about 230 kg (510 lb) while the smallest, the bush moa, was around the size of a turkey. Estimates of the Moa population when Polynesians settled New Zealand circa 1280, vary between 58,000 to c. 2.5 million.

Senecio is a genus of the daisy family (Asteraceae) that includes ragworts and groundsels. The scientific Latin genus name, Senecio, means "old man."

The Haast's eagle is an extinct species of eagle that once lived in the South Island of New Zealand, commonly accepted to be the pouakai of Maori legend. The species was the largest eagle known to have existed, with an estimated weight of 15 kilograms (33 lb) nearly double that of the Harpy eagle at 9 kilograms (20 lb). Its massive size is explained as an evolutionary response to the size of its prey, the flightless moa, the largest of which could weigh 230 kg (510 lb). Haast's eagle became extinct around 1400, after the moa were hunted to extinction by the first Māori.

Hoverflies, also called flower flies or syrphid flies, make up the insect family Syrphidae. As their common name suggests, they are often seen hovering or nectaring at flowers; the adults of many species feed mainly on nectar and pollen, while the larvae (maggots) eat a wide range of foods. In some species, the larvae are saprotrophs, eating decaying plant and animal matter in the soil or in ponds and streams. In other species, the larvae are insectivores and prey on aphids, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects.

Metrosideros is a genus of approximately 60 trees, shrubs, and vines mostly found in the Pacific region in the family Myrtaceae. Most of the tree forms are small, but some are exceptionally large, the New Zealand species in particular. The name derives from the Ancient Greek metra or "heartwood" and sideron or "iron". Perhaps the best-known species are the pōhutukawa, northern rātā, and southern rātā of New Zealand, and ʻōhiʻa lehua,, from the Hawaiian Islands.

Nothofagus, also known as the southern beeches, is a genus of 43 species of trees and shrubs native to the Southern Hemisphere in southern South America and Australasia. The species are ecological dominants in many temperate forests in these regions. Some species are reportedly naturalised in Germany and Great Britain. The genus has a rich fossil record of leaves, cupules, and pollen, with fossils extending into the late Cretaceous period and occurring in Australia, New Zealand, Antarctica, and South America. In the past, they were included in the family Fagaceae, but genetic tests revealed them to be genetically distinct, and they are now included in their own family, the Nothofagaceae.

The kererū or New Zealand pigeon is the only pigeon endemic to the New Zealand mainland. A large conspicuous pigeon with distinctive noisy wingbeats, it is the only remaining New Zealand bird capable of swallowing large fruit, and so is an important seed disperser for native trees. Kererū were a significant food source for Māori and one of the two foods harvested at the New Year. Although widespread in both forest and urban habitats, their numbers have declined significantly since European colonisation and the arrival of rats and possums, and hunting them is now illegal.

The European hedgehog, also known as the West European hedgehog or common hedgehog, is a hedgehog species found in Europe, from Iberia and Italy northwards into Scandinavia. It is a generally common and widely distributed species that can survive across a wide range of habitat types. It is a well-known species, and a favorite in European gardens, both for its endearing appearance and its preference for eating a range of garden pests. While populations are currently stable across much of its range, it is thought to be declining severely in Great Britain.

The tui is an endemic passerine bird of New Zealand, and the only species in the genus Prosthemadera. It is one of the largest species in the diverse Australasian honeyeater family Meliphagidae, and one of two living species of that family found in New Zealand, the other being the New Zealand bellbird. The tui has a wide distribution in the archipelago, ranging from the subtropical Kermadec Islands to the sub-Antarctic Auckland Islands, as well as the main islands.

Passiflora tarminiana is a species of passionfruit. The yellow fruits are edible and their resemblance to small, straight bananas has given it the name banana passionfruit in some countries. It is native to the uplands of tropical South America and is now cultivated in many countries. In Hawaii and New Zealand it is now considered an invasive species. It was given the name banana passionfrui in New Zealand, where passionfruit are also prevalent. In Hawaii, it is called banana poka. In its Latin American homeland, it is known as curuba, curuba de Castilla, or curuba sabanera blanca (Colombia); taxo, tacso, tagso, tauso (Ecuador); parcha, taxo (Venezuela), tumbo or curuba (Bolivia); tacso, tumbo, tumbo del norte, trompos, tintin or purpur (Peru).
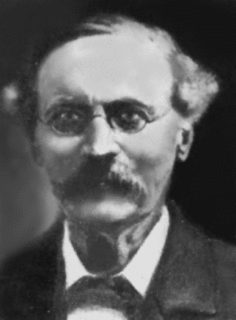
Captain Frederick Wollaston Hutton was an English-New Zealand scientist who applied the theory of natural selection to explain the origins and nature of the natural history of New Zealand. An army officer in early life, he then had an academic career in geology and biology. He became one of the most able and prolific nineteenth century naturalists of New Zealand.

Rhytididae is a taxonomic family of medium-sized predatory air-breathing land snails, carnivorous terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Rhytidoidea.
Arthur William Baden Powell was a New Zealand malacologist, naturalist and palaeontologist, a major influence in the study and classification of New Zealand molluscs through much of the 20th century. He was known to his friends and family by his third name, "Baden".

Mnesarchaeoidea is a superfamily of "New Zealand primitive moths" containing one family, Mnesarchaeidae and a single genus, Mnesarchaea, endemic to New Zealand.

Taniwhasaurus is an extinct genus of mosasaur which inhabited New Zealand, Japan and Antarctica. The genus was a close relative of the genus Tylosaurus.

Macrocystis pyrifera, commonly known as giant kelp or giant bladder kelp, is a species of kelp, and one of four species in the genus Macrocystis. Despite its appearance, it is not a plant; it is a heterokont. Giant kelp is common along the coast of the eastern Pacific Ocean, from Baja California north to southeast Alaska, and is also found in the southern oceans near South America, South Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. Individual algae may grow to more than 45 metres long at a rate of as much as 60 cm (2 ft) per day. Giant kelp grows in dense stands known as kelp forests, which are home to many marine animals that depend on the algae for food or shelter. The primary commercial product obtained from giant kelp is alginate, but humans also harvest this species on a limited basis for use directly as food, as it is rich in iodine, potassium, and other minerals. It can be used in cooking in many of the ways other sea vegetables are used, and particularly serves to add flavor to bean dishes.
William B. Rudman, usually known as Bill Rudman, is a malacologist from New Zealand and Australia. In particular he studies sea slugs, opisthobranch gastropod molluscs, and has named many species of nudibranchs.

Wendy Alison Nelson is a New Zealand marine scientist and world expert in phycology. She is New Zealand's leading authority on seaweeds. Nelson is particularly interested in the biosystematics of seaweeds/macroalgae of New Zealand, with research on floristics, evolution and phylogeny, as well as ecology, and life history studies of marine algae. Recently she has worked on the systematics and biology of red algae including coralline algae, distribution and diversity of seaweeds in harbours and soft sediment habitats, and seaweeds of the Ross Sea and Balleny Islands.