
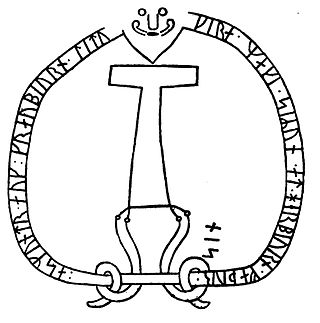
Runestone DR 120, MJy 51, known as Spentrup stone 2 and the Jennum stone, is a Viking Age runestone engraved with the Younger Futhark and a Thor's hammer.

Runestone DR 120, MJy 51, known as Spentrup stone 2 and the Jennum stone, is a Viking Age runestone engraved with the Younger Futhark and a Thor's hammer.
The runestone was first mentioned by 18th-century scholar Søren Abildgaard, who wrote that it was found at the end of a stone bridge in the village of Jennum. It was lost for a long time until it was rediscovered in 1913, but by then it had been split into seven pieces. It was repaired and raised at the museum in the town of Randers. [1] [2] In the 1960s it was transferred to the new Museum Østjylland , during which it broke into 14 or 15 pieces; it has been restored. [2]
The stone is granite, with a memorial inscription in the Younger Futhark in the RAK style, dated to 970-1020 [2] or to 1000–1050. [3] The top of the stone, including part of the inscription band, is missing. [4]
The stone shows one of several pictorial representations of Thor's hammer, following the last punctuation mark (x) at the end of the inscription on the left; [3] it resembles a cross or hammer on the front of the Karlevi Runestone, Öl 1. [4] Other stones with Thor's hammer include DR 26, VG 113, Sö 86 and Sö 111. [5]
oskatla
Askatla
×
risþi
resþi
(×)
-…
…
…-ls
…[gi]sl,
×
sbaka
Spaka
×
sun
sun,
×
stin
sten
×
¶
þonsi
þænsi.
×
⁓
Áskatla raised this stone … …-gísl, Spaki's son. [3]

The Stone of Eric, listed as DR 1 in the Rundata catalog, is a memorial runestone that was found in Northern Germany. This area was part of Denmark during the Viking Age.

The Glavendrup stone, designated as DR 209 by Rundata, is a runestone on the island of Funen in Denmark and dates from the early 10th century. It contains Denmark's longest runic inscription and ends in a curse.

The Hällestad Runestones are three runestones located in the walls of Hällestad Church in Torna-Hällestad, about 20 kilometers east of Lund in Skåne, southern Sweden. Their Rundata identifiers are DR 295, 296, and 297. DR 295 is notable because it is held to be raised in memory of a warrior who fell in the legendary Battle of the Fýrisvellir, near Uppsala, Sweden between the Jomsvikings led by Styrbjörn the Strong and Styrbjörn's uncle Eric the Victorious, the king of Sweden, c. 985. The other stones were raised by the same people, and they probably formed a monument together in memory of comrades lost in the battle. The Karlevi Runestone, the Egtved Runestone and the Sjörup Runestone may be connected to them.
Sö 86 is the Rundata catalog number for a Viking Age memorial runic inscription located in Åby, which is about one kilometer north of Ålberga, Södermanland County, Sweden, and in the historic province of Södermanland. The inscription features a depiction of the hammer of the Norse pagan god Thor named Mjöllnir and a facial mask.

The Dagstorp Runestone, designated as DR 325 in the Rundata catalog, is a Viking Age memorial runestone that was discovered at Dagstorp, which is about two kilometers northwest of Kävlinge, Scania, Sweden.

The Sønder Kirkeby Runestone, listed as runic inscription DR 220 in the Rundata catalog, is a Viking Age memorial runestone that was discovered in Sønder Kirkeby, which is located about 5 kilometers east of Nykøbing Falster, Denmark.

The Skern Runestone, designated as Danish Runic Inscription 81 or DR 81 in the Rundata catalog, is a Viking Age memorial runestone located in the small village of Skjern, Denmark between Viborg and Randers. The stone features a facial mask and a runic inscription which ends in a curse. A fragment of a second runestone designated as DR 80 was also found in Skjern.

