
The luna moth, also called the American moon moth, is a Nearctic moth in the family Saturniidae, subfamily Saturniinae, a group commonly named the giant silk moths.

Hyalophora cecropia, the cecropia moth, is North America's largest native moth. It is a member of the family Saturniidae, or giant silk moths. Females have been documented with a wingspan of five to seven inches or more. These moths can be found all across North America as far west as Washington and north into the majority of Canadian provinces. Cecropia moth larvae are most commonly found on maple trees, but they have also been found on cherry and birch trees among many others. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

Sphinx perelegans, commonly known as the elegant sphinx, is a species of hawkmoth described by Henry Edwards in 1874. It is a large gray moth native to western North America.

Orgyia antiqua, the rusty tussock moth or vapourer, is a moth in the family Erebidae.

Lithacodes fasciola, the yellow-shouldered slug or ochre-winged hag moth, is a moth of the family Limacodidae.

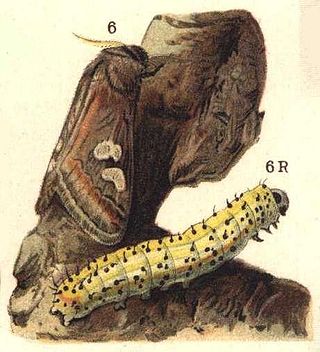
The Sulawesi moon moth or Isis moon moth is a moth of the family Saturniidae first described by Léon Sonthonnax in 1899.

Ayres's hawk-eagle, also referred to as Ayres' eagle, is a medium-sized bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. It is native to African woodlands. Its name honors South African ornithologist Thomas Ayres.

Spodoptera littoralis, also referred to as the African cotton leafworm or Egyptian cotton leafworm or Mediterranean brocade, is a species of moth in the family Noctuidae. S. littoralis is found widely in Africa, Mediterranean Europe and Middle Eastern countries. It is a highly polyphagous organism that is a pest of many cultivated plants and crops. As a result, this species was assigned the label of A2 quarantine pest by the EPPO and was cautioned as a highly invasive species in the United States. The devastating impacts caused by these pests have led to the development of both biological and chemical control methods. This moth is often confused with Spodoptera litura.
Diloba caeruleocephala, the figure of eight, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in the Palearctic.

Niphopyralis is a genus of snout moths of the subfamily Spilomelinae in the family Crambidae.

Parornix anglicella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae found in Asia and Europe. It was described in 1850, by the English entomologist Henry Tibbats Stainton, from a specimen from Lewisham, Kent.

Stigmella cypracma is a species of moth of the family Nepticulidae. It is endemic to New Zealand and has been observed in the North and South Islands. The larvae of this species are leaf miners and pupate within their mines. The larval host species is Brachyglottis repanda. Adult moths are on the wing in February and September to November. This species has two generations per year.

Epicephala relictella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from the Russian Far East, China and Korea.

Conopomorpha flueggella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Tianjin, China.

Pandemis corylana, the chequered fruit-tree tortrix, hazel tortrix moth, filbert tortricid or barred fruit tree moth, is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found from northern and central Europe to Siberia, Korea and Japan.

Heterocrossa gonosemana is a species of moth in the family Carposinidae. It is endemic to New Zealand and is found throughout the country. It inhabits native forest. Larvae feed on seeds and fruit of Griselinia lucida and possibly Griselinia littoralis. They can be extremely active when disturbed. This species overwinters as a pupa, enclosed in a cocoon, underneath its host plant. Adults are on the wing from November until February and can be found during the day resting on lichen covered tree trunks where they are well camouflaged. The adult is nocturnal and is attracted to light.

Isonomeutis amauropa is a species of moth in the Copromorphidae family. It is endemic to New Zealand where it can be found on both the North and South Islands. I. amauropa inhabits native forest particularly forest dominated by Rimu and native beech trees. The larvae of this species consumes margarodid scale insects that live under the bark of these trees. When mature the larvae pupate in a cocoon made of silk and covered in twigs and frass. This cocoon is normally placed under the bark of the same tree the larvae inhabited. Adults of I. amauropa are on the wing from September to February.

Andesobia jelskii is a species of moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Charles Oberthür in 1881. It is found in the Department of Junín in Peru.

Ichneutica arotis is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. This species is found throughout the North and South Islands but has yet to be recorded on Stewart Island. I. arotis is variable in appearance and have been described as having a "northern dark form", a "typical" form and a "swamp" form. Robert Hoare hypothesised that this species may be in the process of evolving into several distinct species. However, as these forms show no difference in antennae or genitalia so, as at 2019, they are not regarded as separate species. Larval hosts include species in the genera Cortaderia and Schoenus as well as Phormium tenax. The caterpillar feeds at night and rests in during the day amongst dead flax leaves. It pupates in a loose cocoon either hidden at the base of a stem of flax or on the ground. The adults of this species is on the wing from September to April. In the North Island there have also been records of adults being on the wing in June to August.

Chersadaula ochrogastra is a species of moth in the family Oecophoridae. This species is endemic to New Zealand. It is classified as "Data Deficient" by the Department of Conservation.

















