
Masonry is the craft of building a structure with brick, stone, or similar material, including mortar plastering which are often laid in, bound, and pasted together by mortar. The term masonry can also refer to the building units themselves.

Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used.
AutoLISP is a dialect of the programming language Lisp built specifically for use with the full version of AutoCAD and its derivatives, which include AutoCAD Map 3D, AutoCAD Architecture and AutoCAD Mechanical. Neither the application programming interface (API) nor the interpreter to execute AutoLISP code is included in the AutoCAD LT product line. A subset of AutoLISP functions is included in the browser-based AutoCAD web app.
Autodesk, Inc. is an American multinational software corporation that provides software products and services for the architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, media, education, and entertainment industries. Autodesk is headquartered in San Francisco, California, and has offices worldwide. Its U.S. offices are located in the states of California, Oregon, Colorado, Texas, Michigan, New Hampshire and Massachusetts. Its Canada offices are located in the provinces of Ontario, Quebec, and Alberta.
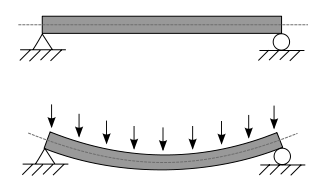
A beam is a structural element that primarily resists loads applied laterally across the beam's axis. Its mode of deflection is primarily by bending, as loads produce reaction forces at the beam's support points and internal bending moments, shear, stresses, strains, and deflections. Beams are characterized by their manner of support, profile, equilibrium conditions, length, and material.

In engineering, a foundation is the element of a structure which connects it to the ground or more rarely, water, transferring loads from the structure to the ground. Foundations are generally considered either shallow or deep. Foundation engineering is the application of soil mechanics and rock mechanics in the design of foundation elements of structures.

A curtain wall is an exterior covering of a building in which the outer walls are non-structural, instead serving to protect the interior of the building from the elements. Because the curtain wall façade carries no structural load beyond its own dead load weight, it can be made of lightweight materials. The wall transfers lateral wind loads upon it to the main building structure through connections at floors or columns of the building.
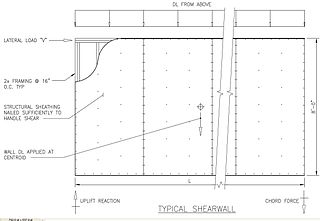
In structural engineering, a shear wall is a two-dimensional vertical element of a system that is designed to resist in-plane lateral forces, typically wind and seismic loads.

Steel frame is a building technique with a "skeleton frame" of vertical steel columns and horizontal I-beams, constructed in a rectangular grid to support the floors, roof and walls of a building which are all attached to the frame. The development of this technique made the construction of the skyscraper possible. Steel frame has displaced its predecessor, the iron frame, in the early 20th century.

A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths. A pile or piling is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven or drilled deep into the ground at the building site.
Tekla Structures is a building information modeling software able to model structures that incorporate different kinds of building materials, including steel, concrete, timber and glass. Tekla allows structural drafters and engineers to design a building structure and its components using 3D modeling, generate 2D drawings and access building information. Tekla Structures was formerly known as Xsteel.

A steel plate shear wall (SPSW) consists of steel infill plates bounded by boundary elements.

Structural engineering depends on the knowledge of materials and their properties, in order to understand how different materials resist and support loads.
STAAD or (STAAD.Pro) is a structural analysis and design software application originally developed by Research Engineers International (REI) in 1997. In late 2005, Research Engineers International was bought by Bentley Systems. STAAD stands for STructural Analysis And Design.
The applied element method (AEM) is a numerical analysis used in predicting the continuum and discrete behavior of structures. The modeling method in AEM adopts the concept of discrete cracking allowing it to automatically track structural collapse behavior passing through all stages of loading: elastic, crack initiation and propagation in tension-weak materials, reinforcement yield, element separation, element contact and collision, as well as collision with the ground and adjacent structures.
The PLPAK developers, BE4E, describe it as "The PLPAK is special purpose software package for structural analysis of building slabs and foundations based on the Boundary Element Method". The PLPAK uses the shear-deformable plate bending theory according to Reissner.
PROKON Structural Analysis and Design is a suite of commercial software for structural analysis and design. PROKON software is produced by Irish company Prokon Software Limited.
This glossary of structural engineering terms pertains specifically to structural engineering and its sub-disciplines. Please see glossary of engineering for a broad overview of the major concepts of engineering.
cadwork informatik CI AG is a multinational software company headquartered in Basel, Switzerland. It develops and markets software products primarily for the construction industry. These products include timber industry products in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) as well as products in building information model (BIM) and virtual design and construction (VDC). These products are suitable for designers, structural engineers, construction engineers, civil engineering draftspeople, building contractors, and in the case of BIMTeam VDC, the construction crews.