The Bjäresjö Runestones are three Viking Age memorial runestones originally located adjacent to Bjäresjö Church in Bjäresjö, which is about 3 kilometers northwest of Ystad, Skåne County, Sweden. Two of the stones were discovered near the church, and two of the stones have been moved to other nearby locations. Although these three stones are located in Sweden, they have been given Danish designations because Scania was part of the historic Denmark.

The Fölene Runestones are two Viking Age memorial runestones which are located near the church in Fölene, which is about 2 km (1.2 mi) west of Herrljunga, Västra Götaland County, Sweden, which was in the historic province of Västergötland. The stones are memorials to two men who were described as holding the title drengr.
The Bjärby Runestones are two Viking Age memorial runestones located near Grästorp, Sweden, in Bjärby synod, which was in the historic province of Västergötland. The two stones are memorials to men who held the titles thegn and drengr, and one has a depiction of the hammer of the Norse pagan deity Thor.

Danish Runic Inscription 48 or DR 48 is the Rundata catalog number for a Viking Age memorial runestone from Hanning, which is about 8 km north of Skjern, Denmark. The runic inscription features a depiction of a hammer, which some have interpreted as a representation of the Norse pagan god Thor, although this interpretation is controversial.

Danish Runic Inscription 107 or DR 107 is the Rundata listing for a Viking Age memorial runestone that was found at Egå, Denmark.

The Västra Nöbbelöv Runestone, listed as DR 278 in the Rundata catalog, is a Viking Age memorial runestone located in Västra Nöbbelöv, which is about 3 kilometers east of Skivarp, Skåne County, Sweden, and was in the historic province of Scania.

The Læborg or Laeborg Runestone, listed as DR 26 in the Rundata catalog, is a Viking Age memorial runestone located outside of the village hall or Forsamlinghus in Læborg, which is about 3 kilometers north of Vejen, Denmark. The stone includes two depictions of the hammer of the Norse pagan god Thor.

The Ålum Runestones are four Viking Age memorial runestones which are located at the church in Ålum, which is 9 km west of Randers, Denmark. One of the stones refers to a man with the title drengr and two of the other stones were raised by the same family.

The Asferg Runestone, listed as DR 121 in the Rundata catalog, is a Viking Age memorial runestone found at Asferg, which is about 10 km northeast of Randers, Aarhus County, Region Midtjylland, Denmark.

DR 110, or the Virring stone, is a runestone made of granite that measures 155 cm (61 in) in height, 120 cm (47 in) in width and 27 cm (11 in) in thickness. It is written in Old East Norse in the Younger Futhark, and the runestone style is in a form called RAK.

The Sønder Vinge stone 2 or DR 83 is a Viking Age runestone engraved in Old Norse with the Younger Futhark runic alphabet. The stone is in granite and was discovered in 1866 as a corner stone of Sønder Vinge Church, positioned with the runic inscription outwards. It is presently located in the porch of the church. It is probably from the period 970-1020 due to runic and linguistic features. It is 180 cm tall, 132 cm wide and 35 cm thick. Parts of the runic inscription have eroded which makes some runes hard to read. The style of the runestone is the runestone style RAK.
The Tvorup/Torup stone or DR 154 † was a Viking Age runestone engraved in Old Norse with the Younger Futhark runic alphabet, which has disappeared. According to Skonvig the stone would have been located just inside the door of church of Torup, having been moved there from a mound east of the church. The stone must have been lost while being transported to Copenhagen because nothing more is known about it. Skonvig reported that the stone was 2.5 Danish ells high and 1 ell wide. It was made by the same runemaster who made DR 155, and Lerche Nielsen (2010:244f) suggests that the two stones may actually be the same stone. The stone is dated to the period 970–1020, and the style of the runestone was the runestone style RAK.

The Fuglie stone 1 or DR 259 is a Viking Age runestone engraved in Old Norse with the Younger Futhark runic alphabet. It was first mentioned by Skonvig and it is still located in its original location on a Nordic Bronze Age mound next to the church of Fuglie, Skåne, Sweden. There are many local legends and traditions about the stone. The stone is 105 cm tall, 63 cm wide, and 33 cm thick. The stone is dated to the period 970–1020, and the style of the runestone was the runestone style RAK.