
Papua New Guinea is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia. Officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, it shares its only land border with Indonesia to the west and it is directly adjacent to Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of 462,840 km2 (178,700 sq mi).

Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.

The Ramu River is a major river in northern Papua New Guinea. The headwaters of the river are formed in the Kratke Range from where it then travels about 640 km (398 mi) northwest to the Bismarck Sea.

Samarai is an island and former administrative capital in Milne Bay Province, Papua New Guinea.

Nepenthes neoguineensis is a tropical pitcher plant native to the island of New Guinea, after which it is named.

Tetragnatha is a genus of long-jawed orb-weavers found all over the world. It was first described by Pierre André Latreille in 1804, and it contains hundreds of species. Most occur in the tropics and subtropics, and many can run over water. They are commonly called stretch spiders in reference to their elongated body form and their ability to hide on blades of grass or similar elongated substrates by stretching their front legs forward and the others behind them. The name Tetragnatha is derived from Greek, tetra- a numerical prefix referring to four and gnatha meaning "jaw". Evolution to cursorial behavior occurred long ago in a few different species, the most studied being those found on the Hawaiian islands. One of the biggest and most common species is T. extensa, which has a holarctic distribution. It can be found near lakes, river banks or swamps. Large numbers of individuals can often be found in reeds, tall grass, and around minor trees and shrubs.

Hendrikus Albertus Lorentz was a Dutch explorer in New Guinea and diplomat in South Africa.

Sir George Hamilton Kenrick FRES was an English entomologist who specialised in Lepidoptera especially those of New Guinea. He was a prominent liberal educationist and was a councillor in Birmingham.
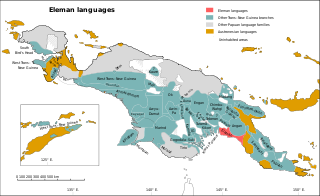
The Eleman languages are a family spoken around Kerema Bay, Papua New Guinea.

New Guinea is the world's second-largest island, with an area of 785,753 km2 (303,381 sq mi). Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Australia by the 150-kilometre wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the African region of Guinea.

Dichocrocis is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae. The genus was described by Julius Lederer in 1863.

The Erionotini are a tribe of skipper butterflies in the subfamily Hesperiinae.
Dichocrocis macrostidza is a species of moth of the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1912 and it is known from Myanmar.
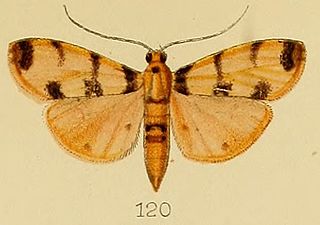
Dichocrocis pardalis is a species of moth of the family Crambidae. It is found in Papua New Guinea.
Dichocrocis albilunalis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1912. It is found in Papua New Guinea.
Dichocrocis nigricinctalis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1912. It is found in Papua New Guinea and Kenya.
Dichocrocis xanthoplagalis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1912. It is found in Nigeria.
Dichocrocis xanthocyma is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1898. It is found in Papua New Guinea.
Dichocrocis pseudpoeonalis is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by George Hampson in 1898. It is found in Western New Guinea, Indonesia.
Dichocrocis definita is a moth in the family Crambidae. It was described by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1889. It is found in India (Assam).













