
Polyurea is a type of elastomer that is derived from the reaction product of an isocyanate component and a synthetic resin blend component through step-growth polymerization. The isocyanate can be aromatic or aliphatic in nature. It can be monomer, polymer, or any variant reaction of isocyanates, quasi-prepolymer or a prepolymer. The prepolymer, or quasi-prepolymer, can be made of an amine-terminated polymer resin, or a hydroxyl-terminated polymer resin.
A polyol is an organic compound containing multiple hydroxyl groups. The term "polyol" can have slightly different meanings depending on whether it is used in food science or polymer chemistry. Polyols containing two, three and four hydroxyl groups are diols, triols, and tetrols, respectively.

Propylparaben, the n-propyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, occurs as a natural substance found in many plants and some insects, although it is manufactured synthetically for use in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and foods. It is a member of the class of parabens. It is a preservative typically found in many water-based cosmetics, such as creams, lotions, shampoos, and bath products. As a food additive, it has the E number E216.
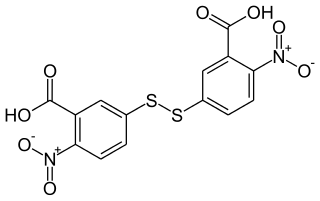
Ellman's reagent is a chemical used to quantify the number or concentration of thiol groups in a sample. It was developed by George L. Ellman.

Dilazep is a vasodilator that acts as an adenosine reuptake inhibitor.

Demeton, sold as an amber oily liquid with a sulphur like odour under the name Systox™, is an organophosphate derivative causing irritability and shortness of breath to individuals repeatedly exposed. It was used as a phosphorothioate insecticide and acaricide and has the chemical formula C8H19O3PS2. Although it was previously used as an insecticide, it is now largely obsolete due to its relatively high toxicity to humans. Demeton consists of two components, demeton-S and demeton-O in a ratio of approximately 2:1 respectively. The chemical structure of demeton is closely related to military nerve agents such as VX and a derivative with one of the ethoxy groups replaced by methyl was investigated by both the US and Soviet chemical-weapons programs under the names V.sub.X and GD-7.
In chemistry, methanetetracarboxylate is a tetravalent anion with formula C
5O4−
8 or C(COO−)4. It has four carboxylate groups attached to a central carbon atom; so it has the same carbon backbone as neopentane. It is an oxocarbon anion, that is, consists only of carbon and oxygen.
In polymer chemistry, the term pre-polymer or prepolymer, refers to a monomer or system of monomers that have been reacted to an intermediate molecular mass state. This material is capable of further polymerization by reactive groups to a fully cured, high molecular weight state. As such, mixtures of reactive polymers with un-reacted monomers may also be referred to as pre-polymers. The term “pre-polymer” and “polymer precursor” may be interchanged.
Polyaspartic ester chemistry was first introduced in the early 1990s making it a relatively new technology. The patents were issued to Bayer in Germany and Miles Corporation in the United States. It utilizes the Michael addition reaction. These products are then used in coatings, adhesives, sealants and elastomers. Pure polyurea reacts extremely quickly making them almost unusable without plural component spray equipment. Polyaspartic technology utilizes a partially blocked amine to react more slowly with the isocyanates and thus produce a modified polyurea. The amine/diamine or even triamine functional coreactant for aliphatic polyisocyanate is typically reacted with a maleate. Polyaspartic esters (PAE) initially found use in conventional solvent-borne two-component polyurethane coatings.
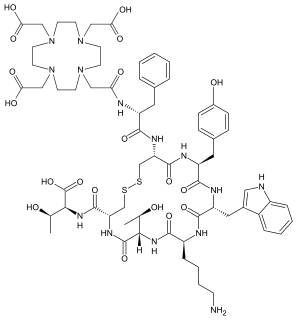
DOTA-TATE is an eight amino acid long peptide, with a covalently bonded DOTA bifunctional chelator.
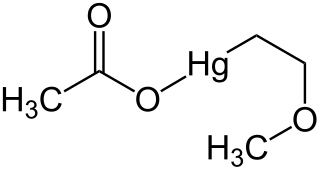
Methoxyethylmercuric acetate is a chemical compound formerly used as a pesticide for seeds of cotton and small grains. It is highly toxic, and can pose a threat to the brain and central nervous system.

Lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide, often simply referred to as LiTFSI, is a hydrophilic salt with the chemical formula LiC2F6NO4S2. It is commonly used as Li-ion source in electrolytes for Li-ion batteries as a safer alternative to commonly used lithium hexafluorophosphate. It is made up of one Li cation and a bistriflimide anion.
Polyurethane Dispersion, or PUD, is understood to be a polyurethane polymer resin dispersed in water, rather than a solvent. Its manufacture involves the synthesis of polyurethanes having carboxylic acid functionality or nonionic hydrophiles like PEG incorporated into, or pendant from, the polymer backbone.
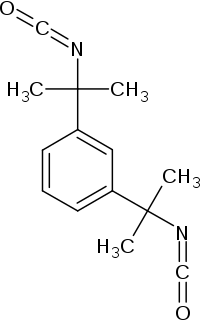
Tetramethylxylylene diisocyanate (TMXDI) is an organic compound is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CMe2NCO)2 (Me = CH3). The molecule features two isocyanate groups. It was introduced in the 1980s by American Cyanamid. TMXDI is generally classified as an aliphatic isocyanate. Aliphatic isocyanates generally exhibit enhanced UV stability compared to their aromatic counterparts.
Dibutyl maleate is an organic compound with the formula (CHCO2Bu)2 (Bu = butyl). It is the diester of the unsaturated dicarboxylic acid maleic acid. It is a colorless oily liquid, although impure samples can appear yellow.

Dimethylol propionic acid -DMPA is a chemical compound that has the full IUPAC name of 2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)propionic acid and is an organic compound with one carboxyl and two hydroxy groups. It has the CAS Registry Number of 4767-03-7.

Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), is a cannabinoid found in cannabis plants. It is most abundant in the glandular trichomes on the female seedless flowers or more accurately infructescence often colloquially referred to as buds. CBDA is the chemical precursor to cannabidiol (CBD). Through the process of decarboxylation cannabidol is derived via a loss of a carbon and two oxygen atoms from the 1 position of the benzoic acid ring.
Hydrogenated MDI (H12MDI or 4,4′-diisocyanato dicyclohexylmethane) is an organic compound in the class known as isocyanates. More specifically, it is an aliphatic diisocyanate. It is a water white liquid at room temperature and is manufactured in relatively small quantities. It is also known as 4,4'-methylenedi(cyclohexyl isocyanate) or methylene bis(4-cyclohexylisocyanate) and has the formula CH2[(C6H10)NCO]2.
Diethyl toluene diamine (DETDA) is a liquid aromatic organic molecule with formula C11H18N2. It is chemically a diamine and has the CAS Registry number of 68479-98-1. It has more than one isomer and the mixture of the two main isomers is given a different CAS number of 75389-89-8. It is often marketed as a less toxic version of MDA (4,4'-Methylenedianiline). It is also used to replace the more toxic MOCA 4,4'-Methylenebis(2-chloroaniline). The toxicology is reasonably well understood.












