
Mimosine or leucenol is a toxic non-protein amino acid chemically similar to tyrosine. It occurs in some Mimosa spp. and all members of the closely related genus Leucaena.
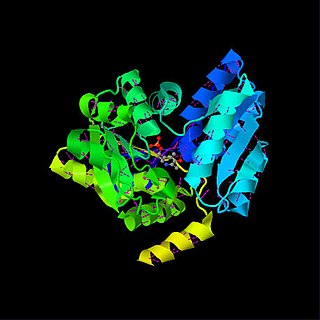
Serine dehydratase or L-serine ammonia lyase (SDH) is in the β-family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent (PLP) enzymes. SDH is found widely in nature, but its structure and properties vary among species. SDH is found in yeast, bacteria, and the cytoplasm of mammalian hepatocytes. SDH catalyzes the deamination of L-serine to yield pyruvate, with the release of ammonia.
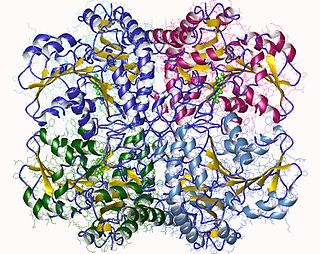
The enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (EC 4.4.1.1, CTH or CSE; also cystathionase; systematic name L-cystathionine cysteine-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming)) breaks down cystathionine into cysteine, 2-oxobutanoate (α-ketobutyrate), and ammonia:

The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.
The enzyme 3-chloro-D-alanine dehydrochlorinase (EC 4.5.1.2) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme carbamoyl-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.13) catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cystathionine beta-lyase, also commonly referred to as CBL or β-cystathionase, is an enzyme that primarily catalyzes the following α,β-elimination reaction
The enzyme cysteine-S-conjugate β-lyase (EC 4.4.1.13) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme D-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.18), with systematic name D-serine ammonia-lyase (pyruvate-forming), catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme erythro-3-hydroxyaspartate ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.20) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme L-cysteate sulfo-lyase (EC 4.4.1.25) catalyzes the reaction
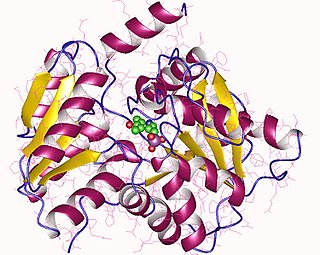
The enzyme L-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a S-alkylcysteine lyase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Threonine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.19, systematic name L-threonine ammonia-lyase (2-oxobutanoate-forming), also commonly referred to as threonine deaminase or threonine dehydratase, is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of L-threonine into α-ketobutyrate and ammonia:
The enzyme 2,2-dialkylglycine decarboxylase (pyruvate) (EC 4.1.1.64) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme phosphatidylserine decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.65) catalyzes the chemical reaction
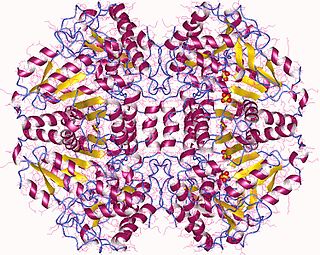
The enzyme tryptophanase (EC 4.1.99.1) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme tyrosine phenol-lyase (EC 4.1.99.2) catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2,3-diaminopropionate N-oxalyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.58) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In molecular biology, the Cys/Met metabolism PLP-dependent enzyme family is a family of proteins including enzymes involved in cysteine and methionine metabolism which use PLP (pyridoxal-5'-phosphate) as a cofactor.









