
Delias belladonna, the hill Jezebel, is a medium-sized mountain butterfly of India and adjacent countries. It belongs to the family Pieridae, that is, the yellows and whites.

Delias is a genus of butterflies. There are about 250 species of the genus Delias, found in South Asia and Australia. The genus is considered to have its evolutionary origins in the Australian region.
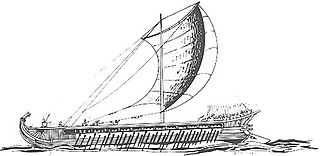
Athenian sacred ships were ancient Athenian ships, often triremes, which had special religious functions such as serving in sacred processions (theoria) or embassies or racing in boat races during religious festivals. The two most famous such ships were the Paralus and the Salaminia, which also served as the messenger ships of the Athenian government in the 5th and 4th centuries BC. Other notable ships included one possibly named the Delias, a triakonter believed to be the ship in which Theseus had sailed to Crete, and which was involved in several traditional theoria to Delos; the vessel was constantly repaired by replacing individual planks to keep it seaworthy while maintaining its identity as the same ship. After the reforms of Cleisthenes, a ship was named for each of the ten tribes that political leader had created; these ships may also have been sacred ships.

Delia flies are members of the Anthomyiidae family within the superfamily Muscoidae. The identification of different species of Delia can be very difficult for non-specialists as the diagnostic characteristics used for immature and/or female specimens may be inconsistent between species. Past taxonomic keys were not as comprehensive in their identification of Delia specimens; they were either too reliant on genetic characteristics, focused solely on a specific life stage, or were focused only on certain species. However current taxonomic keys aim to be more thorough by not only including morphological diagnostics for males, females, and immature specimens of various species, but also their genetic make-up or molecular barcode.

Abraxas, the magpie moths, is a genus of moths in the family Geometridae. It was first described by William Elford Leach in 1815.

Apithecia is a monotypic moth genus in the family Geometridae described by Prout in 1914. Its only species, Apithecia viridata, described by Frederic Moore in 1868, is found in India, Nepal, Bhutan, China and Taiwan.

Ambulyx is a genus of moths in the family Sphingidae, described by Westwood in 1847.
The Secret of the Sahara is an Italian television miniseries directed by Alberto Negrin and broadcast in 1988 in four episodes of approximately 90 minutes each. A version comprising seven approximately 50-minute episodes also exists. Produced by RAI, ZDF, Televisión Española and TF1, a condensed version was later shown in cinemas. It takes its main inspiration from the books of Emilio Salgari with some elements from Pierre Benoit's Atlantida.

Creatonotos transiens is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. The species was first scientifically described by Francis Walker in 1855.
Endotricha wilemani is a species of snout moth in the genus Endotricha. It was described by Reginald James West in 1931, and is known from the Philippines.

Spilosoma wilemani is a species of moth of the family Erebidae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1914. It is found in Taiwan and Japan's southern Ryukyu Islands.

Delias meeki is a butterfly from the family Pieridae. It occurs in seven subspecies in New Guinea. The specific name commemorates English naturalist Albert Stewart Meek who collected the type series in May 1903 at Owgarra north of head of the Aroa River in Papua New Guinea. It forms a species group with the sympatric species Delias niepelti

Arhopala athada, the vinous oakblue is a species of butterfly belonging to the lycaenid family described by Otto Staudinger in 1889. It is found in Southeast Asia - Singapore, Peninsular Malaya, Sumatra, Borneo, Bangka, Bawean, Assam, Burma, Mergui, Thailand and the Philippines.

Delias geraldina is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It was described by Henley Grose-Smith in 1894. It is found in the Australasian realm where it is endemic to New Guinea.

Delias mira is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1904. It is endemic to New Guinea.

Delias nais is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It was described by Karl Jordan in 1912. It is endemic to New Guinea.

Delias schoenbergi is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1895. It is found in the Australasian realm.

Delias jordani is a butterfly in the family Pieridae. It was described by George Hamilton Kenrick in 1909. It is found in New Guinea. The name honours Karl Jordan.
















