Related Research Articles

In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or in the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins.

In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group. They have the general formula R−O−R′, where R and R′ represent the organyl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the organyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether". Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.

In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. These compounds contain a distinctive functional group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
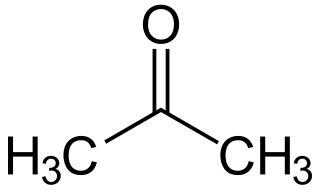
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure R−C(=O)−R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group −C(=O)−. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula (CH3)2CO. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.
The MIT License is a permissive software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the late 1980s. As a permissive license, it puts very few restrictions on reuse and therefore has high license compatibility.
In chemistry, a structural isomer of a compound is another compound whose molecule has the same number of atoms of each element, but with logically distinct bonds between them. The term metamer was formerly used for the same concept.

In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity R2C(OR')2. Here, the R groups can be organic fragments or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments not hydrogen. The two R' groups can be equivalent to each other or not. Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon, but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it, and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry.
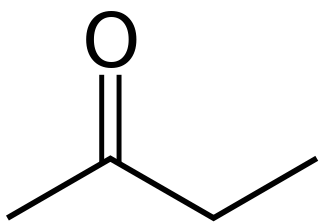
Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) or ethyl methyl ketone, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colorless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in nature only in trace amounts. It is partially soluble in water, and is commonly used as an industrial solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, tetrahydrofuran.

Rubbing alcohol, also known as surgical spirit in some regions, refers to a group of denatured alcohols commonly used as topical antiseptics. These solutions are primarily composed of either isopropyl alcohol (isopropanol) or ethanol, with isopropyl alcohol being the more widely available formulation. Rubbing alcohol is rendered undrinkable by the addition of bitterants or other denaturants.
In software engineering, a project fork happens when developers take a copy of source code from one software package and start independent development on it, creating a distinct and separate piece of software. The term often implies not merely a development branch, but also a split in the developer community; as such, it is a form of schism. Grounds for forking are varying user preferences and stagnated or discontinued development of the original software.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.
In computing, a clone is hardware or software that is designed to function in exactly the same way as another system. A specific subset of clones are remakes, which are revivals of old, obsolete, or discontinued products.

An extension cord (US), extension cable, power extender, drop cord, or extension lead (UK) is a length of flexible electrical power cable (flex) with a plug on one end and one or more sockets on the other end. The term usually refers to mains extensions but is also used to refer to extensions for other types of cabling. If the plug and power outlet are of different types, the term "adapter cord" may be used. Most extension cords range from around 2 to 30 feet in length although they are made up to 300 feet (91.44 m) in length.
A permissive software license, sometimes also called BSD-like or BSD-style license, is a free-software license which instead of copyleft protections, carries only minimal restrictions on how the software can be used, modified, and redistributed, usually including a warranty disclaimer. Examples include the GNU All-permissive License, MIT License, BSD licenses, Apple Public Source License and Apache license. As of 2016, the most popular free-software license is the permissive MIT license.

The bisulfite ion (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogensulfite) is the ion HSO−
3. Salts containing the HSO−
3 ion are also known as "sulfite lyes". Sodium bisulfite is used interchangeably with sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5). Sodium metabisulfite dissolves in water to give a solution of Na+HSO−
3.
A Norrish reaction, named after Ronald George Wreyford Norrish, is a photochemical reaction taking place with ketones and aldehydes. Such reactions are subdivided into Norrish type I reactions and Norrish type II reactions. While of limited synthetic utility these reactions are important in the photo-oxidation of polymers such as polyolefins, polyesters, certain polycarbonates and polyketones.

NEMA connectors are power plugs and sockets used for AC mains electricity in North America and other countries that use the standards set by the US National Electrical Manufacturers Association. NEMA wiring devices are made in current ratings from 15 to 60 amperes (A), with voltage ratings from 125 to 600 volts (V). Different combinations of contact blade widths, shapes, orientations, and dimensions create non-interchangeable connectors that are unique for each combination of voltage, electric current carrying capacity, and grounding system.

Miscibility is the property of two substances to mix in all proportions, forming a homogeneous mixture. Such substances are said to be miscible. The term is most often applied to liquids but also applies to solids and gases. An example in liquids is the miscibility of water and ethanol as they mix in all proportions.

The GNU Free Documentation License is a copyleft license for free documentation, designed by the Free Software Foundation (FSF) for the GNU Project. It is similar to the GNU General Public License, giving readers the rights to copy, redistribute, and modify a work and requires all copies and derivatives to be available under the same license. Copies may also be sold commercially, but, if produced in larger quantities, the original document or source code must be made available to the work's recipient.

A cheater plug, AC ground lifter or three-prong/two-prong adapter is an adapter that allows a NEMA 5-15P grounding-type plug to connect to a NEMA 1-15R non-grounding receptacle. They are needed to allow appliances with 3-wire power cords to plug into legacy ungrounded receptacles found in older buildings. The use of such an adapter avoids the need to replace receptacles, but is potentially hazardous if the grounding tab is not connected to electrical ground. These adapters are illegal in some jurisdictions, in particular throughout Canada. A safer and more reliable alternative identified in the US and Canadian electrical codes is to replace the outlet with a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) breaker outlet.
References
- 1 2 "JEP 277: Enhanced Deprecation". openjdk.java.net. Archived from the original on 19 September 2018. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- ↑ Shea, Ammon. "A New Meaning of 'Deprecate'". Words We're Watching. Merriam-Webster . Retrieved 1 March 2023.
- ↑ Raymond, Eric S.; Steele, Guy L., eds. (July 1992). The Jargon File, Version 2.9.10 . Retrieved 1 March 2023– via Project Gutenberg.
- ↑ Stewart, Meghan (27 February 2023). "Windows client features lifecycle". What's new in Windows. Microsoft . Retrieved 1 March 2023.
- ↑ "On the future of smbfs". LWN.net. 15 May 2006. Retrieved 1 March 2023.
- ↑ GNU. "Line Input". The GNU C Library. GNU. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 2 August 2008.
Deprecated function: char * gets (char *s). ... The
getsfunction is very dangerous because it provides no protection against overflowing the strings. The GNU library includes it for compatibility only. You should always usefgetsorgetlineinstead. - ↑ "Java Thread Primitive Deprecation". Oracle. Archived from the original on 15 October 2011. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ↑ Musciano, Chuck; Kennedy, Bill (2007). "HTML's Obsolete Expanded Font Handling". HTML & XHTML : the definitive guide (6th ed.). Beijing: O'Reilly. ISBN 978-0-596-52732-7. OCLC 77574682.
- ↑ Simenel, Éric (2000). "Carbonization 101". MacTech. Vol. 16, no. 12. Retrieved 1 March 2023.
- ↑ "The cross-platform streaming solution". VideoLAN. Retrieved 1 March 2023.
- ↑ "Brontosaurus Finally Validated as a Distinct Dinosaur". ABC News . Archived from the original on 9 April 2020. Retrieved 27 June 2020.
- ↑ Upchurch, Paul; Barrett, Paul M.; Dodson, Peter (2004). "Sauropoda". In Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; Osmólska, Halszka (eds.). The Dinosauria (2nd ed.). Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 259–322. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.
- ↑ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 725. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.