Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others. The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all pesticide use globally. Most pesticides are used as plant protection products, which in general protect plants from weeds, fungi, or insects. In general, a pesticide is a chemical or biological agent that deters, incapacitates, kills, or otherwise discourages pests. Target pests can include insects, plant pathogens, weeds, molluscs, birds, mammals, fish, nematodes (roundworms), and microbes that destroy property, cause nuisance, or spread disease, or are disease vectors. Along with these benefits, pesticides also have drawbacks, such as potential toxicity to humans and other species.
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with formula CH3Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is produced both industrially and biologically. It is a recognized ozone-depleting chemical. It was used extensively as a pesticide until being phased out by most countries in the early 2000s. From a chemistry perspective, it is one of the halomethanes.

Fumigation is a method of pest control or the removal of harmful microorganisms by completely filling an area with gaseous pesticides, or fumigants, to suffocate or poison the pests within. It is used to control pests in buildings, soil, grain, and produce. Fumigation is also used during the processing of goods for import or export to prevent the transfer of exotic organisms.
Demeton-S-methyl is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H15O3PS2. It was used as an organothiophosphate acaricide and organothiophosphate insecticide. It is flammable. With prolonged storage, Demeton-S-methyl becomes more toxic due to formation of a sulfonium derivative which has greater affinity to the human form of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, and this may present a hazard in agricultural use.
Chloropicrin, also known as PS and nitrochloroform, is a chemical compound currently used as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial, fungicide, herbicide, insecticide, and nematicide. It was used as a poison gas in World War I and the Russian military has been accused of using it in the Russo-Ukrainian War. Its chemical structural formula is Cl3C−NO2.

Fipronil is a broad-spectrum insecticide that belongs to the phenylpyrazole insecticide class. Fipronil disrupts the insect central nervous system by blocking the ligand-gated ion channel of the GABAA receptor and glutamate-gated chloride (GluCl) channels. This causes hyperexcitation of contaminated insects' nerves and muscles. Fipronil's specificity towards insects is believed to be due to its greater binding affinity for the GABAA receptors of insects than to those of mammals, and for its action on GluCl channels, which do not exist in mammals. As of 2017, there does not appear to be significant resistance among fleas to fipronil.
Iodomethane, also called methyl iodide, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH3I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by an atom of iodine. It is naturally emitted in small amounts by rice plantations. It is also produced in vast quantities estimated to be greater than 214,000 tons annually by algae and kelp in the world's temperate oceans, and in lesser amounts on land by terrestrial fungi and bacteria. It is used in organic synthesis as a source of methyl groups.

Methyl isothiocyanate is the organosulfur compound with the formula CH3N=C=S. This low melting colorless solid is a powerful lachrymator. As a precursor to a variety of valuable bioactive compounds, it is the most important organic isothiocyanate in industry.
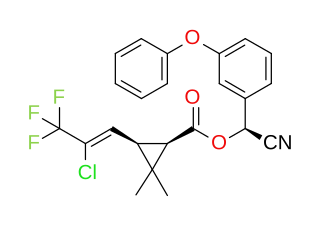
Cyhalothrin is an organic compound that, in specific isomeric forms, is used as a pesticide. It is a pyrethroid, a class of synthetic insecticides that mimic the structure and properties of the naturally occurring insecticide pyrethrin which is present in the flowers of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium. Pyrethroids, such as cyhalothrin, are often preferred as an active ingredient in agricultural insecticides because they are more cost-effective and longer acting than natural pyrethrins. λ-and γ-cyhalothrin are now used to control insects and spider mites in crops including cotton, cereals, potatoes and vegetables.

The environmental effects of pesticides describe the broad series of consequences of using pesticides. The unintended consequences of pesticides is one of the main drivers of the negative impact of modern industrial agriculture on the environment. Pesticides, because they are toxic chemicals meant to kill pest species, can affect non-target species, such as plants, animals and humans. Over 98% of sprayed insecticides and 95% of herbicides reach a destination other than their target species, because they are sprayed or spread across entire agricultural fields. Other agrochemicals, such as fertilizers, can also have negative effects on the environment.

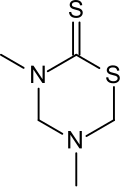
Metam sodium is an organosulfur compound with the formula CH3NHCS2Na. The compound is a sodium salt of a dithiocarbamate. The compound exists as a colorless dihydrate, but most commonly it is encountered as an aqueous solution. It is used as a soil fumigant, pesticide, herbicide, and fungicide. It is one of the most widely used pesticides in the United States, with approximately 60 million pounds used in 2001.

Etofenprox is a pyrethroid derivative which is used as an insecticide. Mitsui Chemicals Agro Inc. is the main manufacturer of the chemical. It is also used as an ingredient in flea medication for cats and dogs.
This is an index of articles relating to pesticides.

Acetamiprid is an organic compound with the chemical formula C10H11ClN4. It is an odorless neonicotinoid insecticide produced under the trade names Assail, and Chipco by Aventis CropSciences. It is systemic and intended to control sucking insects (Thysanoptera, Hemiptera, mainly aphids) on crops such as leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, pome fruits, grapes, cotton, cole crops, and ornamental plants. It is also a key pesticide in commercial cherry farming due to its effectiveness against the larvae of the cherry fruit fly.

The California Department of Pesticide Regulation, also known as DPR or CDPR, is one of six boards and departments of the California Environmental Protection Agency (Cal/EPA).

Thiamethoxam is the ISO common name for a mixture of cis-trans isomers used as a systemic insecticide of the neonicotinoid class. It has a broad spectrum of activity against many types of insects and can be used as a seed dressing.

Tefluthrin is the ISO common name for an organic compound that is used as a pesticide. It is a pyrethroid, a class of synthetic insecticides that mimic the structure and properties of the naturally occurring insecticide pyrethrin which is present in the flowers of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium. Pyrethroids such as tefluthrin are often preferred as active ingredients in agricultural insecticides because they are more cost-effective and longer acting than natural pyrethrins. It is effective against soil pests because it can move as a vapour without irreversibly binding to soil particles: in this respect it differs from most other pyrethroids.

Etridiazole is a fungicide and pesticide used for prevention of pythium ultimum on cotton plants.

Fenpropathrin, or fenopropathrin, is a widely used pyrethroid insecticide in agriculture and household. Fenpropathrin is an ingestion and contact synthetic pyrethroid. Its mode of action is similar to other natural (pyrethrum) and synthetic pyrethroids where in they interfere with the kinetics of voltage gated sodium channels causing paralysis and death of the pest. Fenpropathrin was the first of the light-stable synthetic pyrethroids to be synthesized in 1971, but it was not commercialized until 1980. Like other pyrethroids with an α-cyano group, fenpropathrin also belongs to the termed type II pyrethroids. Type II pyrethroids are a more potent toxicant than type I in depolarizing insect nerves. Application rates of fenpropathrin in agriculture according to US environmental protection agency (EPA) varies by crop but is not to exceed 0.4 lb ai/acre.
Biofumigation is a method of pest control in agriculture, a variant of fumigation where the gaseous active substance—fumigant—is produced by decomposition of plant material freshly chopped and buried in the soil for this purpose.