
Dartmouth is a built-up community of Halifax Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia, Canada. Located on the eastern shore of Halifax Harbour, Dartmouth has 72,139 residents as of 2021.

Citadel Hill is a hill that is a National Historic Site in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. Four fortifications have been constructed on Citadel Hill since the city was founded by the English in 1749, and were referred to as Fort George—but only the third fort was officially named Fort George. According to General Orders of October 20, 1798, it was named after King George III. The first two and the fourth and current fort, were officially called the Halifax Citadel. The last is a concrete star fort.

On the morning of 6 December 1917, the French cargo ship SS Mont-Blanc collided with the Norwegian vessel SS Imo in the harbour of Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. Mont-Blanc, laden with high explosives, caught fire and exploded, devastating the Richmond district of Halifax. At least 1,782 people were killed, largely in Halifax and Dartmouth, by the blast, debris, fires, or collapsed buildings, and an estimated 9,000 others were injured. The blast was the largest human-made explosion at the time. It released the equivalent energy of roughly 2.9 kilotons of TNT (12 TJ).

Halifax is the capital and most populous municipality of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, and the most populous municipality in Atlantic Canada. As of 2023, it is estimated that the population of the Halifax CMA was 518,711, with 348,634 people in its urban area. The regional municipality consists of four former municipalities that were amalgamated in 1996: Halifax, Dartmouth, Bedford, and Halifax County.

Irving Oil Ltd. is a Canadian privately-owned intergenerational gasoline, oil, and natural gas producing and exporting company, a subsidiary of the parent company Irving Group of Companies,—one of the largest "private conglomerates" in North America. Irving Oil was one established in 1924 by Canadian oil baron and billionaire, Kenneth "K.C." Irving, whose family fortune when he died in 1992 was estimated by Forbes at USD$5 billion. His son, Arthur, became chairman and president of Irving Oil. Arthur Irving died in 2024

Eastern Passage is an unincorporated suburban community in Halifax Regional Municipality Nova Scotia, Canada.

Canadian Forces Base (CFB) Halifax is Canada's east coast naval base and home port to the Royal Canadian Navy Atlantic fleet, known as Canadian Fleet Atlantic (CANFLTLANT), that forms part of the formation Maritime Forces Atlantic (MARLANT).
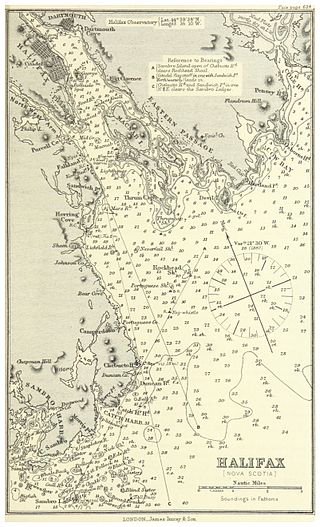
Halifax Harbour is a large natural harbour on the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia, Canada, located in the Halifax Regional Municipality. Halifax largely owes its existence to the harbour, being one of the largest and deepest ice-free natural harbours in the world. Before Confederation it was one of the most important commercial ports on the Atlantic seaboard. In 1917, it was the site of the world's largest man-made accidental explosion, when the SS Mont-Blanc blew up in the Halifax Explosion on December 6.

The Port of Halifax comprises various port facilities in Halifax Harbour in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. It covers 10 km2 (3.9 sq mi) of land, and looks after 150 km2 (58 sq mi) of water.

Halifax Transit is a Canadian public transport service operating buses and ferries in Halifax, Nova Scotia. Founded as Metro Transit in March 1981, the agency runs two ferry routes, 66 conventional bus routes, three regional express routes, and three rural routes. Halifax Transit also operates Access-a-Bus, a door-to-door paratransit service for senior and disabled citizens.

The Eastern Shore is a region of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It is the Atlantic coast running northeast from Halifax Harbour to the eastern end of the peninsula at the Strait of Canso.
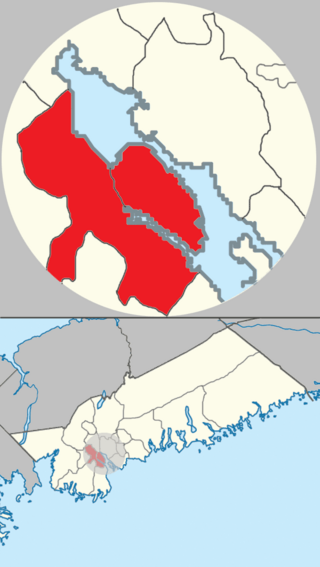
The community of Halifax, Nova Scotia was created on 1 April 1996, when the City of Dartmouth, the City of Halifax, the Town of Bedford, and the County of Halifax amalgamated and formed the Halifax Regional Municipality. The former City of Halifax was dissolved, and transformed into the Community of Halifax within the municipality.

Petroleum production in Canada is a major industry which is important to the overall economy of North America. Canada has the third largest oil reserves in the world and is the world's fourth largest oil producer and fourth largest oil exporter. In 2019 it produced an average of 750,000 cubic metres per day (4.7 Mbbl/d) of crude oil and equivalent. Of that amount, 64% was upgraded from unconventional oil sands, and the remainder light crude oil, heavy crude oil and natural-gas condensate. Most of the Canadian petroleum production is exported, approximately 600,000 cubic metres per day (3.8 Mbbl/d) in 2019, with 98% of the exports going to the United States. Canada is by far the largest single source of oil imports to the United States, providing 43% of US crude oil imports in 2015.

Woodside is an unincorporated middle income urban locality of Dartmouth, within the Halifax Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia. The community is divided into North Woodside and South Woodside. Woodside is home to two hospitals: the Dartmouth General Hospital and the Nova Scotia Hospital.
Imperoyal is a small neighbourhood on the eastern side of Halifax Harbour in the community of Dartmouth, Nova Scotia. The area is mostly taken up by the former Dartmouth Refinery and by petroleum storage and transfer facility owned by Irving Oil Limited. A book on the topic is written by John D. Hartley entitled Imperoyal Village.
The Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM) is a major generator of economic activity in Atlantic Canada.

National Iranian Oil Refining and Distribution Company (NIORDC) is part of the Ministry of Petroleum of Iran. NIORDC was established on 8 March 1991 and undertook to perform all operations relating to refining and distribution of oil products.

The Halifax Shipyard Limited is a Canadian shipbuilding company located in Halifax, Nova Scotia.

Fort Clarence was a British coastal fort built in 1754 at the beginning of the French and Indian War in Dartmouth, Nova Scotia, Canada. The battery was built on the grant of Capt. John Rous. Governor Edward Cornwallis’ principal engineer John Brewse designed the fort which was 35 to 40 feet above sea level - at the start there was a small battery of seven 12-pounder smooth bore cannon. In spring 1759, a Mi'kmaq attack on the Eastern Battery killed five soldiers.

The Halifax–Dartmouth Ferry is the oldest saltwater ferry in North America, and the second oldest in the world. Today the service is operated by Halifax Transit and links Downtown Halifax with two locations, Alderney Landing and Woodside, in Dartmouth, NS.


















