N,N-Dimethylaniline (DMA) is an organic chemical compound, a substituted derivative of aniline. It consists of a tertiary amine, featuring dimethylamino group attached to a phenyl group. This oily liquid is colourless when pure, but commercial samples are often yellow. It is an important precursor to dyes such as crystal violet.
Acrylates are the salts, esters, and conjugate bases of acrylic acid. The acrylate ion is the anion CH2=CHCO−2. Often, acrylate refers to esters of acrylic acid, the most common member being methyl acrylate. These acrylates contain vinyl groups. These compounds are of interest because they are bifunctional: the vinyl group is susceptible to polymerization and the carboxylate group carries myriad functionalities.
Methylamine is an organic compound with a formula of CH3NH2. This colorless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one hydrogen atom being replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine.

Allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) is an organosulfur compound (formula CH2CHCH2NCS). The colorless oil is responsible for the pungent taste of mustard, radish, horseradish, and wasabi. This pungency and the lachrymatory effect of AITC are mediated through the TRPA1 and TRPV1 ion channels. It is slightly soluble in water, but more soluble in most organic solvents.

In organic chemistry, sulfonic acid refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula R−S(=O)2−OH, where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the S(=O)2(OH) group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent, it is known as a sulfo group. A sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. The parent compound is the parent sulfonic acid, HS(=O)2(OH), a tautomer of sulfurous acid, S(=O)(OH)2. Salts or esters of sulfonic acids are called sulfonates.
Benzyl chloride, or α-chlorotoluene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH2Cl. This colorless liquid is a reactive organochlorine compound that is a widely used chemical building block.
Chlorotoluene is a group of three isomeric chemical compounds. They consist of a disubstituted benzene ring with one chlorine atom and one methyl group.
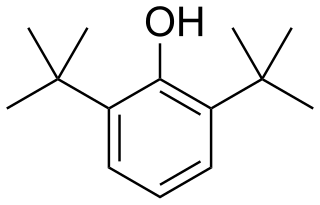
2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol is an organic compound with the structural formula 2,6-((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH. This colorless solid alkylated phenol and its derivatives are used industrially as UV stabilizers and antioxidants for hydrocarbon-based products ranging from petrochemicals to plastics. Illustrative of its usefulness, it prevents gumming in aviation fuels.

Allylamine is an organic compound with the formula C3H5NH2. This colorless liquid is the simplest stable unsaturated amine.

Methyl vinyl ketone (MVK, IUPAC name: butenone) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH=CH2. It is a reactive compound classified as an enone, in fact the simplest example thereof. It is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic liquid with a pungent odor. It is soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It is a useful intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds.

Crotonaldehyde is a chemical compound with the formula CH3CH=CHCHO. The compound is usually sold as a mixture of the E- and Z-isomers, which differ with respect to the relative position of the methyl and formyl groups. The E-isomer is more common (data given in Table is for the E-isomer). This lachrymatory liquid is moderately soluble in water and miscible in organic solvents. As an unsaturated aldehyde, crotonaldehyde is a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis. It occurs in a variety of foodstuffs, e.g. soybean oils.
Acetone cyanohydrin (ACH) is an organic compound used in the production of methyl methacrylate, the monomer of the transparent plastic polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), also known as acrylic. It liberates hydrogen cyanide easily, so it is used as a source of such. For this reason, this cyanohydrin is also highly toxic.

Durene, or 1,2,4,5-tetramethylbenzene, is an organic compound with the formula C6H2(CH3)4. It is a colourless solid with a sweet odor. The compound is classified as an alkylbenzene. It is one of three isomers of tetramethylbenzene, the other two being prehnitene (1,2,3,4-tetramethylbenzene) and isodurene (1,2,3,5-tetramethylbenzene). Durene has an unusually high melting point (79.2 °C), reflecting its high molecular symmetry.

Methyl acrylate is an organic compound, more accurately the methyl ester of acrylic acid. It is a colourless liquid with a characteristic acrid odor. It is mainly produced to make acrylate fiber, which is used to weave synthetic carpets. It is also a reagent in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical intermediates. Owing to the tendency of methyl acrylate to polymerize, samples typically contain an inhibitor such as hydroquinone.
In chemistry, carbonylation refers to reactions that introduce carbon monoxide (CO) into organic and inorganic substrates. Carbon monoxide is abundantly available and conveniently reactive, so it is widely used as a reactant in industrial chemistry. The term carbonylation also refers to oxidation of protein side chains.

1-Methylimidazole or N-methylimidazole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula CH3C3H3N2. It is a colourless liquid that is used as a specialty solvent, a base, and as a precursor to some ionic liquids. It is a fundamental nitrogen heterocycle and as such mimics for various nucleoside bases as well as histidine and histamine.

Metam sodium is an organosulfur compound with the formula CH3NHCS2Na. The compound is a sodium salt of a dithiocarbamate. The compound exists as a colorless dihydrate, but most commonly it is encountered as an aqueous solution. It is used as a soil fumigant, pesticide, herbicide, and fungicide. It is one of the most widely used pesticides in the United States, with approximately 60 million pounds used in 2001.

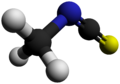
Methyl thiocyanate is an organic compound with the formula CH3SCN. The simplest member of the organic thiocyanates, it is a colourless liquid with an onion-like odor. It is produced by the methylation of thiocyanate salts. The compound is a precursor to the more useful isomer methyl isothiocyanate (CH3NCS).
4-Nitrotoluene or para-nitrotoluene is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4NO2. It is a pale yellow solid. It is one of three isomers of nitrotoluene.

Organic thiocyanates are organic compounds containing the functional group RSCN. the organic group is attached to sulfur: R−S−C≡N has a S–C single bond and a C≡N triple bond.