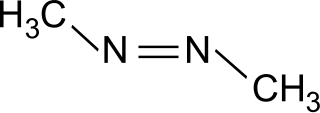In organic chemistry, a methyl group is an alkyl derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, having chemical formula CH3. In formulas, the group is often abbreviated as Me. This hydrocarbon group occurs in many organic compounds. It is a very stable group in most molecules. While the methyl group is usually part of a larger molecule, bounded to the rest of the molecule by a single covalent bond, it can be found on its own in any of three forms: methanide anion, methylium cation or methyl radical. The anion has eight valence electrons, the radical seven and the cation six. All three forms are highly reactive and rarely observed.
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.

An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one- or two-step mechanism. The one-step mechanism is known as the E2 reaction, and the two-step mechanism is known as the E1 reaction. The numbers refer not to the number of steps in the mechanism, but rather to the kinetics of the reaction: E2 is bimolecular (second-order) while E1 is unimolecular (first-order). In cases where the molecule is able to stabilize an anion but possesses a poor leaving group, a third type of reaction, E1CB, exists. Finally, the pyrolysis of xanthate and acetate esters proceed through an "internal" elimination mechanism, the Ei mechanism.

Benzophenone is the organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CO, generally abbreviated Ph2CO. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. Benzophenone is a widely used building block in organic chemistry, being the parent diarylketone.
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carries a partial positive charge, or have an atom that does not have an octet of electrons.
In chemistry, an oxonium ion is any cation containing an oxygen atom that has three bonds and 1+ formal charge. The simplest oxonium ion is the hydronium ion.

Ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2[Ce(NO3)6]. This orange-red, water-soluble cerium salt is a specialised oxidizing agent in organic synthesis and a standard oxidant in quantitative analysis.

In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure R−CH2−C6H5. Benzyl features a benzene ring attached to a methylene group group.
Thiazole, or 1,3-thiazole, is a 5-membered heterocyclic compound that contains both sulfur and nitrogen. The term 'thiazole' also refers to a large family of derivatives. Thiazole itself is a pale yellow liquid with a pyridine-like odor and the molecular formula C3H3NS. The thiazole ring is notable as a component of the vitamin thiamine (B1).

A trimethylsilyl group (abbreviated TMS) is a functional group in organic chemistry. This group consists of three methyl groups bonded to a silicon atom [−Si(CH3)3], which is in turn bonded to the rest of a molecule. This structural group is characterized by chemical inertness and a large molecular volume, which makes it useful in a number of applications.
Clemmensen reduction is a chemical reaction described as a reduction of ketones or aldehydes to alkanes using zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl). This reaction is named after Erik Christian Clemmensen, a Danish-American chemist.

1,4-Benzoquinone, commonly known as para-quinone, is a chemical compound with the formula C6H4O2. In a pure state, it forms bright-yellow crystals with a characteristic irritating odor, resembling that of chlorine, bleach, and hot plastic or formaldehyde. This six-membered ring compound is the oxidized derivative of 1,4-hydroquinone. The molecule is multifunctional: it exhibits properties of a ketone, being able to form oximes; an oxidant, forming the dihydroxy derivative; and an alkene, undergoing addition reactions, especially those typical for α,β-unsaturated ketones. 1,4-Benzoquinone is sensitive toward both strong mineral acids and alkali, which cause condensation and decomposition of the compound.

Organosilicon chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds, to which they are called organosilicon compounds. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.

Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are chemical compounds with the general formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride Cl−Mg−CH3 and phenylmagnesium bromide (C6H5)−Mg−Br. They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds.
Barrelene is a bicyclic organic compound with chemical formula C8H8 and systematic name bicyclo[2.2.2]octa-2,5,7-triene. First synthesized and described by Howard Zimmerman in 1960, the name derives from the resemblance to a barrel, with the staves being three ethylene units attached to two methine groups. It is the formal Diels–Alder adduct of benzene and acetylene. Due to its unusual molecular geometry, the compound is of considerable interest to theoretical chemists.
Metal carbon dioxide complexes are coordination complexes that contain carbon dioxide ligands. Aside from the fundamental interest in the coordination chemistry of simple molecules, studies in this field are motivated by the possibility that transition metals might catalyze useful transformations of CO2. This research is relevant both to organic synthesis and to the production of "solar fuels" that would avoid the use of petroleum-based fuels.
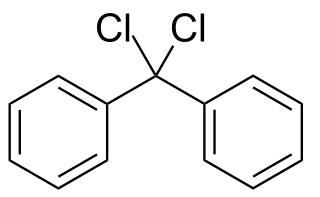
Diphenyldichloromethane is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CCl2. It is a colorless solid that is used as a precursor to other organic compounds.

Phosphenium ions, not to be confused with phosphonium or phosphirenium, are divalent cations of phosphorus of the form [PR2]+. Phosphenium ions have long been proposed as reaction intermediates.
Manganese(III) chloride is the hypothetical inorganic compound with the formula MnCl3.
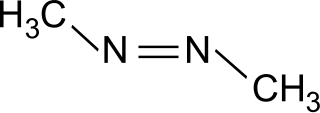
Azomethane is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3-N=N-CH3. It exhibits cis-trans isomerism. It can be produced by the reaction of 1,2-dimethylhydrazine dihydrochloride with copper(II) chloride in sodium acetate solution. The reaction produces the azomethane complex of copper(I) chloride, which can produce free azomethane by thermal decomposition. It is the source of methyl radical in laboratory.