
Dalea searlsiae, commonly known as Searls' prairie clover, is a perennial legume species belonging to the Dalea genus. The species is found through arid regions of the southwestern United States and can survive in low moisture conditions. The species forms symbiotic relationships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria that can improve soil nutrient levels. Its large inflorescence attracts many species of pollinators, and it lacks toxins found in similar legume species. As a result, the species has been considered for use in rangeland restoration and revegetation projects.

Sophora chrysophylla, known as māmane in Hawaiian, is a species of flowering plant in the pea and bean family, Fabaceae, that is endemic to Hawaii. It is highly polymorphic, growing as a shrub or tree, and able to reach a height of 15 m (49 ft) in tree form. Yellow flowers are produced in winter and spring.

The palila is a critically endangered finch-billed species of Hawaiian honeycreeper. It has a golden-yellow head and breast, with a light belly, gray back, and greenish wings and tail. The bird has a close ecological relationship with the māmane tree, and became endangered due to destruction of the trees and accompanying dry forests. The first specimen of the palila was collected in 1876 at the Greenwell Ranch on the Big Island by Pierre Étienne Théodore Ballieu (1828–1885), who was French consul in Hawai‘i from 1869 to 1878. The type specimen is housed at the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle in Paris.

Dalea is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. Members of the genus are commonly known as prairie clover or indigo bush. Its name honors English apothecary Samuel Dale (1659–1739). They are native to the New World, where they are distributed from Canada to Argentina. Nearly half of the known species are endemic to Mexico. Two species of Dalea have been considered for rangeland restoration.

The statue of Queen Victoria by Joseph Edgar Boehm stands on College Green, Bristol, England. It is Grade II listed.
Dalea humifusa is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in Ecuador. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry shrubland.
Dalea jamesonii is a species of legume in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in Ecuador. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical dry shrubland.

The Hawaiʻi ʻamakihi, also known as the common ʻamakihi, is a species of Hawaiian honeycreeper.

Hibiscadelphus hualalaiensis is a species of flowering plant in the mallow family, Malvaceae, that is endemic to the Big Island of Hawaii. The last known plant died in 1992, making it most likely extinct in the wild; any remaining plants are threatened by habitat loss. It inhabits dry and mixed mesic forests on the slopes of Hualālai at elevations of 915–1,020 m (3,002–3,346 ft). Associated plants include ʻōhiʻa lehua, lama, māmane, naio, ʻālaʻa, pāpala, ʻaiea, poʻolā, and Kikuyu Grass. H. hualalaiensis is a small tree, reaching a height of 5–7 m (16–23 ft) and trunk diameter of 30 cm (12 in).

Kokia drynarioides, commonly known as Hawaiian tree cotton, is a species of flowering plant in the mallow family, Malvaceae, that is endemic to the Big Island of Hawaii. It inhabits dry forests at elevations of 455–1,915 m (1,493–6,283 ft). Associated plants include ʻāheahea, ʻaʻaliʻi, hala pepe, wiliwili, uhiuhi, kōlea, ʻaiea, kuluʻī, ʻālaʻa, ʻohe kukuluāeʻo, māmane, and maua. It is threatened by habitat loss and competition with invasive species, such as Fountain Grass.
Dracaena konaensis, synonym Pleomele hawaiiensis, the Hawaiʻi hala pepe, is a rare species of flowering plant that is endemic to the island of Hawaiʻi in the state of Hawaii.

Psorothamnus is a genus of plants in the legume family. These are shrubs and small trees. Many are known by the general common name indigo bush. Some are referred to as daleas, as this genus was once included in genus Dalea. These are generally thorny, thickly branched, strongly scented bushes. Most species bear lupinlike raceme inflorescences of bright purple legume flowers and gland-rich pods. Psorothamnus species are native to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The genus is paraphyletic and it has been proposed that the genus Psorodendron be reinstated to accommodate sections Xylodalea, Capnodendron, and Winnemucca.

The great Maui rail or great Maui crake is an extinct bird species from Maui, one of two flightless rails which survived on Maui until people arrived in 150 C.E.

Zerene cesonia, the southern dogface, is a North and South American butterfly in the family Pieridae, subfamily Coliadinae.

Dalea foliosa, commonly called leafy prairie clover, is a species of flowering plant in the legume family (Fabaceae). It is an endangered species in the United States, where it occurs in three states: Illinois, Tennessee, and Alabama.

Psorothamnus polydenius is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common names Nevada dalea and Nevada indigobush. It is native to the deserts of the southwestern United States from the Mojave Desert in California to Utah.

Dalea purpurea is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known as purple prairie clover. Native to central north America, purple prairie clover is a relatively common member of the Great Plains and prairie ecosystems. It blooms in the summer with dense spikes of bright purple flowers that attract many species of insects.

Chrysolepis chrysophylla is a species of flowering shrub or tree in the beech family known by the common names golden chinquapin, giant chinquapin, and western chinquapin. It is native to the Pacific coast of the United States.

The Hawaiʻi ʻelepaio, also Hawaiian ʻelepaio, is a monarch flycatcher found on the Big Island of Hawaii. Until 2010, all three ʻelepaio species, the Kauaʻi ʻelepaio, the Oʻahu ʻelepaio and this species were considered conspecific.
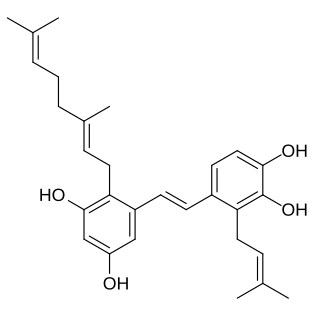
Pawhuskin A is a naturally occurring prenylated stilbene isolated from Dalea purpurea which acts as a competitive silent antagonist of the κ-, μ-, and δ-opioid receptors. The compound was named after Pawhuska, Oklahoma, a place near where the samples of Dalea purpurea that led to its discovery were taken from. Other isolates of the plant with affinity for opioid receptors include Pawhuskin B and Pawhuskin C, though these compounds produce comparatively weak opioid receptor displacement relative to Pawhuskin A. Dalea purpurea was used in traditional Native American medicine to treat various ailments, and pawhuskin A and related isolates may be some of the constituents of the plant which underlay this use.

















