Computer-aided engineering (CAE) is the general usage of technology to aid in tasks related to engineering analysis. Any use of technology to solve or assist engineering issues falls under this umbrella.
Seismic analysis is a subset of structural analysis and is the calculation of the response of a building structure to earthquakes. It is part of the process of structural design, earthquake engineering or structural assessment and retrofit in regions where earthquakes are prevalent.

Ansys, Inc. is an American multinational company with its headquarters based in Canonsburg, Pennsylvania. It develops and markets CAE/multiphysics engineering simulation software for product design, testing and operation and offers its products and services to customers worldwide.
Earthquake engineering is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that designs and analyzes structures, such as buildings and bridges, with earthquakes in mind. Its overall goal is to make such structures more resistant to earthquakes. An earthquake engineer aims to construct structures that will not be damaged in minor shaking and will avoid serious damage or collapse in a major earthquake. A properly engineered structure does not necessarily have to be extremely strong or expensive. It has to be properly designed to withstand the seismic effects while sustaining an acceptable level of damage.
Micromechanics is the analysis of heterogeneous materials including of composite, and anisotropic and orthotropic materials on the level of the individual constituents that constitute them and their interactions.

NEi Nastran was an engineering analysis and simulation software product of NEi Software. Based on NASA's Structural Analysis program NASTRAN, the software is a finite element analysis (FEA) solver used to generate solutions for linear and nonlinear stress, dynamics, and heat transfer characteristics of structures and mechanical components. NEi Nastran software is used with all major industry pre- and post-processors, including Femap, a product of Siemens PLM Software, and the in-house brands NEi Nastran in-CAD, NEi Fusion, and NEi Works for SolidWorks. This software was acquired by Autodesk in May 2014.
Z88 is a software package for the finite element method (FEM) and topology optimization. A team led by Frank Rieg at the University of Bayreuth started development in 1985 and now the software is used by several universities, as well as small and medium-sized enterprises. Z88 is capable of calculating two and three dimensional element types with a linear approach. The software package contains several solvers and two post-processors and is available for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Unix/Linux computers in 32-bit and 64-bit versions. Benchmark tests conducted in 2007 showed a performance on par with commercial software.

Klaus-Jürgen Bathe is a civil engineer, professor of mechanical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and founder of ADINA R&D, who specializes in computational mechanics. Bathe is considered to be one of the pioneers in the field of finite element analysis and its applications.
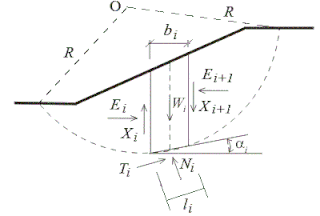
Slope stability analysis is a static or dynamic, analytical or empirical method to evaluate the stability of slopes of soil- and rock-fill dams, embankments, excavated slopes, and natural slopes in soil and rock. It is performed to assess the safe design of a human-made or natural slopes and the equilibrium conditions. Slope stability is the resistance of inclined surface to failure by sliding or collapsing. The main objectives of slope stability analysis are finding endangered areas, investigation of potential failure mechanisms, determination of the slope sensitivity to different triggering mechanisms, designing of optimal slopes with regard to safety, reliability and economics, and designing possible remedial measures, e.g. barriers and stabilization.
Weakened weak form is used in the formulation of general numerical methods based on meshfree methods and/or finite element method settings. These numerical methods are applicable to solid mechanics as well as fluid dynamics problems.

VisualFEA is a finite element analysis software program for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X. It is developed and distributed by Intuition Software, Inc. of South Korea, and used chiefly for structural and geotechnical analysis. Its strongest point is its intuitive, user-friendly design based on graphical pre- and postprocessing capabilities. It has educational features for teaching and learning structural mechanics, and finite element analysis through graphical simulation. It is widely used in college-level courses related to structural mechanics and finite element methods.
The Sarma method is a method used primarily to assess the stability of soil slopes under seismic conditions. Using appropriate assumptions the method can also be employed for static slope stability analysis. It was proposed by Sarada K. Sarma in the early 1970s as an improvement over the other conventional methods of analysis which had adopted numerous simplifying assumptions.

Flexcom is a finite element analysis software package used in the offshore oil and gas and marine renewable energy industries. An educational version is also available for universities.

Ernest Hinton was a British civil engineer and engineering professor. He was born in Liverpool, England in 1946 and was educated at University of Wales Swansea. After receiving the BSc (1967), MSc (1968) and PhD (1971) at Swansea he joined the faculty of the Department of Civil Engineering where served until his death in 1999.

René de Borst is a Dutch civil engineer who is known for his work on computational mechanics and fracture mechanics. Since January 2016 he is the Centenary Professor of Civil Engineering at the University of Sheffield.

Medhat Haroun was an Egyptian-American expert on earthquake engineering. He wrote more than 300 technical papers and received the Charles Martin Duke Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Award (2006) and the Walter Huber Civil Engineering Research Prize (1992) from the American Society of Civil Engineers.

Plaxis is a computer program that performs finite element analyses (FEA) within the realm of geotechnical engineering, including deformation, stability and water flow. The input procedures enable the enhanced output facilities provide a detailed presentation of computational results. PLAXIS enables new users to work with the package after only a few hours of training.
FEATool Multiphysics is a physics, finite element analysis (FEA), and partial differential equation (PDE) simulation toolbox. FEATool Multiphysics features the ability to model fully coupled heat transfer, fluid dynamics, chemical engineering, structural mechanics, fluid-structure interaction (FSI), electromagnetics, as well as user-defined and custom PDE problems in 1D, 2D (axisymmetry), or 3D, all within a graphical user interface (GUI) or optionally as script files. FEATool has been employed and used in academic research, teaching, and industrial engineering simulation contexts.

Magd Abdel Wahab is a Belgian academic, researcher, author and Imam of Islam. He is full professor and chair of applied mechanics at Ghent University, Belgium, where he is also the Head of Finite Element Modelling Research Group of Laboratory Soete.