Related Research Articles

The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one of the bankers for the government of the United Kingdom, it is the world's second oldest central bank.

Reserve Bank of India, abbreviated as RBI, is the central bank of India, and regulatory body responsible for regulation of the Indian banking system and Indian currency. Owned by the Ministry of Finance, Government of India, it is responsible for the control, issue, and maintenance of the supply of the Indian rupee. It also manages the country's main payment systems and works to promote its economic development.

The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) is Australia's central bank and banknote issuing authority. It has had this role since 14 January 1960, when the Reserve Bank Act 1959 removed the central banking functions from the Commonwealth Bank.
The Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) is a statutory authority of the Australian Government and the prudential regulator of the Australian financial services industry. APRA was established on 1 July 1998 in response to the recommendations of the Wallis Inquiry. APRA's authority and scope is determined pursuant to the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority Act, 1998 (Cth).
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) is the central bank of New Zealand. It was established in 1934 and is currently constituted under the Reserve Bank of New Zealand Act 2021. The governor of the Reserve Bank, currently Adrian Orr, is responsible for New Zealand's currency and operating monetary policy.
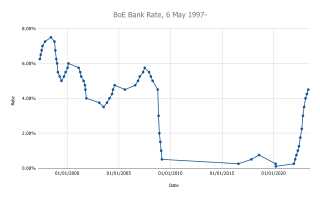
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is a committee of the Bank of England, which meets for three and a half days, eight times a year, to decide the official interest rate in the United Kingdom.

The Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas is the central bank of the Philippines. It was established on January 3, 1949, and then re-established on July 3, 1993 pursuant to the provision of Republic Act 7653 or the New Central Bank Act of 1993 as amended by Republic Act 11211 or the New Central Bank Act of 2019. The principal author was Senator Franklin Drilon. It was signed by President Rodrigo Duterte.

The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) is a committee of banking supervisory authorities that was established by the central bank governors of the Group of Ten (G10) countries in 1974. The committee expanded its membership in 2009 and then again in 2014. As of 2019, the BCBS has 45 members from 28 jurisdictions, consisting of central banks and authorities with responsibility of banking regulation.

The Reserve Bank of Fiji is the central bank of the Pacific island country of Fiji. Its responsibilities include the issue of currency, control of the money supply, currency exchange, monetary stability, promotion of sound finances, and fostering economic development.

The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) is the central bank and apex monetary authority of Nigeria established by the CBN Act of 1958 and commenced operations on 1 July 1959. The major regulatory objectives of the bank as stated in the CBN Act are to: maintain the external reserves of the country; promote monetary stability and a sound financial environment, and act as a banker of last resort and financial adviser to the federal government. The central bank's role as lender of last resort and adviser to the federal government has sometimes pushed it into murky political controversies. After the end of colonial rule, the desire of the government to become proactive in the development of the economy became visible, especially after the end of the Nigerian civil war, the bank followed the government's desire and took a determined effort to supplement any show shortfalls, credit allocations to the real sector. The bank became involved in lending directly to consumers, contravening its original intention to work through commercial banks in activities involving consumer lending.
The Bank of Papua New Guinea is the central bank of Papua New Guinea, which has a core mandate to ensure price stability and maintain macroeconomic growth. To achieve this, it discharges four main functions; 1. responsible for the formulation and implementation of monetary policy, 2. ensure financial system development and stability, 3. ensure the payment system remain efficient, and 4. provide a banking role to the Government. It also manages the country's foreign reserves, issue the country's currency, manages the gold and foreign exchange of Papua New Guinea.
Sir Paul Tucker is a British central banker and author. He was formerly the Deputy Governor of the Bank of England, with responsibility for financial stability, and served on the Bank's Monetary Policy Committee from June 2002 until October 2013 and its interim and then full Financial Policy Committee from June 2011. In November 2012 he was turned down for the position of governor in favour of Mark Carney. In June 2013, Tucker announced that he would leave the Bank of England, and later that he would be moving to Harvard. He was knighted in the 2014 New Year Honours for services to central banking. His first book, Unelected Power, was published in May 2018 and his second book, Global Discord was published in November 2022.
Shyamala Gopinath is Chairperson of HDFC Bank, India's largest lender by market capitalization. Ms. Gopinath is a former deputy governor of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), a position she served for seven years.
United Kingdom banking law refers to banking law in the United Kingdom, to control the activities of banks.

The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) is a financial regulatory body in the United Kingdom. It operates independently of the UK Government and is financed by charging fees to members of the financial services industry. The FCA regulates financial firms providing services to consumers and maintains the integrity of the financial markets in the United Kingdom.
The Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) is a United Kingdom financial services regulatory body, formed as one of the successors to the Financial Services Authority (FSA). The authority is responsible for the prudential regulation and supervision of banks, building societies, credit unions, insurers and major investment firms. It sets standards and supervises financial institutions at the level of the individual firm. Although it was initially structured as a limited company wholly owned by the Bank of England, the PRA's functions have now been taken over by the Bank and are exercised through the Prudential Regulation Committee. The company has since been liquidated.
Financial regulation in Australia is extensive and detailed.
Charlotte Mary Hogg is a British management consultant and senior executive in financial services and central banking. In October 2017 she was appointed as CEO of Visa's European operations. Hogg was the chief operating officer of the Bank of England between 2013 and 2017, and additionally served briefly as Deputy Governor at the Bank of England from 1 March 2017 to 14 March 2017, before resigning from both positions because she had failed to declare that her brother was employed in the banking industry.

The Governor of the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas is the chief executive officer of the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, the Philippines' central bank. This position succeeds and replaces the earlier post of Governor of the Central Bank of the Philippines.
Michael Debabrata Patra is an Indian economist and former central banker. A career Reserve Bank of India officer, he served as one of its four deputy governors.
References
- ↑ Richards, Richard. The Early History of Banking in England (Rle Banking and Finance). p. 152.
- ↑ "Governors". Bank of England. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- 1 2 "News Release – Appointment of Chief Operating Officer". Bank of England. 18 June 2013. Retrieved 3 September 2015.
- ↑ "Governors". Bank of England. Retrieved 3 September 2015.