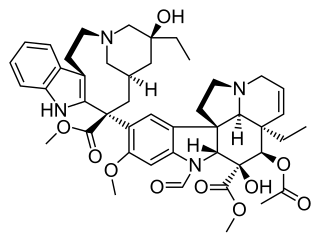
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and marketed under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin's disease, neuroblastoma, and small cell lung cancer among others. It is given intravenously.

Vinca is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, native to Europe, northwest Africa and southwest Asia. The English name periwinkle is shared with the related genus Catharanthus.

Catharanthus roseus, commonly known as bright eyes, Cape periwinkle, graveyard plant, Madagascar periwinkle, old maid, pink periwinkle, rose periwinkle, is a perennial species of flowering plant in the family Apocynaceae. It is native and endemic to Madagascar, but grown elsewhere as an ornamental and medicinal plant. It is a source of the drugs vincristine and vinblastine, used to treat cancer. It was formerly included in the genus Vinca as Vinca rosea.

Vinca alkaloids are a set of anti-mitotic and anti-microtubule alkaloid agents originally derived from the periwinkle plant Catharanthus roseus and other vinca plants. They block beta-tubulin polymerization in a dividing cell.
In enzymology, a desacetoxyvindoline 4-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.11.20) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.73) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Strictosidine synthase (EC 4.3.3.2) is an enzyme in alkaloid biosynthesis that catalyses the condensation of tryptamine with secologanin to form strictosidine in a formal Pictet–Spengler reaction:
In enzymology, a deacetylvindoline O-acetyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Ajmalicine, also known as δ-yohimbine or raubasine, is an antihypertensive drug used in the treatment of high blood pressure. It has been marketed under numerous brand names including Card-Lamuran, Circolene, Cristanyl, Duxil, Duxor, Hydroxysarpon, Iskedyl, Isosarpan, Isquebral, Lamuran, Melanex, Raunatin, Saltucin Co, Salvalion, and Sarpan. It is an alkaloid found naturally in various plants such as Rauvolfia spp., Catharanthus roseus, and Mitragyna speciosa.

Akuammicine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is found in the Apocynaceae family of plants including Picralima nitida, Vinca minor and the Aspidosperma.

Catharanthine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus and Tabernaemontana divaricata. Catharanthine is derived from strictosidine, but the exact mechanism by which this happens is currently unknown. Catharanthine is one of the two precursors that form vinblastine, the other being vindoline.

Vincoline is an alkaloid isolated from Catharanthus roseus. In a mouse model, it has been found to stimulate insulin secretion.

Tabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid found in the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus and also in the genus Voacanga. Tabersonine is hydroxylated at the 16 position by the enzyme tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (T16H) to form 16-hydroxytabersonine. The enzyme leading to its formation is currently unknown. Tabersonine is the first intermediate leading to the formation of vindoline one of the two precursors required for vinblastine biosynthesis.

16-Hydroxytabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the plant Catharanthus roseus. The metabolite is an intermediate in the formation of vindoline, a precursor needed for formation of the pharmaceutically valuable vinblastine and vincristine. 16-hydroxytabersonine is formed from the hydroxylation of tabersonine by tabersonine 16-hydroxylase (T16H). Tabersonine 16-O-methyltransferase (16OMT) methylates the hydroxylated 16 position to form 16-methoxytabersonine.

3-Hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by Catharanthus roseus. The metabolite is a substrate for 3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine N-methyltransferase (NMT) which transfers a methyl group to the nitrogen of the indole ring forming desacetoxyvindoline. The enzyme catalyzing the formation of 3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine from 16-methoxytabersonine is currently unknown, but is a result of hydration of the double bond connecting the 6 and 13 position carbons.
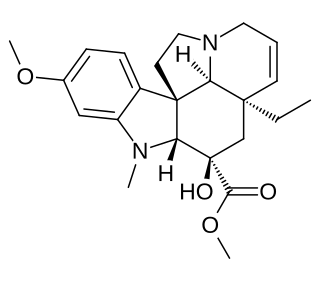
Desacetoxyvindoline is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the plant Catharanthus roseus. Desacetoxyvindoline is a product formed by the methylation of the nitrogen on the indole ring by the enzyme 3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine N-methyltransferase (NMT). The metabolite is a substrate for desacetoxyvindoline 4-hydroxylase (D4H) which catalyzes a hydroxylation to yield deacetylvindoline.

16-Methoxytabersonine is a terpene indole alkaloid produced by the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus. 16-methoxytabersonine is synthesized by methylation of the hydroxyl group at the 16 position of 16-hydroxytabersonine by tabersonine 16-O-methyltransferase (16OMT). The compound is a substrate for hydration by two concerted enzymes Tabersonine-3-Oxidase (T3O) and Tabersonine-3-Reductase (T3R), which leads to the formation of 3-hydroxy-16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine.

7-Deoxyloganic acid is an iridoid monoterpene. 7-Deoxyloganic acid is produced from 7-deoxyloganetic acid by the enzyme 7-deoxyloganetic acid glucosyltransferase (7-DLGT). The metabolite is a substrate for the enzyme 7-deoxyloganic acid hydroxylase (7-DLH) which synthesizes loganic acid.
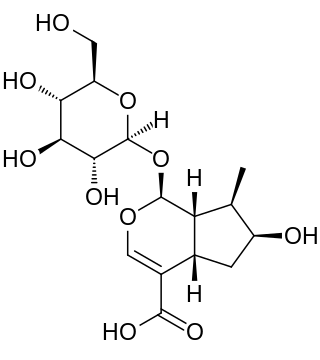
Loganic acid is an iridoid. Loganic acid is synthesized from 7-deoxyloganic acid by the enzyme 7-deoxyloganic acid hydroxylase (7-DLH). It is a substrate for the enzyme loganate O-methyltransferase for the production of loganin.














